Therapeutic Strategies For Tay-Sachs Disease
- PMID: 35865957
- PMCID: PMC9294361
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.906647
Therapeutic Strategies For Tay-Sachs Disease
Abstract
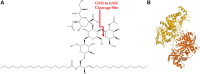
Tay-Sachs disease (TSD) is an autosomal recessive disease that features progressive neurodegenerative presentations. It affects one in 100,000 live births. Currently, there is no approved therapy or cure. This review summarizes multiple drug development strategies for TSD, including enzyme replacement therapy, pharmaceutical chaperone therapy, substrate reduction therapy, gene therapy, and hematopoietic stem cell replacement therapy. In vitro and in vivo systems are described to assess the efficacy of the aforementioned therapeutic strategies. Furthermore, we discuss using MALDI mass spectrometry to perform a high throughput screen of compound libraries. This enables discovery of compounds that reduce GM2 and can lead to further development of a TSD therapy.
Keywords: drug development; enzymatic assay; high throughput screen (HTS); mass spectrometry; phenotypic screen; tay-sachs disease (TSD).
Copyright © 2022 Picache, Zheng and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Administration U. S. F. D. U.S.F.D. Administration (2018a). Drug Approval Package: Galafold (Migalastat).
-
- Administration U. S. F. D. (2018b). FDA Approves New Treatment for a Rare Genetic Disorder, Fabry Disease. U.S. Food & Drug Administration.
-
- Akeboshi H., Chiba Y., Kasahara Y., Takashiba M., Takaoka Y., Ohsawa M., et al. (2007). Production of Recombinant Beta-Hexosaminidase A, a Potential Enzyme for Replacement Therapy for Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff Diseases, in the Methylotrophic Yeast Ogataea Minuta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73 (15), 4805–4812. 10.1128/AEM.00463-07 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashe K. M., Bangari D., Li L., Cabrera-Salazar M. A., Bercury S. D., Nietupski J. B., et al. (2011). Iminosugar-based Inhibitors of Glucosylceramide Synthase Increase Brain Glycosphingolipids and Survival in a Mouse Model of Sandhoff Disease. PLoS One 6 (6), e21758. 10.1371/journal.pone.0021758 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

