Porous NH2-MIL-101(Fe) metal organic framework for effective photocatalytic degradation of azo dye in wastewater treatment
- PMID: 35865975
- PMCID: PMC9293744
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09942
Porous NH2-MIL-101(Fe) metal organic framework for effective photocatalytic degradation of azo dye in wastewater treatment
Abstract
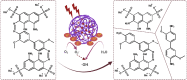
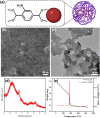
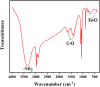
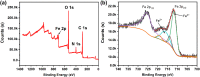
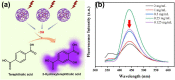
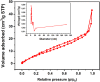
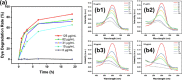
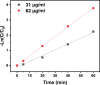
The porous iron-based metal organic frameworks (NH2-MIL-101(Fe)), which consists of 2-amino benzene dicarboxylic acid (H2BDC-NH2) and ferrous ions were synthesized through one-step hydrothermal method. The surface area and pore volume of as-synthesized NH2-MIL-101(Fe) were 66.48 m2/g and 0.09 cm3/g, respectively. The excellent photocatalytic performance endows NH2-MIL-101(Fe) to generate hydroxyl radical (•OH), which then acting as efficiently active sites for azo dye degradation in wastewater. Meanwhile, the outstanding stability ability of NH2-MIL-101(Fe) indicates the potential candidate for wastewater treatment.
Keywords: Azo dye; Hydroxyl radical; NH2-MIL-101(Fe); Wastewater treatment.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A green synthesized recyclable ZnO/MIL-101(Fe) for Rhodamine B dye removal via adsorption and photo-degradation under UV and visible light irradiation.Environ Technol. 2021 Feb;42(6):842-859. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2019.1647290. Epub 2019 Aug 11. Environ Technol. 2021. PMID: 31327310
-
Degradation of Orange G Using PMS Triggered by NH2-MIL-101(Fe): An Amino-Functionalized Metal-Organic Framework.Molecules. 2024 Mar 27;29(7):1488. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071488. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611767 Free PMC article.
-
MOF-Derived Hollow Spheres of MIL-100(Fe)-NH2(20) with Well-Developed Hierarchical Mesoporous and Uniform Distribution of Fe and N Active Phases for the Photocatalytic Removal of Organic Dyes.Langmuir. 2023 Jul 4;39(26):9130-9143. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c00846. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Langmuir. 2023. PMID: 37345822
-
[Activating Efficiency of Iron-copper Bimetallic Organic Framework MIL-101(Fe,Cu) Toward H2 O2 for Degradation of Dyes].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2020 Oct 8;41(10):4607-4614. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202003024. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2020. PMID: 33124393 Chinese.
-
MIL-100(Fe) and its derivatives: from synthesis to application for wastewater decontamination.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Feb;27(5):4703-4724. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07318-w. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31919822 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficient Adsorption and Removal of the Herbicide 2,4-Dichlorophenylacetic Acid from Aqueous Solutions Using MIL-88(Fe)-NH2.ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 20;8(43):40775-40784. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05818. eCollection 2023 Oct 31. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37929154 Free PMC article.
-
Rational synthesis, biological screening of azo derivatives of chloro-phenylcarbonyl diazenyl hydroxy dipyrimidines/thioxotetrahydropyrimidines and their metal complexes.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 27;9(1):e12492. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12492. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36699273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed S.F., Mofijur M., Nuzhat S., Chowdhury A.T., Rafa N., Uddin Md.A., Inayat A., Mahlia T.M.I., Ong H.C., Chia W.Y., Show P.L. Recent developments in physical, biological, chemical, and hybrid treatment techniques for removing emerging contaminants from wastewater. J. Hazard Mater. 2021;416 - PubMed
-
- Alothman Z. A review: fundamental aspects of silicate mesoporous materials. Materials. 2012;5:2874–2902.
-
- Alves de Lima R.O., Bazo A.P., Salvadori D.M.F., Rech C.M., de Palma Oliveira D., de Aragão Umbuzeiro G. Mutagenic and carcinogenic potential of a textile azo dye processing plant effluent that impacts a drinking water source. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2007;626:53–60. - PubMed
-
- Barreto J.C., Smith G.S., Strobel N.H.P., McQuillin P.A., Miller T.A. Terephthalic acid: a dosimeter for the detection of hydroxyl radicals in vitro. Life Sci. 1994;56:89–96. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

