Integrated analysis of the clinical consequence and associated gene expression of ALK in ALK-positive human cancers
- PMID: 35865984
- PMCID: PMC9293659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09878
Integrated analysis of the clinical consequence and associated gene expression of ALK in ALK-positive human cancers
Abstract
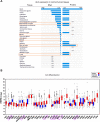
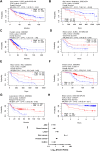
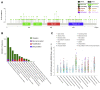
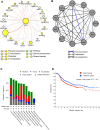
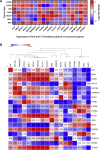
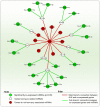
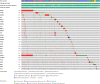
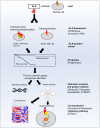
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a tyrosine kinase receptor that is genetically altered in several cancers, including NSCLC, melanoma, lymphoma, and other tumors. Although ALK is associated with various cancers, the relationship between ALK expression and patient prognosis in different cancers is poorly understood. Here, using multidimensional approaches, we revealed the correlation between ALK expression and the clinical outcomes of patients with LUAD, melanoma, OV, DLBC, AML, and BC. We analyzed ALK transcriptional expression, patient survival rate, genetic alteration, protein network, and gene and microRNA (miRNA) co-expression. Compared to that in normal tissues, higher ALK expression was found in LUAD, melanoma, and OV, which are associated with poor patient survival rates. In contrast, lower transcriptional expression was found to decrease the survival rate of patients with DLBC, AML, and BC. A total of 202 missense mutations, 17 truncating mutations, 7 fusions, and 3 in-frame mutations were identified. Further, 17 genes and 19 miRNAs were found to be exclusively co-expressed and echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 (EML4) was identified as the most positively correlated gene (log odds ratio >3). The gene ontology and signaling pathways of the genes co-expressed with ALK in these six cancers were also identified. Our findings offer a basis for ALK as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in cancers, which will potentially contribute to precision oncology and assist clinicians in identifying suitable treatment options.
Keywords: ALK expression; Cancers; Co-expression; LUAD; Patient prognosis.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Soda M., Choi Y.L., Enomoto M., Takada S., Yamashita Y., Ishikawa S., Fujiwara S.-i., Watanabe H., Kurashina K., Hatanaka H., et al. Identification of the transforming EML4–ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Saifullah, Tsukahara T. Integrated analysis of ALK higher expression in human cancer and downregulation in LUAD using RNA molecular scissors. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022 - PubMed
-
- Morris S., Kirstein M., Valentine M., Dittmer K., Shapiro D., Saltman D., Look A. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–1284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

