Self-blame Attributions of Patients: a Systematic Review Study
- PMID: 35866087
- PMCID: PMC9295847
- DOI: 10.5195/cajgh.2020.419
Self-blame Attributions of Patients: a Systematic Review Study
Abstract
Introduction: Psychological aspects are important issues in patients that will have significant effects on disease progression. A new and important psychological concern is self-blame. This review was performed with the aim of systematic review on studies around patient's self-blame.
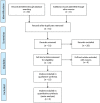
Methods: This is a systematic review using international databases including PubMed (since 1950), Scopus (since 2004), Web ofSciences (since 1900), and ProQuest (since 1938) and Irani an databases including SID (since 2004) and Magiran (since 2001). Mesh terms including "patient," "regret," and "guilt" and non-Mesh terms including "self-blame attribution," "characterological self-blame," "behavioral self-blame," and "blame" were used in Iranian and international databases with OR and AND operators.
Results: The review yielded 59 articles; 15 articles were included in the present study. The ages of patients ranged from 29-68.4 years. Most of studies (86.6%) had cross-sectional design and use characterological self-blame and behavioral self-blame variablesfor assessing self-blame attributions. The results showed that in most studies, a significant relationship among self-blame and psychological distress, anxiety, and depression were reported.
Conclusions: A significant relation was reported between self-blaming and the degree of distress, anxiety, and depression in patients in most of the studies.
Keywords: Anxiety; Depression; Patient; Self-blame; Systematic review.
Copyright © 2020 Yadollah Jannati, Hamid Sharif Nia, Erika Sivarajan Froelicher, Amir Hossein Goudarzian, Ameneh Yaghoobzadeh.
References
-
- Vos T, Barber RM, Bell B, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743–800. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Callebaut L, Molyneux P, Alexander T. The Relationship Between Self-Blame for the Onset of a Chronic Physical Health Condition and Emotional Distress: A Systematic Literature Review. Clinical psychology & psychotherapy. 2017;24(4):965–986. - PubMed
-
- Health Do. Long term conditions compendium of information. Department of Health London; 2012.
-
- Dornelas EA, Sears SF. Living with heart despite recurrent challenges: Psychological care for adults with advanced cardiac disease. American Psychologist. 2018;73(8):1007. - PubMed
-
- Bennett KK, Compas BE, Beckjord E, Glinder JG. Self-blame and distress among women with newly diagnosed breast cancer. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 2005;28(4):313–323. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials