Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 35866452
- PMCID: PMC9305720
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
Background: Accurate rapid diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2 infection would be a useful tool to help manage the COVID-19 pandemic. Testing strategies that use rapid antigen tests to detect current infection have the potential to increase access to testing, speed detection of infection, and inform clinical and public health management decisions to reduce transmission. This is the second update of this review, which was first published in 2020.
Objectives: To assess the diagnostic accuracy of rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. We consider accuracy separately in symptomatic and asymptomatic population groups. Sources of heterogeneity investigated included setting and indication for testing, assay format, sample site, viral load, age, timing of test, and study design.
Search methods: We searched the COVID-19 Open Access Project living evidence database from the University of Bern (which includes daily updates from PubMed and Embase and preprints from medRxiv and bioRxiv) on 08 March 2021. We included independent evaluations from national reference laboratories, FIND and the Diagnostics Global Health website. We did not apply language restrictions.
Selection criteria: We included studies of people with either suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection, known SARS-CoV-2 infection or known absence of infection, or those who were being screened for infection. We included test accuracy studies of any design that evaluated commercially produced, rapid antigen tests. We included evaluations of single applications of a test (one test result reported per person) and evaluations of serial testing (repeated antigen testing over time). Reference standards for presence or absence of infection were any laboratory-based molecular test (primarily reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR)) or pre-pandemic respiratory sample.
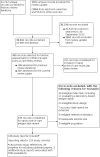
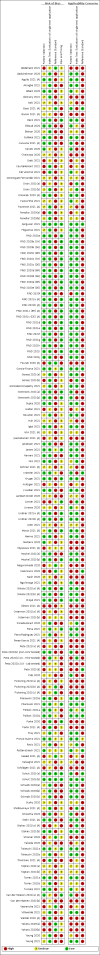
Data collection and analysis: We used standard screening procedures with three people. Two people independently carried out quality assessment (using the QUADAS-2 tool) and extracted study results. Other study characteristics were extracted by one review author and checked by a second. We present sensitivity and specificity with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for each test, and pooled data using the bivariate model. We investigated heterogeneity by including indicator variables in the random-effects logistic regression models. We tabulated results by test manufacturer and compliance with manufacturer instructions for use and according to symptom status.
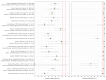
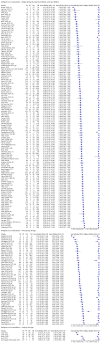
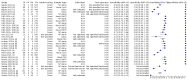
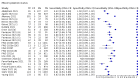
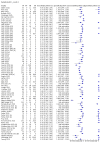
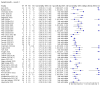
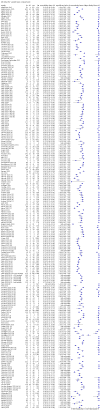
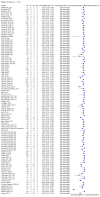
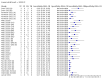
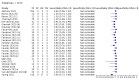
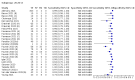
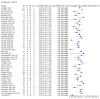
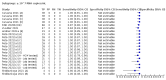
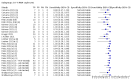
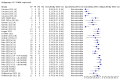
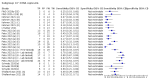
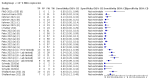
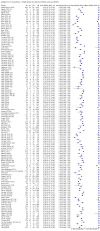
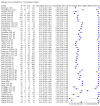
Main results: We included 155 study cohorts (described in 166 study reports, with 24 as preprints). The main results relate to 152 evaluations of single test applications including 100,462 unique samples (16,822 with confirmed SARS-CoV-2). Studies were mainly conducted in Europe (101/152, 66%), and evaluated 49 different commercial antigen assays. Only 23 studies compared two or more brands of test. Risk of bias was high because of participant selection (40, 26%); interpretation of the index test (6, 4%); weaknesses in the reference standard for absence of infection (119, 78%); and participant flow and timing 41 (27%). Characteristics of participants (45, 30%) and index test delivery (47, 31%) differed from the way in which and in whom the test was intended to be used. Nearly all studies (91%) used a single RT-PCR result to define presence or absence of infection. The 152 studies of single test applications reported 228 evaluations of antigen tests. Estimates of sensitivity varied considerably between studies, with consistently high specificities. Average sensitivity was higher in symptomatic (73.0%, 95% CI 69.3% to 76.4%; 109 evaluations; 50,574 samples, 11,662 cases) compared to asymptomatic participants (54.7%, 95% CI 47.7% to 61.6%; 50 evaluations; 40,956 samples, 2641 cases). Average sensitivity was higher in the first week after symptom onset (80.9%, 95% CI 76.9% to 84.4%; 30 evaluations, 2408 cases) than in the second week of symptoms (53.8%, 95% CI 48.0% to 59.6%; 40 evaluations, 1119 cases). For those who were asymptomatic at the time of testing, sensitivity was higher when an epidemiological exposure to SARS-CoV-2 was suspected (64.3%, 95% CI 54.6% to 73.0%; 16 evaluations; 7677 samples, 703 cases) compared to where COVID-19 testing was reported to be widely available to anyone on presentation for testing (49.6%, 95% CI 42.1% to 57.1%; 26 evaluations; 31,904 samples, 1758 cases). Average specificity was similarly high for symptomatic (99.1%) or asymptomatic (99.7%) participants. We observed a steady decline in summary sensitivities as measures of sample viral load decreased. Sensitivity varied between brands. When tests were used according to manufacturer instructions, average sensitivities by brand ranged from 34.3% to 91.3% in symptomatic participants (20 assays with eligible data) and from 28.6% to 77.8% for asymptomatic participants (12 assays). For symptomatic participants, summary sensitivities for seven assays were 80% or more (meeting acceptable criteria set by the World Health Organization (WHO)). The WHO acceptable performance criterion of 97% specificity was met by 17 of 20 assays when tests were used according to manufacturer instructions, 12 of which demonstrated specificities above 99%. For asymptomatic participants the sensitivities of only two assays approached but did not meet WHO acceptable performance standards in one study each; specificities for asymptomatic participants were in a similar range to those observed for symptomatic people. At 5% prevalence using summary data in symptomatic people during the first week after symptom onset, the positive predictive value (PPV) of 89% means that 1 in 10 positive results will be a false positive, and around 1 in 5 cases will be missed. At 0.5% prevalence using summary data for asymptomatic people, where testing was widely available and where epidemiological exposure to COVID-19 was suspected, resulting PPVs would be 38% to 52%, meaning that between 2 in 5 and 1 in 2 positive results will be false positives, and between 1 in 2 and 1 in 3 cases will be missed.
Authors' conclusions: Antigen tests vary in sensitivity. In people with signs and symptoms of COVID-19, sensitivities are highest in the first week of illness when viral loads are higher. Assays that meet appropriate performance standards, such as those set by WHO, could replace laboratory-based RT-PCR when immediate decisions about patient care must be made, or where RT-PCR cannot be delivered in a timely manner. However, they are more suitable for use as triage to RT-PCR testing. The variable sensitivity of antigen tests means that people who test negative may still be infected. Many commercially available rapid antigen tests have not been evaluated in independent validation studies. Evidence for testing in asymptomatic cohorts has increased, however sensitivity is lower and there is a paucity of evidence for testing in different settings. Questions remain about the use of antigen test-based repeat testing strategies. Further research is needed to evaluate the effectiveness of screening programmes at reducing transmission of infection, whether mass screening or targeted approaches including schools, healthcare setting and traveller screening.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. on behalf of The Cochrane Collaboration.
Conflict of interest statement
Jonathan J Deeks: JD has published or been quoted in opinion pieces in scientific publications, and in the mainstream and social media related to diagnostic testing. JD was the statistician on the Birmingham evaluation of the Innova test which is mentioned in the discussion of the paper. There was no funding for this evaluation of the Innova test. JD is a member of the Royal Statistical Society (RSS) COVID‐19 taskforce steering group, and co‐chair of the RSS Diagnostic Test Advisory Group. He is a consultant adviser to the World Health Organization (WHO) Essential Diagnostic List. JD receives payment from the BMJ as their Chief Statistical advisor.
Jacqueline Dinnes: none known
Yemisi Takwoingi: none known
Clare Davenport: none known
Mariska MG Leeflang: none known
René Spijker: none known
Lotty Hooft: none known
Ann Van den Bruel: none known
Devy Emperador: is employed by FIND with funding from DFID and KFW. FIND is a global non‐for profit product development partnership and WHO Diagnostic Collaboration Centre. It is FIND’s role to accelerate access to high‐quality diagnostic tools for low‐resource settings and this is achieved by supporting both research and development and access activities for a wide range of diseases, including COVID‐19. FIND has several clinical research projects to evaluate multiple new diagnostic tests against published Target Product Profiles that have been defined through consensus processes. These studies are for diagnostic products developed by private sector companies who provide access to know‐how, equipment/reagents, and contribute through unrestricted donations as per FIND policy and external SAC review.
Sabine Dittrich: is employed by FIND with funding from DFID and Australian Aid. FIND is a global non‐for profit product development partnership and WHO Diagnostic Collaboration Centre. It is FIND’s role to accelerate access to high‐quality diagnostic tools for low‐resource settings and this is achieved by supporting both research and development and access activities for a wide range of diseases, including COVID‐19. FIND has several clinical research projects to evaluate multiple new diagnostic tests against published Target Product Profiles that have been defined through consensus processes. These studies are for diagnostic products developed by private sector companies who provide access to know‐how, equipment/reagents, and contribute through unrestricted donations as per FIND policy and external SAC review.
Sian Taylor‐Phillips: none known
Sarah Berhane: none known
Jane Cunningham: none known
Figures













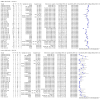

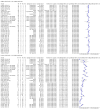
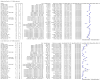






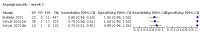
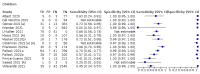

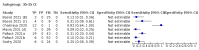

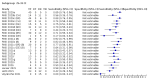
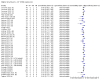
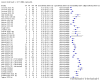
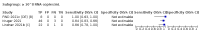
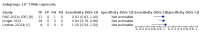
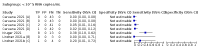
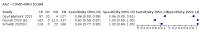
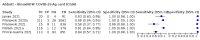
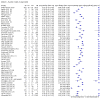
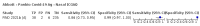
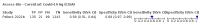
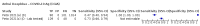
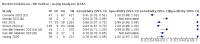
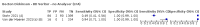
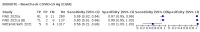
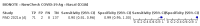
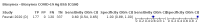
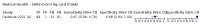

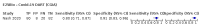
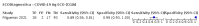
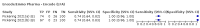
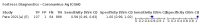
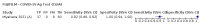

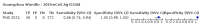
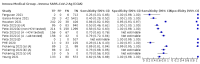
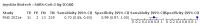
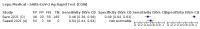
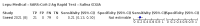
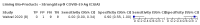
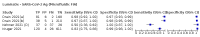
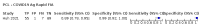
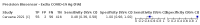
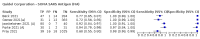
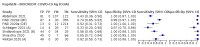
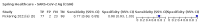
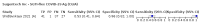
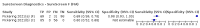
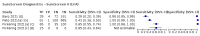
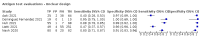
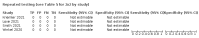
Update of
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 24;3(3):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7:CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. PMID: 33760236 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Abdelrazik 2021 {published data only}
Abdulrahman 2020 {published data only}
-
- Abdulrahman A, Mustafa F, AlAwadhi AI, Alansari Q, AlAlawi B, AlQahtani M. Comparison of SARS-COV-2 nasal antigen test to nasopharyngeal RT-PCR in mildly symptomatic patients. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Agullo 2021 [A] {published data only}
Agullo 2021 [B] {published data only}
Agullo 2021 [C] {published data only}
Akingba 2021 {published data only}
Albert 2020 {published data only}
-
- Albert E, Torres I, Bueno F, Huntley D, Molla E, Fernández-Fuentes MA, et al. Field evaluation of a rapid antigen test (Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device) for COVID-19 diagnosis in primary healthcare centers. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2020 Nov 13 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Alemany 2021 {published data only}
Aoki 2021 {published data only}
Baro 2021 [A] {published data only}
Baro 2021 [B] {published data only}
Baro 2021 [C] {published data only}
Baro 2021 [D] {published data only}
Baro 2021 [E] {published data only}
Basso 2021 [A] {published data only}
Basso 2021 [B] {published data only}
Basso 2021 [C] {published data only}
Beck 2021 {published data only}
Billaud 2020 {published data only}
-
- Billaud G, Gaymard A, Lina B, Laboratoire de Virologie des HCL CNR des virus des infections respiratoires. Evaluation du Test Antigénique ABBOTT SARS-COV2 ABBOT. Lyon, France: SFM (French Society of Microbiology), 2020.
Blairon 2020 {published data only}
Bulilete 2021 {published data only}
-
- Bulilete O, Lorente P, Leiva A, Carandell E, Oliver A, Rojo E, et al. Evaluation of the Panbio rapid antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 in primary health care centers and test sites. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Caruana 2021 [A] {published data only}
Caruana 2021 [B] {published data only}
Caruana 2021 [C] {published data only}
Caruana 2021 [D] {published data only}
Cerutti 2020 {published data only}
Chaimayo 2020 {published data only}
Ciotti 2021 {published data only}
Courtellemont 2021 {published data only}
Del Vecchio 2021 {published data only}
-
- Del Vecchio C, Brancaccio G, Brazzale AR, Lavezzo E, Onelia F, Franchin E, et al. Emergence of N antigen SARS-CoV-2 genetic variants escaping detection of antigenic tests. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Dominguez Fernandez 2021 {published data only}
Drain 2021(a) {published data only}
Drain 2021(b) {published data only}
Drevinek 2020 [A] {published data only}
-
- Drevinek P, Hurych J, Kepka Z, Briksi A, Kulich M, Zajac M, et al. The sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests in the view of large-scale testing. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Drevinek 2020 [B] {published data only}
-
- Drevinek P, Hurych J, Kepka Z, Briksi A, Kulich M, Zajac M, et al. The sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests in the view of large-scale testing. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Faico‐Filho 2021 {published data only}
Favresse 2021 [A] {published data only}
Favresse 2021 [B] {published data only}
Favresse 2021 [C] {published data only}
Favresse 2021 [D] {published data only}
Fenollar 2020(a) {published data only}
Fenollar 2020(b) {published data only}
Ferguson 2021 {published data only}
-
- Ferguson J, Dunn S, Best A, Mirza J, Percival B, Mayhew M, et al. Validation testing to determine the sensitivity of lateral flow testing for asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 detection in low prevalence settings: Testing frequency and public health messaging is key. PLoS Biology 2021;19(4). [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Filgueiras 2021 {published data only}
-
- Filgueiras PS, Corsini CA, Almeida NBF, Assis JV, Pedrosa MLC, Oliveira AK, et al. COVID-19 Rapid Antigen Test at hospital admission associated to the knowledge of individual risk factors allow overcoming the difficulty of managing suspected patients in hospitals. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
FIND 2020a {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of Bionote, Inc. NowCheck COVID-19 Ag Test - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020b (CH) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of Abbott Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020b (DE) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of Abbott Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020c (BR) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020c (CH) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020c (DE) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). FIND Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc.STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test External Report. Vol. version 2.1. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
-
- Krüger LJ, Gaeddert M, Köppel L, Brümmer LE, Gottschalk C, Miranda IB, et al. Evaluation of the accuracy, ease of use and limit of detection of novel, rapid, antigen-detecting point-of-care diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
FIND 2020d (BR) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020d (DE) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD F COVID-19 Ag FIA - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020e (BR) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of RapiGEN Inc. BIOCREDIT COVID-19 Ag - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020e (DE) {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). Evaluation of RapiGEN Inc. BIOCREDIT COVID-19 Ag - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
FIND 2020f {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). FIND Evaluation of Coris BioConcept COVID-19 Ag Respi-Strip - External Report. Vol. v1.2. Switzerland: FIND, 2020.
-
- Krüger LJ, Gaeddert M, Köppel L, Brümmer LE, Gottschalk C, Miranda IB, et al. Evaluation of the accuracy, ease of use and limit of detection of novel, rapid, antigen-detecting point-of-care diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
FIND 2021a [A] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Bionote, Inc. NowCheck COVID-19 Ag TestTest, nasal swab - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021a [B] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Bionote, Inc. NowCheck COVID-19 Ag TestTest, nasal swab - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021b [A] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Abbott Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device [NASAL] - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021b [B] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Abbott Panbio COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test Device [NASAL] - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021c (BR) [A] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test, nasal swab - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021c (BR) [B] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test, nasal swab - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021c (DE) [A] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test, nasal swab - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021c.
FIND 2021c (DE) [B] {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of SD Biosensor, Inc. STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag Test, nasal swab - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021d {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Fujirebio Inc. Espline SARS-CoV-2 - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021e {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Joysbio (Tianjin) Biotechnology Co., Ltd. SARS-CoV-2 Antigen Rapid Test Kit (Colloidal Gold) - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021f {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Mologic Ltd, COVID 19 RAPID ANTIGEN TEST - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021g {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of NADAL COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021h {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Boditech Medical, Inc. iChroma COVID-19 Ag Test - External Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021i {published data only}
-
- FIND. FIND Evaluation of Guangzhou Wondfo Biotech Co., Ltd Wondfo 2019-nCoV Antigen Test (Lateral Flow Method) Public Report. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
FIND 2021j {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). FIND Evaluation of Shenzhen Bioeasy Biotechnology Co. Ltd.2019-nCoV Ag Rapid Test Kit (Fluorescence) External Report. Vol. Version 1.0. Switzerland: FIND, 2021.
-
- Krüger LJ, Gaeddert M, Köppel L, Brümmer LE, Gottschalk C, Miranda IB, et al. Evaluation of the accuracy, ease of use and limit of detection of novel, rapid, antigen-detecting point-of-care diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Fourati 2020 [A] {published data only}
-
- Fourati S, Audureau E, Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. Évaluation de la performance diagnostique des tests rapides d’orientation diagnostique antigéniques COVID-19. France: AP-HP Hopitaux universitaires Henri-Mondor, 2020.
Fourati 2020 [B] {published data only}
-
- Fourati S, Audureau E, Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. Évaluation de la performance diagnostique des tests rapides d’orientation diagnostique antigéniques COVID-19. France: AP-HP Hopitaux universitaires Henri-Mondor, 2020.
Fourati 2020 [C] {published data only}
-
- Fourati S, Audureau E, Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. Évaluation de la performance diagnostique des tests rapides d’orientation diagnostique antigéniques COVID-19. France: AP-HP Hopitaux universitaires Henri-Mondor, 2020.
Fourati 2020 [D] {published data only}
-
- Fourati S, Audureau E, Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. Évaluation de la performance diagnostique des tests rapides d’orientation diagnostique antigéniques COVID-19. France: AP-HP Hopitaux universitaires Henri-Mondor, 2020.
Fourati 2020 [E] {published data only}
-
- Fourati S, Audureau E, Chevaliez S, Pawlotsky JM. Évaluation de la performance diagnostique des tests rapides d’orientation diagnostique antigéniques COVID-19. France: AP-HP Hopitaux universitaires Henri-Mondor, 2020.
Garcia‐Finana 2021 {published data only}
Gomez 2021(a) {published data only}
-
- Gomez Marti JL, Gribschaw J, McCullough M, Mallon A, Acero J, Kinzler A, et al. Differences in detected viral loads guide use of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detection assays towards symptomatic college students and children. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Gomez 2021(b) {published data only}
-
- Gomez Marti JL, Gribschaw J, McCullough M, Mallon A, Acero J, Kinzler A, et al. Differences in detected viral loads guide use of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detection assays towards symptomatic college students and children. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Gonzalez‐Donapetry 2021 {published data only}
-
- Gonzalez-Donapetry P, Garcia-Clemente P, Bloise I, Garcia-Sanchez C, Sanchez Castellano MA, Romero MP, et al. Think of the children: evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test in pediatric population. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2021;40(5):385-8. - PubMed
Gremmels 2021(a) {published data only}
Gremmels 2021(b) {published data only}
-
- Gremmels H, Winkel BM, Schuurman R, Rosingh A, Rigter NA, Rodriguez O, et al. Real-life validation of the PanbioTM COVID-19 antigen rapid test (Abbott) in community-dwelling subjects with symptoms of potential SARS-CoV-2 infection. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020:10.1101/2020.10.16.20214189. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Gupta 2020 {published data only}
-
- Gupta A, Khurana S, Das R, Srigyan D, Singh A, Mittal A, et al. Rapid chromatographic immunoassay-based evaluation of COVID-19: a cross-sectional, diagnostic test accuracy study & its implications for COVID-19 management in India. Indian Journal of Medical Research 2020 Oct 31 [Epub ahead of print]:10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_3305_20. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Halfon 2021 {published data only}
Houston 2021 {published data only}
Huh 2021 {published data only}
-
- Huh HJ, Chae SL, Kim D-M. Comparison and analysis of various complementary diagnosis methods for the current situation and problems of COVID-19 diagnosis. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Igloi 2021 {published data only}
-
- Igloi Z, Velzing J, Van Beek J, Van de Vijver D, Aron G, Ensing R, et al. Clinical evaluation of the Roche/SD Biosensor rapid antigen test with symptomatic, non-hospitalized patients in a municipal health service drive-through testing site. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Ishii 2021 [A] {published data only}
Ishii 2021 [B] {published data only}
Jaaskelainen 2021 [A] {published data only}
Jaaskelainen 2021 [B] {published data only}
Jaaskelainen 2021 [C] {published data only}
Jakobsen 2021 {published data only}
-
- Jakobsen KK, Jensen JS, Todsen T, Lippert F, Martel CJ-M, Klokker M, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection by rapid antigen test in comparison with RT-PCR in a public setting. medRxiv[Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
-
- Jakobsen KK, Jensen JS, Todsen T, Tolsaard MG, Kirkby N, Lippert F, et al. Accuracy and cost description of rapid antigen test compared with reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Danish Medical Journal 2021;68(7):A03210217. - PubMed
James 2021 {published data only}
-
- James AE, Gulley T, Kothari A, Holder K, Garner K, Patil N. Performance of the BinaxNOW coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Antigen Card test relative to the severe acute respiratory coronavirus virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) assay among symptomatic and asymptomatic healthcare employees. Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology 2021:1-3. - PMC - PubMed
Kerneis 2021 {published data only}
-
- Kernéis S, Elie C, Fourgeaud J, Choupeaux L, Delarue SM, Alby M-L, et al. Accuracy of antigen and nucleic acid amplification testing on saliva and naopharyngeal samples for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in ambulatory care. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Kilic 2021 {published data only}
Kohmer 2021 [A] {published data only}
Kohmer 2021 [B] {published data only}
Kohmer 2021 [C] {published data only}
Kohmer 2021 [D] {published data only}
Kriemler 2021 {published data only}
Kruger 2021 {published data only}
Kruttgen 2021 {published data only}
L'Huillier 2021 {published data only}
Lambert‐Niclot 2020 {published data only}
Lanser 2021 {published data only}
Linares 2020 {published data only}
Lindner 2021a [A] {published data only}
-
- Lindner AK, Nikolai O, Rohardt C, Kausch F, Wintel M, Gertler M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 patient self-testing with an antigen-detecting rapid test: a head-to-head comparison with professional testing. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Lindner 2021a [B] {published data only}
Lindner 2021b [A] {published data only}
Lindner 2021b [B] {published data only}
Lindner 2021b [C] {published data only}
Liotti 2021 {published data only}
Love 2021 {published data only}
-
- Love NK, Ready D, Turner C, Yardley L, Rubin GJ, Hopkins S, et al. The acceptability of testing contacts of confirmed COVID-19 cases using serial, self-administered lateral flow devices as an alternative to self-isolation. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Masia 2021 [A] {published data only}
-
- Masiá M, Fernández-González M, Sánchez M, Carvajal M, García JA, Gonzalo-Jiménez N, et al. Nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 Antigen performed at point-of-care has a high sensitivity in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with higher risk for transmission and older age. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2021;8(3):ofab059. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Masia M, Fernandez-Gonzalez M, Sanchez M, Carvajal M, Garcia JA, Gonzalo N, et al. Nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 antigen performed at point-of-care has a high sensitivity in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with higher risk for transmission and older age. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Masia 2021 [B] {published data only}
-
- Masiá M, Fernández-González M, Sánchez M, Carvajal M, García JA, Gonzalo-Jiménez N, et al. Nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 Antigen performed at point-of-care has a high sensitivity in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with higher risk for transmission and older age. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2021;8(3):ofab059. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Masia 2021 [C] {published data only}
-
- Masiá M, Fernández-González M, Sánchez M, Carvajal M, García JA, Gonzalo-Jiménez N, et al. Nasopharyngeal Panbio COVID-19 Antigen performed at point-of-care has a high sensitivity in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients with higher risk for transmission and older age. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2021;8(3):ofab059. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Merino 2021 {published data only}
-
- Merino-Amador P, Guinea J, Muñoz-Gallego I, González-Donapetry P, Galán J-C, Antona N, et al. Multicenter evaluation of the Panbio™ COVID-19 Rapid Antigen-Detection Test for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Mertens 2020 {published data only}
Miyakawa 2021 [A] {published data only}
-
- Miyakawa K, Funabashi R, Yamaoka Y, Jeremiah SS, Katada J, Wada A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic test enhanced with silver amplification technology. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Miyakawa 2021 [B] {published data only}
-
- Miyakawa K, Funabashi R, Yamaoka Y, Jeremiah SS, Katada J, Wada A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic test enhanced with silver amplification technology. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Miyakawa 2021 [C] {published data only}
-
- Miyakawa K, Funabashi R, Yamaoka Y, Jeremiah SS, Katada J, Wada A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic test enhanced with silver amplification technology. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Miyakawa 2021 [D] {published data only}
-
- Miyakawa K, Funabashi R, Yamaoka Y, Jeremiah SS, Katada J, Wada A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic test enhanced with silver amplification technology. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Mockel 2021(a) {published data only}
Mockel 2021(b) {published data only}
Nagura‐Ikeda 2020 {published data only}
-
- Nagura-Ikeda M, Imai K, Tabata S, Miyoshi K, Murahara N, Mizuno T, et al. Clinical evaluation of self-collected saliva by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR), direct RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and a rapid antigen test to diagnose COVID-19. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2020;58(9):e01438-20. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Nalumansi 2020 {published data only}
Nash 2020 {published data only}
-
- Nash B, Badea A, Reddy A, Bosch M, Salcedo N, Gomez AR, et al. The impact of high frequency rapid viral antigen screening on COVID-19 spread and outcomes: a validation and modeling study. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Ngo Nsoga 2021 {published data only}
Nikolai 2021(a) [A] {published data only}
Nikolai 2021(a) [B] {published data only}
Nikolai 2021(b) [A] {published data only}
Nikolai 2021(b) [B] {published data only}
Okoye 2021 {published data only}
Olearo 2021 [A] {published data only}
Olearo 2021 [B] {published data only}
Olearo 2021 [C] {published data only}
Olearo 2021 [D] {published data only}
-
- Olearo F, Noerz D, Heinrich F, Sutter JP, Roedel K, Schultze A, et al. Handling and accuracy of four rapid antigen tests for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 compared to RT-qPCR. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.05.20244673] - PMC - PubMed
Osterman 2021(a) [A] {published data only}
Osterman 2021(a) [B] {published data only}
Osterman 2021(b) {published data only}
Parada‐Ricart 2020 {published data only}
Pena 2021 {published data only}
Pena‐Rodriguez 2021 {published data only}
Perez‐Garcia 2021 [A] {published data only}
Perez‐Garcia 2021 [B] {published data only}
Peto 2021(a) [A] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Public Health England (PHE). Preliminary report from the Joint PHE Porton Down & University of Oxford SARS-CoV-2 test development and validation cell: rapid evaluation of lateral flow viral antigen detection devices (LFDs) for mass community testing. Public Health England, 2020.
Peto 2021(a) [B] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [EMBASE: httpa://doi,org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(a) [C] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(a) [D] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(a) [E] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(a) [F] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(a) [G] {published data only}
Peto 2021(b) [non‐HCW tested] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Public Health England (PHE). Preliminary report from the Joint PHE Porton Down & University of Oxford SARS-CoV-2 test development and validation cell: rapid evaluation of lateral flow viral antigen detection devices (LFDs) for mass community testing. Public Health England, 2020.
Peto 2021(c) [A ‐ HCW tested] {published data only}
-
- Public Health England (PHE). Preliminary report from the Joint PHE Porton Down & University of Oxford SARS-CoV-2 test development and validation cell: rapid evaluation of lateral flow viral antigen detection devices (LFDs) for mass community testing. Public Health England, 2020.
Peto 2021(c) [A ‐ Lab tested] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Public Health England (PHE). Preliminary report from the Joint PHE Porton Down & University of Oxford SARS-CoV-2 test development and validation cell: rapid evaluation of lateral flow viral antigen detection devices (LFDs) for mass community testing. Public Health England, 2020.
Peto 2021(c) [B ‐ Lab tested] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(c) [C ‐ Lab tested] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(c) [D ‐ Lab tested] {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: a national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Peto 2021(d) {published data only}
-
- Peto T, Affron D, Afrough B, Agasu A, Ainsworth M, Allanson A, et al. COVID-19: Rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 by lateral flow assay: A national systematic evaluation of sensitivity and specificity for mass-testing. EClinicalMedicine 2021;36:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100924. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Public Health England (PHE). Preliminary report from the Joint PHE Porton Down & University of Oxford SARS-CoV-2 test development and validation cell: rapid evaluation of lateral flow viral antigen detection devices (LFDs) for mass community testing. Public Health England, 2020.
PHE 2020 {published data only}
-
- Public Health England (PHE). Preliminary report from the Joint PHE Porton Down & University of Oxford SARS-CoV-2 test development and validation cell: rapid evaluation of lateral flow viral antigen detection devices (LFDs) for mass community testing. Public Health England, 2020.
Pickering 2021(a) [A] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(a) [B] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(a) [C] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(a) [D] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(a) [E] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(a) [F] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(b) [A] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(b) [B] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(b) [C] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(c) [A] {published data only}
Pickering 2021(c) [B] {published data only}
-
- Pickering S, Batra R, Snell LB, Merrick B, Nebbia G, Douthwaite S, et al. Comparative performance of SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow antigen tests demonstrates their utility for high sensitivity detection of infectious virus in clinical specimens. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021:10.1101/2021.02.27.21252427. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Pilarowski 2020a {published data only}
Pilarowski 2021 {published data only}
-
- Pilarowski G, Lebel P, Sunshine S, Liu J, Crawford E, Marquez C, et al. Performance characteristics of a rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection assay at a public plaza testing site in San Francisco. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2021;23(7):1139-44. [EMBASE: https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiaa802] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pilarowski G, Lebel P, Sunshine S, Liu J, Crawford E, Marquez C, et al. Performance characteristics of a rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection assay at a public plaza testing site in San Francisco. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [EMBASE: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.02.20223891] - PMC - PubMed
Pollock 2021a {published data only}
-
- Pollock NR, Jacobs JR, Tran K, Cranston AE, Smith S, O'Kane CY, et al. Performance and implementation evaluation of the Abbott BinaxNOW Rapid Antigen Test in a high-throughput drive-through community testing site in Massachusetts. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2021;59(5):e00083-21. - PMC - PubMed
Pollock 2021b {published data only}
-
- Pollock NR, Tran K, Jacobs JR, Cranston AE, Smith S, O'Kane CY, et al. Performance and operational evaluation of the Access Bio CareStart Rapid Antigen Test in a high-throughput drive-through community testing site in Massachusetts. Open Forum Infectious Diseases 2021;8(7):ofab243. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Porte 2020 {published data only}
Porte 2021 [A] {published data only}
-
- Porte L, Legarraga P, Iruretagoyena M, Vollrath V, Pizarro G, Munita JM, et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection by immunofluorescence – a new tool to detect infectivity. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Porte 2021 [B] {published data only}
-
- Porte L, Legarraga P, Iruretagoyena M, Vollrath V, Pizarro G, Munita JM, et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection by immunofluorescence – a new tool to detect infectivity. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Pray 2021 {published data only}
Prince‐Guerra 2021 {published data only}
-
- Prince-Guerra JL, Almendares O, Nolen LD, Gunn JKL, Dale AP, Buono SA, et al. Evaluation of Abbott BinaxNOW Rapid Antigen Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection at two community-based testing sites - Pima County, Arizona, November 3-17, 2020. MMWR: Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2021;70(3):100-5. - PMC - PubMed
Ristic 2021 {published data only}
Rottenstreich 2021 {published data only}
Saeed 2021 [A] {published data only}
Saeed 2021 [B] {published data only}
Salvagno 2021 {published data only}
-
- Salvagno GL, Gianfilippi G, Bragantini D, Henry BM, Lippi G. Clinical assessment of the Roche SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test. Diagnosis (Berl) 2021;8(3):322-6. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Schildgen 2021 [A] {published data only}
Schildgen 2021 [B] {published data only}
Schildgen 2021 [C] {published data only}
Schuit 2021(a) {published data only}
Schuit 2021(b) {published data only}
Schwob 2020(a) {published data only}
Schwob 2020(b) {published data only}
Schwob 2020(c) {published data only}
-
- Schwob JM, Miauton A, Petrovic D, Perdrix J, Senn N, Jaton K, et al. Antigen rapid tests, nasopharyngeal PCR and saliva PCR to detect SARS-CoV-2: a prospective comparative clinical trial. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [EMBASE: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.23.20237057] - PMC - PubMed
Scohy 2020 {published data only}
Shidlovskaya 2021 [A] {published data only}
Shidlovskaya 2021 [B] {published data only}
Shrestha 2020 {published data only}
-
- Shrestha B, Neupane AK, Pant S, Shrestha A, Bastola A. Sensitivity and specificity of lateral flow antigen test kits for COVID-19 in asymptomatic population of quarantine centre of Province 3. Kathmandu University Medical Journal 2020;18(70):36-9. - PubMed
Smith 2021 {published data only}
Stohr 2021 [A] {published data only}
-
- Stohr JJ, Zwart VF, Goderski G, Meijer A, Nagel-Imming CR, Kluytmans-van den Bergh MF, et al. Self-testing for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection with rapid antigen tests. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021;40(8):1721-6. [EMBASE: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.21.21252153] - PMC - PubMed
Stohr 2021 [B] {published data only}
Stokes 2021(a) [A] {published data only}
-
- Stokes W, Berenger BM, Portnoy D, Scott B, Szelewicki J, Singh T, et al. Clinical performance of the Abbott Panbio with nasopharyngeal, throat, and saliva swabs among symptomatic individuals with COVID-19. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 2021;40(8):1721-6. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Stokes 2021(a) [B] {published data only}
-
- Stokes W, Berenger BM, Portnoy D, Scott B, Szelewicki J, Singh T, et al. Clinical performance of the Abbott Panbio with nasopharyngeal, throat, and saliva swabs among symptomatic individuals with COVID-19. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Disease 2021;40(8):1721-6. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Stokes 2021(a) [C] {published data only}
-
- Stokes W, Berenger BM, Portnoy D, Scott B, Szelewicki J, Singh T, et al. Clinical performance of the Abbott Panbio with nasopharyngeal, throat, and saliva swabs among symptomatic individuals with COVID-19. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2021;40(8):1721-6. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Stokes 2021(b) {published data only}
-
- Stokes W, Berenger BM, Portnoy D, Scott B, Szelewicki J, Singh T, et al. Clinical performance of the Abbott Panbio with nasopharyngeal, throat, and saliva swabs among symptomatic individuals with COVID-19. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2021;40(8):1721-6. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Stromer 2020 {published data only}
Takeda 2020 {published data only}
-
- Takeda Y, Mori M, Omi K. SARS-CoV-2 qRT-PCR Ct value distribution in Japan and possible utility of rapid antigen testing kit. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Takeuchi 2021a {published data only}
-
- Takeuchi Y, Akashi Y, Kato D, Kuwahara M, Muramatsu S, Ueda A, et al. The evaluation of a newly developed antigen test (QuickNaviTM-COVID19 Ag) for SARS-CoV-2: A prospective observational study in Japan. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [EMBASE: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.27.20248876] - PMC - PubMed
Takeuchi 2021b {published data only}
Thommes 2021 [A] {published data only}
Thommes 2021 [B] {published data only}
Thommes 2021 [C] {published data only}
Thommes 2021 [D] {published data only}
Toptan 2021(a) {published data only}
Toptan 2021(b) {published data only}
Torres 2021a {published data only}
Torres 2021b {published data only}
Turcato 2021 {published data only}
-
- Turcato G, Zaboli A, Pfeifer N, Ciccariello L, Sibilio S, Tezza G, et al. Clinical application of a rapid antigen test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients evaluated in the emergency department: a preliminary report. Journal of Infection 2021;82(3):e14-6. - PMC - PubMed
Van der Moeren 2021(a) [A] {published data only}
-
- Van der Moeren N, Zwart VF, Lodder EB, Van den Bijllaardt W, Van Esch HR, Stohr JJ, et al. Performance evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test: test performance in the community in the Netherlands. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Van der Moeren 2021(a) [B] {published data only}
-
- Van der Moeren N, Zwart VF, Lodder EB, Van den Bijllaardt W, Van Esch HR, Stohr JJ, et al. Performance evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test: test performance in the community in the Netherlands. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Van der Moeren 2021(b) {published data only}
-
- Van der Moeren N, Zwart VF, Lodder EB, Van den Bijllaardt W, Van Esch HR, Stohr JJ, et al. Performance evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test: test performance in the community in the Netherlands. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Veyrenche 2021 {published data only}
Villaverde 2021 {published data only}
-
- Villaverde S, Dominguez-Rodriguez S, Sabrido G, Perez-Jorge C, Plata M, Romero MP, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the Panbio severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 antigen rapid test compared with reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction testing of nasopharyngeal samples in the pediatric population. Journal of Pediatrics 2021;232:287-289 e4. - PMC - PubMed
Weitzel 2020 [A] {published data only}
Weitzel 2020 [B] {published data only}
Weitzel 2020 [C] {published data only}
Weitzel 2020 [D] {published data only}
Winkel 2020 {published data only}
-
- Winkel BM, Schram E, Gremmels H, Debast SB, Schuurman R, Wensing AM, et al. Screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection in asymptomatic individuals using the Panbio COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test (Abbott) compared to RT-qPCR. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.03.20243311] - PMC - PubMed
Yokota 2020(a) {published data only}
Yokota 2020(b) {published data only}
Young 2020 {published data only}
-
- Young S, Taylor SN, Cammarata CL, Varnado KG, Roger-Dalbert C, Montano A, et al. Clinical evaluation of BD Veritor SARS-CoV-2 point-of-care test performance compared to PCR-based testing and versus the Sofia 2 SARS Antigen point-of-care test. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2020;59(1):e02338-20. [DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02338-20] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ahava 2021 {published data only}
Aoki 2020 {published data only}
Bello‐Chavolla 2021 {published data only}
-
- Bello-Chavolla OY, Antonio-Villa NE, Fernandez-Chirino L, Guerra C, Fermin-Martinez CA, Marquez-Salinas A, et al. Diagnostic performance and clinical implications of rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen testing in Mexico using real-world nationwide COVID-19 registry data. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Chen 2021 {published data only}
Corman 2020 {published data only}
Cubas‐Atienzar 2021 {published data only}
Dalal 2021 {published data only}
Diao 2020 {published data only}
-
- Diao B, Wen K, Chen J, Liu Y, Yuan Z, Han C, et al. Diagnosis of acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection by detection of nucleocapsid protein. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Dohla 2020 {published data only}
Downs 2021 {published data only}
Eshghifar 2021 {published data only}
Frnda 2021 {published data only}
Gili 2021 {published data only}
-
- Gili A, Paggi R, Russo C, Cenci E, Pietrella D, Graziani A, et al. Evaluation of automated test Lumipulse® G SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein (NP) in nasopharyngeal swabs for community and population screening. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2021;105:391-6. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Haage 2021a {published data only}
Haage 2021b {published data only}
Herrera 2020 {published data only}
-
- Herrera V, Hsu V, Adewale A, Hendrix T, Johnson L, Kuhlman J, et al. Testing of healthcare workers exposed to COVID19 with rapid antigen detection. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Hingrat 2020 {published data only}
Hirotsu 2020 {published data only}
-
- Hirotsu Y, Maejima M, Shibusawa M, Nagakubo Y, Hosaka K, Amemiya K, et al. Comparison of automated SARS-CoV-2 antigen test for COVID-19 infection with quantitative RT-PCR using 313 nasopharyngeal swabs, including from seven serially followed patients. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2020;99:397-402. - PMC - PubMed
Hirotsu 2021 {published data only}
-
- Hirotsu Y, Maejima M, Shibusawa M, Amemiya K, Nagakubo Y, Hosaka K et al. Prospective study of 1,308 nasopharyngeal swabs from 1,033 patients using the LUMIPULSE SARS-CoV-2 antigen test: comparison with RT-qPCR. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2021;105:7-14. [DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.02.005] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Hledik 2020 {published data only}
-
- Hledik M, Polechova J, Beiglboeck M, Herdina AN, Strassl R, Posch M. Analysis of the specificity of the SD Biosensor Standard Q Ag-Test based on Slovak mass testing data. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Hoehl 2020 {published data only}
-
- Hoehl S, Schenk B, Rudych O, Goettig S, Foppa I, Kohmer N, et al. At-home self-testing of teachers with a SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test to reduce potential transmissions in schools. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Kannian 2021 {published data only}
-
- Kannian P, Lavanya C, Ravichandran K, Jayaraman BG, Mahanathi P, Ashwini V, et al. Detection of SARS-CoV2 antigen in human saliva may be a reliable tool for large scale screening. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Kashiwagi 2020 {published data only}
Kobayashi 2021 {published data only}
Koskinen 2021 {published data only}
Kotsiou 2021 {published data only}
-
- Kotsiou OS, Pantazopoulos I, Papagiannis D, Fradelos EC, Kanellopoulos N, Siachpazidou D, et al. Repeated antigen-based rapid diagnostic testing for estimating the coronavirus disease 2019 prevalence from the perspective of the workers' vulnerability before and during the lockdown. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2021;18(4):1638. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Kurstjens 2020 {published data only}
-
- Kurstjens S, Van der Horst A, Herpers R, Geerits MW, Kluiters-de Hingh YC, Göttgens E-L, et al. Rapid identification of SARS-CoV-2-infected patients at the emergency department using routine testing. bioRxiv [Preprint] 2020:1-21. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Kyosei 2020 {published data only}
Lefever 2021 {published data only}
Le Hingrat 2020 {published data only}
-
- Le Hingrat Q, Visseaux B, Laouenan C, Tubiana S, Bouadma L, Yazdanpanah Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 N-antigenemia: a new alternative to nucleic acid amplification techniques. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Li 2021 {published data only}
Liu 2021 {published data only}
Mahari 2020 {published data only}
-
- Mahari S, Roberts A, Shahdeo D, Gandhi S. eCovSens-Ultrasensitive novel in-house built printed circuit board based electrochemical device for rapid detection of nCOVID-19 antigen, a spike protein domain 1 of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Mak 2020a {published data only}
Mak 2020b {published data only}
Marzinotto 2020 {published data only}
Mboumba 2021 {published data only}
-
- Mboumba Bouassa R-S, Veyer D, Péré H, Bélec L. Analytical performances of the point-of-care SIENNATM COVID-19 Antigen Rapid Test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in nasopharyngeal swabs: a prospective evaluation during the COVID-19 second wave in France. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2021;106:8-12. - PMC - PubMed
McAulay 2020 {published data only}
-
- McAulay K, Kaleta EJ, Grys TE. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen from serum in a hospitalized population. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
McDonald 2020 {published data only}
Menchinelli 2021 {published data only}
-
- Menchinelli G, Bordi L, Liotti FM, Palucci I, Capobianchi MR, Sberna G, et al. Lumipulse G SARS-CoV-2 Ag assay evaluation using clinical samples from different testing groups. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine 2021;59(8):1468-76. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Mohamed 2021 {published data only}
-
- Mohamed RA, Junaideen SM. Issues of random sampling with rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 diagnosis: a special reference to Kalmunai RDHS Division. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Moreno 2021 {published data only}
Nachtigall 2020 {published data only}
-
- Nachtigall FM, Pereira A, Trofymchuk OS, Santos LS. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasal swabs using MALDI-MS. Nature Biotechnology 2020;38(10):1168-73. - PubMed
Ogawa 2020 {published data only}
Pavelka 2020 {published data only}
-
- Pavelka M, Van Zandvoort K, Abbott S, Sherratt K, Majdan M, Jarcuska P, et al, CMMID COVID-19 Working Group. The effectiveness of population-wide, rapid antigen test based screening in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infection prevalence in Slovakia. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Pekosz 2021 {published data only}
-
- Pekosz A, Cooper C, Parvu V, Li M, Andrews J, Manabe YCC, et al. Antigen-based testing but not real-time PCR correlates with SARS-CoV-2 virus culture. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: ]
Pellanda 2020 {published data only}
-
- Pellanda LC, Wendland EM, McBride AJ, Tovo-Rodrigues L, Ferreira MR, Dellagostin OA, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of a rapid test for assessment of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in a community-based setting in Brazil. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.05.06.20093476] - DOI
Peng 2020 {published data only}
Perchetti 2020 {published data only}
Pollock 2020a {published data only}
Rastawicki 2021 {published data only}
-
- Rastawicki W, Gierczyński R, Juszczyk G, Mitura K, Henry BM. Evaluation of PCL rapid point of care antigen test for detection of SARS-CoV-2 in nasopharyngeal swabs. Journal of Medical Virology 2021;93(4):1920-2. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Regev‐Yochay 2021 {published data only}
-
- Regev-Yochay G, Kriger O, Beni S, Rubin C, Mina MJ, Mechnik B, et al. Real world performance of SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic tests in various clinical settings. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Ren 2021 {published data only}
-
- Ren A, Sohaei D, Zacharioudakis I, Sigal GB, Stengelin M, Matthew A, et al. Ultrasensitive assay for saliva-based SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Rodriguez‐Manzano 2020 {published data only}
Rusanen 2020 {published data only}
Scheiblauer 2021 {published data only}
Seitz 2021 {published data only}
Seo 2020 {published data only}
-
- Seo G, Lee G, Kim MJ, Baek SH, Choi M, Ku KB, et al. Rapid detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) in human nasopharyngeal swab specimens using field-effect transistor-based biosensor. ACS Nano (American Chemical Society) 2020;14(4):5135-42. - PubMed
Singh 2020a {published data only}
Singh 2020b {published data only}
Wang 2020 {published data only}
-
- Wang D, He S, Wang X, Yan Y, Liu J, Wu S, et al. Rapid lateral flow immunoassay for the fluorescence detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Nature Biomedical Engineering 2020;4:1150-8. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Wu 2020 {published data only}
Yamamoto 2021 {published data only}
Yamayoshi 2020 {published data only}
Yokota 2021 {published data only}
Yu 2020 {published data only}
-
- Yu S, Nimse SB, Kim J, Song KS, Kim T. Development of a lateral flow strip membrane assay for rapid and sensitive detection of the SARS-CoV-2. Analytical Chemistry 2020;92(20):14139-44. - PubMed
Zamecnik 2020 {published data only}
Zeng 2020 {published data only}
Zhang 2020 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Abdul‐Mumin 2021 {published data only}
Abusrewil 2021 {published data only}
Akashi 2021 {published data only}
Amer 2021 {published data only}
-
- Amer RM, Samir M, Gaber OA, El-Deeb NA, Abdelmoaty AA, Ahmed AA, et al. Diagnostic performance of rapid antigen test for COVID-19 and the effect of viral load, sampling time, subject's clinical and laboratory parameters on test accuracy. Journal of Infection Public Health 2021;14(10):1446-53. - PMC - PubMed
Aranda‐Diaz 2021 {published data only}
Baccani 2021 {published data only}
Bianco 2021 {published data only}
Blairon 2021 {published data only}
Bonde 2021 {published data only}
-
- Bonde J, Ejegod DM, Pedersen H, Smith B, Cortes D, Leding C, et al. Clinical validation of point-of-care SARS-COV-2 BD Veritor antigen test by a single throat swab for rapid COVID-19 status on hospital patients predominantly without overt COVID symptoms. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Boum 2021 {published data only}
-
- Boum Y, Fai KN, Nikolay B, Mboringong AB, Bebell LM, Ndifon M, et al. Performance and operational feasibility of antigen and antibody rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 in symptomatic and asymptomatic patients in Cameroon: a clinical, prospective, diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2021;21(8):1089-96. - PMC - PubMed
Brihn 2021 {published data only}
-
- Brihn A, Chang J, OYong K, Balter S, Terashita D, Rubin Z, et al. Diagnostic performance of an antigen test with RT-PCR for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 in a hospital setting - Los Angeles County, California, June-August 2020. MMWR Morbidity & Mortality Weekly Report 2021;70(19):702-6. - PMC - PubMed
Bruins 2021 {published data only}
-
- Bruins MJ, Oliveira dos Santos C, Spoelman-Lunsche M, Van den Bos-Kromhout MI, Debast SB. Evaluation of the PanbioTM rapid antigen test for COVID-19 diagnosis in symptomatic health care workers. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Bruzzone 2021 {published data only}
Caruana 2021 {published data only}
Cento 2021 {published data only}
Chiu 2021 {published data only}
Christensen 2021 {published data only}
Di Domenico 2021 {published data only}
Dierks 2021 {published data only}
Diez Flecha 2021 {published data only}
Eleftheriou 2021 {published data only}
Fernandez 2021 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez MD, Estevez AS, Alfonsin FL, Arevalo GB. Usefulness of the Lumiradx SARS-CoV-2 antigen test in nursing home. Enfermedades Infecciosas y Microbiología Clínica (English Edition) 2021. [DOI: ]
Fernandez‐Montero 2021 {published data only}
Ferte 2021 {published data only}
Fiedler 2021 {published data only}
Ford 2021 {published data only}
-
- Ford L, Lee C, Pray IW, Cole D, Bigouette JP, Abedi GR, et al. Epidemiologic characteristics associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) antigen-based test results, real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR) cycle threshold values, subgenomic RNA, and viral culture results from university testing. Clinical Infectious Disease 2021;73(6):e1348-55. - PMC - PubMed
Frediani 2021 {published data only}
Gitaka 2021 {published data only}
-
- Gitaka J, Muthamia E, Mbugua S, Mungai M, Bandawe G, Qadri F, et al. Assessment of performance and implementation characteristics of rapid point of care SARS-CoV-2 antigen testing in Kenya. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Hagbom 2021 {published data only}
Harmon 2021 {published data only}
-
- Harmon K, St Maurice AM, Brady AC, Swaminathan S, Aukerman DF, Rueda MA, et al. Surveillance testing for SARS-COV-2 infection in an asymptomatic athlete population: a prospective cohort study with 123 362 tests and 23 463 paired RT-PCR/antigen samples. BMJ Open Sport and Exercise Medicine 2021;7(2):e001137. - PMC - PubMed
Harris 2021 {published data only}
Holzner 2021 {published data only}
Homza 2021 {published data only}
Homza 2021a {published data only}
Kanji 2021 {published data only}
-
- Kanji JN, Proctor DT, Stokes W, Berenger BM, Silvius J, Tipples G, et al. Multicentre postimplementation assessment of the positive-predictive value of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-based point-of-care tests used for asymptomatic screening of continuing care staff. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2021;59(11):e0141121. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Kenyeres 2021 {published data only}
Kim 2021 {published data only}
Kiro 2021 {published data only}
Kiyasu 2021 {published data only}
Klein 2021 {published data only}
-
- Klein JA, Kruger LJ, Tobian F, Gaeddert M, Lainati F, Schnitzler P, et al. Head-to-head performance comparison of self-collected nasal versus professional-collected nasopharyngeal swab for a WHO-listed SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic test. Medical Microbiology and Immunology 2021;210(4):181-6. - PMC - PubMed
Koeleman 2021 {published data only}
Kolwijck 2021 {published data only}
-
- Kolwijck E, Brouwers-Boers M, Broertjes J, Van Heeswijk K, Runderkamp N, Meijer A, et al. Validation and implementation of the Panbio COVID-19 Ag rapid test for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in symptomatic hospital healthcare workers. Infection Prevention in Practice 2021;3(2):100142. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Korenkov 2021 {published data only}
-
- Korenkov M, Poopalasingam N, Madler M, Vanshylla K, Eggeling R, Wirtz M, et al. Reliable assessment of in vitro SARS-CoV-2 infectivity by a rapid antigen detection test. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Kritikos 2021 {published data only}
-
- Kritikos A, Caruana G, Brouillet R, Miroz JP, Abed-Maillard S, Stieger G, et al. Sensitivity of rapid antigen testing and RT-PCR performed on nasopharyngeal swabs versus saliva samples in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: results of a prospective comparative trial (RESTART). medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Kumar 2021a {published data only}
-
- Kumar A, Kunjukutty R, Thaha A, Srikumar S, Madhusoodanan H, David S, et al. Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 in pregnant women using a combination of antigen and RT-PCR testing. Le Infezioni in Medicina 2021;29(2):294-6. - PubMed
Kumar 2021b {published data only}
Kurihara 2021 {published data only}
Kweon 2021 {published data only}
Landaas 2021 {published data only}
Lee 2021 {published data only}
Le Goff 2021 {published data only}
Leixner 2021 {published data only}
Lindner 2021 {published data only}
Lv 2021 {published data only}
-
- Lv Y, Ma Y, Si Y, Zhu X, Zhang L, Feng H, et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection potentiates early diagnosis of COVID-19 disease. Bioscience Trends 2021;15(2):93-9. - PubMed
Mack 2021 {published data only}
Matsuda 2021 {published data only}
McKay 2021 {published data only}
Muhi 2021 {published data only}
-
- Muhi S, Tayler N, Hoang T, Ballard SA, Graham M, Rojek A, et al. Multi-site assessment of rapid, point-of-care antigen testing for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in a low-prevalence setting: a validation and implementation study. Lancet Regional Health – Western Pacific 2021;9:100115. - PMC - PubMed
Nordgren 2021 {published data only}
Norizuki 2021 {published data only}
Oh 2021 {published data only}
Orsi 2021 {published data only}
Osmanodja 2021 {published data only}
Perez‐Garcia 2021 {published data only}
Qahtani 2021 {published data only}
Revollo 2021 {published data only}
Reza 2021 {published data only}
Seynaeve 2021 {published data only}
Shah 2021 {published data only}
Shaikh 2021 {published data only}
-
- Shaikh N, Friedlander EJ, Tate PJ, Liu H, Chang CH, Wells A, et al. Performance of a rapid SARS-CoV-2 antigen detection assay in symptomatic children. Pediatrics 2021;148(3):e2021050832. [DOI: ] - PubMed
Smith 2021a {published data only}
-
- Smith RD, Johnson JK, Clay C, Girio-Herrera L, Stevens D, Abraham M, et al. Clinical evaluation of Sofia rapid antigen assay for detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 among emergency department to hospital admissions. Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology 2021 Jun 24 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI: 10.1017/ice.2021.281] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Smits 2021 {published data only}
Sood 2021 {published data only}
Sterbenc 2021 {published data only}
Suliman 2021 {published data only}
Terpos 2021 {published data only}
Thakur 2021 {published data only}
Thell 2021 {published data only}
Trobajo‐Sanmartin 2021 {published data only}
-
- Trobajo-Sanmartin C, Navascues A, Miqueleiz A, Ezpeleta C. Evaluation of the rapid antigen test CerTest SARS-CoV-2 as an alternative COVID-19 diagnosis technique. Infectious Diseases (London) 2021;53(9):730-2. - PubMed
Uwamino 2021 {published data only}
-
- Uwamino Y, Nagata M, Aoki W, Nakagawa T, Inose R, Yokota H, et al. Accuracy of rapid antigen detection test for nasopharyngeal swab specimens and saliva samples in comparison with RT-PCR and viral culture for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy 2021;27(7):1058-62. - PMC - PubMed
Van Honacker 2021 {published data only}
-
- Van Honacker E, Van Vaerenbergh K, Boel A, De Beenhouwer H, Leroux-Roels I, Cattoir L. Comparison of five SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen detection tests in a hospital setting and performance of one antigen assay in routine practice: a useful tool to guide isolation precautions? Journal of Hospital Infection 2021;114:144-52. - PMC - PubMed
Wagenhäuser 2021 {published data only}
Yin 2021 {published data only}
Young 2021a {published data only}
-
- Young BC, Eyre DW, Kendrick S, White C, Smith S, Beveridge G, et al. Daily testing for contacts of individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection and attendance and SARS-CoV-2 transmission in English secondary schools and colleges: an open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2021;398(10307):1217-29. - PMC - PubMed
Additional references
Arevalo‐Rodriguez 2020a
Basile 2021
Behera 2021
-
- Behera BC, Mishra RR, Thatoi H. Recent biotechnological tools for diagnosis of corona virus disease: a review. Biotechnology Progress 2021;37(1):e3078. - PubMed
Bekliz 2021
Binnicker 2020
Bossuyt 2015
Brümmer 2021
Canas 2021
Carter 2020
CDC 2021
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Interim guidance for antigen testing for SARS-CoV-2; 9 Sep 2021. Available from: www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-guidelines....
Cevik 2021
Chen 2020
Cheng 2020
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta-analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331-2. - PubMed
Chung 2021
Clopper 1934
-
- Clopper CJ, Pearson ES. The use of confidence or fiducial limits Illustrated in the case of the binomial. Biometrika 1934;26:404-13.
COVID‐19 Open Access Project 2021
-
- COVID-19 Open Access Project. Living Evidence on COVID-19. Available at ispmbern.github.io/covid-19/living-review/ 2021.
Covidence [Computer program]
-
- Covidence. Version accessed 27 April 2020. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation, 2020. Available at covidence.org.
Crozier 2021
-
- Crozier A, Dunning J, Rajan S, Semple MG, Buchan IE. Could expanding the COVID-19 case definition improve the UK’s pandemic response? BMJ 2021;374:n1625. - PubMed
Deeks 2020a
-
- Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Takwoingi Y, Davenport C, Leeflang MM, Spijker R, et al. Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19: accuracy of signs and symptoms; molecular, antigen, and antibody tests; and routine laboratory markers. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 4. Art. No: CD013596. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013596] - DOI
Deeks 2020b
Deeks 2022
Evans 2021
-
- Evans D, Cowen S, Kammel M, O’Sullivan DM, Stewart G, Grunert H-P, et al. The dangers of using Cq to quantify nucleic acid in biological samples: a lesson from COVID-19. Clinical Chemistry 2021;68(1):153-62. - PubMed
FDA 2021
-
- FDA. Omicron variant: impact on antigen diagnostic tests (as of 12/28/2021). Available at www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/sar....
FIND 2022a
-
- FIND. SARS-COV-2 diagnostic pipeline. www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline/ (accessed 5 January 2022).
FIND 2022b
-
- FIND. Impact of variants on COVID-19 tests. www.finddx.org/covid-19/impact-of-variants-on-covid19-tests/ (accessed 6 January 2022).
Green 2020
-
- Green K, Graziadio S, Turner P, Fanshawe T, Allen J, on behalf of the Oxford COVID-19 Evidence Service Team Centre. Molecular and antibody point-of-care tests to support the screening, diagnosis and monitoring of COVID-19. Available at www.cebm.net/oxford-covid-19/ (7 April 2020) 2020.
Gurdasani 2021
-
- Gurdasani D, Ziauddeen H, Greenhalgh T, Roberts A, Yates K, Haque Z, et al. Daily contact testing trials in schools are unethical and extending them to include the delta variant puts everyone at risk. blogs.bmj.com/bmj/2021/06/17/daily-contact-testing-trials-in-schools-are... 17 Jun 2021.
Healy 2020
Iacobucci 2020
-
- Iacobucci G, Coombes R. COVID-19: government plans to spend £100bn on expanding testing to 10 million a day. BMJ 2020;370:m3520. - PubMed
IDSA 2021
-
- Infectious Diseases Society of America, Assocation for Molecular Pathology. IDSA and AMP joint statement on the use of SARS-CoV-2 PCR cycle threshold (Ct) values for clinical decision-making; 12 March 2021. Available at www.idsociety.org/globalassets/idsa/public-health/covid-19/idsa-amp-stat....
Islam 2021
Jaafar 2020
-
- Jaafar R, Aherfi S, Wurtz N, Grimaldier C, Van Hoang T, Colson P, et al. Correlation between 3790 quantitative polymerase chain reaction–positives samples and positive cell cultures, including 1941 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 isolates. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2020:ciaa1491. [DOI: ] - PMC - PubMed
Jiang 2021
-
- Jiang N, Tansukawat ND, Gonzalez-Macia L, Ates HC, Dincer C, Güder F, et al. Low-cost optical assays for point-of-care diagnosis in resource-limited settings. ACS Sensors 2021;6(6):2108-24. - PubMed
Karon 2021
-
- Karon BS, Donato LJ, Bridgeman AR, Blommel JH, Kipp B, Maus A, et al. Analytical sensitivity and specificity of four point of care rapid antigen diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2 using real-time quantitative PCR, quantitative droplet digital PCR, and a mass spectrometric antigen assay as comparator methods. Clinical Chemistry 2021;67(11):1545-53. - PubMed
Kozel 2017
Kretzschmar 2020
Kucirka 2020
Lai 2021
Larremore 2020
Leeflang 2021
-
- Leeflang MM, Bell K, Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Doust J, Korevaar DA, et al. Electronic and animal noses for detecting SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, Issue 6. Art. No: CD015013. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD015013] - DOI
Lyngse 2021
-
- Lyngse FP, Mølbak K, Træholt Franck K, Nielsen C, Skov RL, Voldstedlund M, et al. Association between SARS-CoV-2 transmissibility, viral load, and age in households. medRxiv [Preprint] 2021. [DOI: ]
Madera 2021
Mak 2021
Marks 2021
Mayers 2020
-
- Mayers C, Baker K, Government Office for Science. Impact of false-positives and false-negatives in the UK’s COVID-19 RT-PCR testing programme. Available from assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attac... 3 Jun 2020.
McInnes 2018
McInnes 2020
Meyerowitz 2020
NHS 2021
-
- NHS. Get tested for coronavirus (COVID-19). www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronavirus-covid-19/testing/get-tested-for-corona... (accessed 6 January 2022).
Noel 2021
-
- Noel RH. Speed meets sensitivity to limit infectious spread in rapid microfluidic antigen testing. Available at: www.mlo-online.com/diagnostics/article/21222539/speed-meets-sensitivity-... 19 May 2021.
ONS 2020
-
- Office for National Statistics. Coronavirus (COVID-19) infection survey, UK: 21 August 2020. Available at: ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/healthandsocialcare/conditionsan....
Pai 2012
Petersen 2021
Reitsma 2005
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.4. Copenhagen: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Riley 2020
-
- Riley S, Ainslie KE, Eales O, Walters CE, Wang H, Atchison C, et al. Transient dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 as England exited national lockdown. medRxiv [Preprint] 2020. [DOI: 10.1101/2020.08.05.20169078] - DOI
RSS 2021
-
- Royal Statistical Society. Royal Statistical Society Diagnostic Tests Working Group Report. London: Royal Statistical Society, 2021.
Singanayagam 2020
Stata [Computer program]
-
- Stata. Version 17. College Station, TX, USA: StataCorp, 2021. Available at www.stata.com.
Stegeman 2020
Struyf 2021
-
- Struyf T, Deeks JJ, Dinnes J, Takwoingi Y, Davenport C, Leeflang MM, et al. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, Issue 2. Art. No: CD013665. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Takwoingi 2017
Tian 2021
UK Department for Education 2022
-
- Department for Education. Schools COVID-19 operational guidance. January 2022. assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attac... (accessed 6 January 2022).
UK DHSC 2021a
-
- Department of Health and Social Care. Daily contact testing study; June 2021. www.gov.uk/guidance/daily-contact-testing-study.
UK DHSC 2021b
-
- UK Department of Health and Social Care, . Asymptomatic testing for SARS-CoV-2 using antigen-detecting lateral flow devices; July 2021. Available at assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attac....
UK HSA 2021a
-
- UK Health Security Agency. Guidance for contacts of people with confirmed coronavirus (COVID-19) infection who do not live with the person; 23 December 2021. Available at www.gov.uk/government/publications/guidance-for-contacts-of-people-with-....
UK HSA 2021b
-
- UK Health Security Agency. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants under investigation in England. Technical briefing 32; 17 December 2021. Available at assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attac....
Vogels 2020
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529-36. - PubMed
WHO 2018
-
- World Health Organization. Diagnostic assessment: invitro diagnostic medical devices (IVDs) used for the detection of high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) genotypes in cervical cancer screening. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO; 3 April 2018. Available at apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/272282.
WHO 2020a
-
- World Health Organization. Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection using rapid immunoassays. Interim guidance; 11 September 2020. Available at apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/334253/WHO-2019-nCoV-Antigen_De....
WHO 2020b
-
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Target product profiles for priority diagnostics to support response to the COVID-19 pandemic v.1.0; 28 September 2020. Available at who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-target-product-profiles-for-priorit....
WHO 2020c
-
- World Health Organization. Laboratory testing of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases: interim guidance; 19 March 2020. Available at www.who.int/publications/i/item/laboratory-testing-for-2019-novel-corona....
WHO 2020d
-
- World Health Organisation. Global surveillance for COVID-19 caused by human infection with COVID-19 virus: interim guidance; 20 March 2020. Available from apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/331506/WHO-2019-nCoV-Surveillan....
Yang 2020a
Yonker 2021
Zhao 2020
Zoe COVID Study 2021
-
- Zoe COVID Study. What are the new top 5 COVID symptoms?; 23 Jun 2021. Available from: covid.joinzoe.com/post/new-top-5-covid-symptoms.
References to other published versions of this review
Dinnes 2020
Dinnes 2021
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

