miR‑491‑3p functions as a tumor suppressor in non‑small cell lung cancer by targeting fibroblast growth factor 5
- PMID: 35866594
- PMCID: PMC9350999
- DOI: 10.3892/or.2022.8379
miR‑491‑3p functions as a tumor suppressor in non‑small cell lung cancer by targeting fibroblast growth factor 5
Abstract
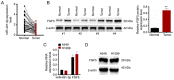
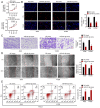
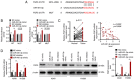
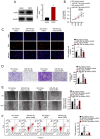
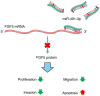
The present study aimed to identify the function of miR‑491‑3p in regulating non‑small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Tumor tissues and adjacent normal tissues were collected from 43 patients with NSCLC. A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with microRNA (miR)‑491‑3p mimic, mimic negative control (NC), miR‑491‑3p inhibitor, inhibitor NC, pcDNA3.1‑FGF5 vector and control vector. Cell counting kit‑8 assay and Edu experiments were performed to assess cell viability and proliferation. Matrigel experiment, wound healing assay and flow cytometric analysis were performed to explore cell invasion, migration and apoptosis, respectively. A dual‑luciferase reporter experiment was performed to identify the relationship between miR‑491‑3p and fibroblast growth factor 5 (FGF5). In vivo study was conducted by using nude mice. The miR‑491‑3p and FGF5 protein expression levels were investigated using reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis. In NSCLC tumor tissues, miR‑491‑3p was downregulated and FGF5 was upregulated (P<0.01). Low miR‑491‑3p expression and high FGF5 mRNA expression was associated with poor outcomes in patients, including advanced TNM stage and lymph node metastasis (P<0.05). upregulation of miR‑491‑3p suppressed viability, proliferation, invasion and migration of NSCLC cells; however, it promoted apoptosis (P<0.01). FGF5 was a target gene for miR‑491‑3p. miR‑491‑3p directly inhibited FGF5 expression. upregulation of FGF5 significantly reversed the inhibitory effects of miR‑491‑3p on malignant phenotypes of NSCLC cells (P<0.01). miR‑491‑3p overexpression suppressed the in vivo growth of NSCLC. Thus, it was identified that miR‑491‑3p functions as a tumor suppressor in NSCLC by directly targeting FGF5.
Keywords: apoptosis; invasion; microRNA‑491‑3p/fibroblast growth factor 5; non‑small cell lung cancer; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hsa_circ_0016760 exacerbates the malignant development of non‑small cell lung cancer by sponging miR‑145‑5p/FGF5.Oncol Rep. 2021 Feb;45(2):501-512. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7899. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33416186 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑497 suppresses malignant phenotype in non‑small cell lung cancer via targeting KDR.Oncol Rep. 2019 Jul;42(1):443-452. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7163. Epub 2019 May 16. Oncol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31115562
-
MicroRNA‑671‑5p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion in non‑small cell lung cancer by targeting MFAP3L.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Jan;25(1):30. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12546. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Mol Med Rep. 2022. Retraction in: Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jun;29(6):101. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13225. PMID: 34841435 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Dysregulated LINC00961 Contributes to the Vitality and Migration of NSCLC Via miR-19a-3p/miR-19b-3p/miR-125b-5p.DNA Cell Biol. 2022 Mar;41(3):319-329. doi: 10.1089/dna.2021.0900. Epub 2022 Mar 3. DNA Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35244469
-
Potential roles of FGF5 as a candidate therapeutic target in prostate cancer.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023 Dec 15;11(6):452-466. eCollection 2023. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023. PMID: 38148937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Importance of the Immune System and Molecular Cell Signaling Pathways in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 12;24(2):1506. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021506. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ceramide Metabolism Regulated by Sphingomyelin Synthase 2 Is Associated with Acquisition of Chemoresistance via Exosomes in Human Leukemia Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 13;23(18):10648. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810648. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142562 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Identification of Targets and New Treatment Modalities.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023 Dec;20(6suppl):646-668. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20413. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 38035705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enrichment of ornithine decarboxylase degron transduced colorectal cancer cells for extended application of cancer stem cell models.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):22886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-04277-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40595888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brozos-Vázquez EM, Díaz-Peña R, García-González J, León-Mateos L, Mondelo-Macía P, Peña-Chilet M, López-López R. Immunotherapy in nonsmall-cell lung cancer: Current status and future prospects for liquid biopsy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021;70:1177–1188. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02752-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

