Principles and correction of 5'-splice site selection
- PMID: 35866748
- PMCID: PMC9311317
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2100971
Principles and correction of 5'-splice site selection
Abstract
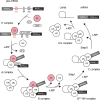
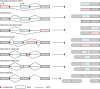
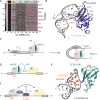
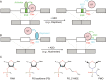
In Eukarya, immature mRNA transcripts (pre-mRNA) often contain coding sequences, or exons, interleaved by non-coding sequences, or introns. Introns are removed upon splicing, and further regulation of the retained exons leads to alternatively spliced mRNA. The splicing reaction requires the stepwise assembly of the spliceosome, a macromolecular machine composed of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs). This review focuses on the early stage of spliceosome assembly, when U1 snRNP defines each intron 5'-splice site (5'ss) in the pre-mRNA. We first introduce the splicing reaction and the impact of alternative splicing on gene expression regulation. Thereafter, we extensively discuss splicing descriptors that influence the 5'ss selection by U1 snRNP, such as sequence determinants, and interactions mediated by U1-specific proteins or U1 small nuclear RNA (U1 snRNA). We also include examples of diseases that affect the 5'ss selection by U1 snRNP, and discuss recent therapeutic advances that manipulate U1 snRNP 5'ss selectivity with antisense oligonucleotides and small-molecule splicing switches.
Keywords: 5’-splice site; RNA splicing; U1 snRNP; antisense oligonucleotides; splicing modifiers.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, and Lewis J.. Molecular biology of the cell. 4th ed. New York: Garland Science. 2003.
-
- Hombach S, Kretz M. Non-coding RNAs: classification, biology and functioning. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;937:3–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
