Autoimmunity, cancer and COVID-19 abnormally activate wound healing pathways: critical role of inflammation
- PMID: 35867145
- PMCID: PMC9305064
- DOI: 10.1007/s00418-022-02140-x
Autoimmunity, cancer and COVID-19 abnormally activate wound healing pathways: critical role of inflammation
Abstract
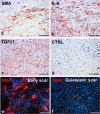
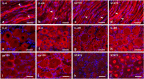
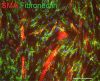
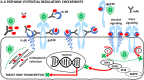
Recent evidence indicates that targeting IL-6 provides broad therapeutic approaches to several diseases. In patients with cancer, autoimmune diseases, severe respiratory infections [e.g. coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)] and wound healing, IL-6 plays a critical role in modulating the systemic and local microenvironment. Elevated serum levels of IL-6 interfere with the systemic immune response and are associated with disease progression and prognosis. As already noted, monoclonal antibodies blocking either IL-6 or binding of IL-6 to receptors have been used/tested successfully in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, many cancer types, and COVID-19. Therefore, in the present review, we compare the impact of IL-6 and anti-IL-6 therapy to demonstrate common (pathological) features of the studied diseases such as formation of granulation tissue with the presence of myofibroblasts and deposition of new extracellular matrix. We also discuss abnormal activation of other wound-healing-related pathways that have been implicated in autoimmune disorders, cancer or COVID-19.
Keywords: Cancer stroma; Granulation tissue; IL-6; Inflammation; Myofibroblast; Peripheral nerve injury; Rheumatoid arthritis; SARS-CoV-2; Wound healing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
K.S.J., M.J. and J.B. are inventors of US patent no. 11,246,874 B1 and cooperate with Oxygen Biotech LLC 108 W 13th St. Wilmington DE 19801. This company had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results. The other authors, i.e. P.G., M.H., A.Š., L.L., A.R., H.H. and K.S., declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adamik B, Zimecki M, Właszczyk A, Kübler A. Immunological status of septic and trauma patients. I. High tumor necrosis factor α serum levels in septic and trauma patients are not responsible for increased mortality; a prognostic value of serum interleukin 6. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. 1997;45(2–3):169–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

