Intratympanic corticosteroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss
- PMID: 35867413
- PMCID: PMC9307133
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008080.pub2
Intratympanic corticosteroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is common, and defined as a sudden decrease in sensorineural hearing sensitivity of unknown aetiology. Systemic corticosteroids are widely used, however their value remains unclear. Intratympanic injections of corticosteroids have become increasingly common in the treatment of ISSNHL.
Objectives: To assess the effects of intratympanic corticosteroids in people with ISSNHL.
Search methods: The Cochrane ENT Information Specialist searched the Cochrane ENT Trials Register; CENTRAL (2021, Issue 9); PubMed; Ovid Embase; CINAHL; Web of Science; ClinicalTrials.gov; ICTRP and additional sources for published and unpublished trials (search date 23 September 2021).
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) involving people with ISSNHL and follow-up of over a week. Intratympanic corticosteroids were given as primary or secondary treatment (after failure of systemic therapy).
Data collection and analysis: We used standard Cochrane methods, including GRADE to assess the certainty of the evidence. Our primary outcome was change in hearing threshold with pure tone audiometry. Secondary outcomes included the proportion of people whose hearing improved, final hearing threshold, speech audiometry, frequency-specific hearing changes and adverse effects.
Main results: We included 30 studies, comprising 2133 analysed participants. Some studies had more than two treatment arms and were therefore relevant to several comparisons. Studies investigated intratympanic corticosteroids as either primary (initial) therapy or secondary (rescue) therapy after failure of initial treatment. 1. Intratympanic corticosteroids versus systemic corticosteroids as primary therapy We identified 16 studies (1108 participants). Intratympanic therapy may result in little to no improvement in the change in hearing threshold (mean difference (MD) -5.93 dB better, 95% confidence interval (CI) -7.61 to -4.26; 10 studies; 701 participants; low-certainty). We found little to no difference in the proportion of participants whose hearing was improved (risk ratio (RR) 1.04, 95% CI 0.97 to 1.12; 14 studies; 972 participants; moderate-certainty). Intratympanic therapy may result in little to no difference in the final hearing threshold (MD -3.31 dB, 95% CI -6.16 to -0.47; 7 studies; 516 participants; low-certainty). Intratympanic therapy may increase the number of people who experience vertigo or dizziness (RR 2.53, 95% CI 1.41 to 4.54; 1 study; 250 participants; low-certainty) and probably increases the number of people with ear pain (RR 15.68, 95% CI 6.22 to 39.49; 2 studies; 289 participants; moderate-certainty). It also resulted in persistent tympanic membrane perforation (range 0% to 3.9%; 3 studies; 359 participants; very low-certainty), vertigo/dizziness at the time of injection (1% to 21%, 3 studies; 197 participants; very low-certainty) and ear pain at the time of injection (10.5% to 27.1%; 2 studies; 289 participants; low-certainty). 2. Intratympanic plus systemic corticosteroids (combined therapy) versus systemic corticosteroids alone as primary therapy We identified 10 studies (788 participants). Combined therapy may have a small effect on the change in hearing threshold (MD -8.55 dB better, 95% CI -12.48 to -4.61; 6 studies; 435 participants; low-certainty). The evidence is very uncertain as to whether combined therapy changes the proportion of participants whose hearing is improved (RR 1.27, 95% CI 1.15 to 1.41; 10 studies; 788 participants; very low-certainty). Combined therapy may result in slightly lower (more favourable) final hearing thresholds but the evidence is very uncertain, and it is not clear whether the change would be important to patients (MD -9.11 dB, 95% CI -16.56 to -1.67; 3 studies; 194 participants; very low-certainty). Some adverse effects only occurred in those who received combined therapy. These included persistent tympanic membrane perforation (range 0% to 5.5%; 5 studies; 474 participants; very low-certainty), vertigo or dizziness at the time of injection (range 0% to 8.1%; 4 studies; 341 participants; very low-certainty) and ear pain at the time of injection (13.5%; 1 study; 73 participants; very low-certainty). 3. Intratympanic corticosteroids versus no treatment or placebo as secondary therapy We identified seven studies (279 participants). Intratympanic therapy may have a small effect on the change in hearing threshold (MD -9.07 dB better, 95% CI -11.47 to -6.66; 7 studies; 280 participants; low-certainty). Intratympanic therapy may result in a much higher proportion of participants whose hearing is improved (RR 5.55, 95% CI 2.89 to 10.68; 6 studies; 232 participants; low-certainty). Intratympanic therapy may result in lower (more favourable) final hearing thresholds (MD -11.09 dB, 95% CI -17.46 to -4.72; 5 studies; 203 participants; low-certainty). Some adverse effects only occurred in those who received intratympanic injection. These included persistent tympanic membrane perforation (range 0% to 4.2%; 5 studies; 185 participants; very low-certainty), vertigo or dizziness at the time of injection (range 6.7% to 33%; 3 studies; 128 participants; very low-certainty) and ear pain at the time of injection (0%; 1 study; 44 participants; very low-certainty). 4. Intratympanic plus systemic corticosteroids (combined therapy) versus systemic corticosteroids alone as secondary therapy We identified one study with 76 participants. Change in hearing threshold was not reported. Combined therapy may result in a higher proportion with hearing improvement, but the evidence is very uncertain (RR 2.24, 95% CI 1.10 to 4.55; very low-certainty). Adverse effects were poorly reported with only data for persistent tympanic membrane perforation (rate 8.1%, very low-certainty).
Authors' conclusions: Most of the evidence in this review is low- or very low-certainty, therefore it is likely that further studies may change our conclusions. For primary therapy, intratympanic corticosteroids may have little or no effect compared with systemic corticosteroids. There may be a slight benefit from combined treatment when compared with systemic treatment alone, but the evidence is uncertain. For secondary therapy, there is low-certainty evidence that intratympanic corticosteroids, when compared to no treatment or placebo, may result in a much higher proportion of participants whose hearing is improved, but may only have a small effect on the change in hearing threshold. It is very uncertain whether there is additional benefit from combined treatment over systemic steroids alone. Although adverse effects were poorly reported, the different risk profiles of intratympanic treatment (including tympanic membrane perforation, pain and dizziness/vertigo) and systemic treatment (for example, blood glucose problems) should be considered when selecting appropriate treatment.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. on behalf of The Cochrane Collaboration.
Conflict of interest statement
Stefan K Plontke served as study co‐ordinator and the second author (CM) as the responsible biostatistician of a randomised controlled trial within the focus of this review (Plontke 2009). The sponsor of this completed trial was the University of Tübingen Medical School (academic sponsor, non‐industrial). These authors were not involved in data extraction or risk of bias assessment for this study.
Stefan K Plontke also serves as co‐ordinating investigator and the second author (CM) as the responsible biostatistician of a randomised controlled trial on the efficacy and safety of systemic high‐dose glucocorticoid treatment for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in adults (HODOKORT) (EudraCT Nr. 2015‐002602‐36).
Stefan K Plontke: AudioCure PharmaGmbH, Berlin, Germany; Astellas Pharma Inc., Tokyo (no payment), Japan: consultant; MED‐EL Austria and MED‐EL Germany: travel reimbursement for speaking engagement; MED‐EL Austria and MED‐EL Germany, OticonMedical, Denmark; Cochlear Ltd., Australia; Federal Ministry of Education and Research in Germany (Bundesministeriumfür Bildung und Forschung): research projects; Society of ENT physicians in Germany (BV‐HNO e.V); Merck Serono, Darmstadt; Infectopharm, Heppenheim; Dr. Willmar Schwabe GmbH&Co. KG, Kralsruhe, Germany: lecture fees and travel reimbursement. The above industry relations were not related to any treatment in this review. The above industry relations did not sponsor any part of this work.
Christoph Meisner: AudioCure PharmaGmbH, Berlin, Germany: consultant; palleos healthcare GmbH, Wiesbaden, Germany; WSG ‐ Westdeutsche Studiengruppe GmbH, Mönchengladbach, Germany: Member of DSMB. The above industry relations were not related to any treatment in this review. The above industry relations did not sponsor any part of this work.
Arne Liebau: MED‐EL Austria and MED‐EL Germany; Dr. Willmar Schwabe GmbH&Co. KG, Karlsruhe, Germany (research projects).
Sumit Agrawal: none known.
Per Caye‐Thomasen: none known.
Kevin Galbraith: none known.
Anthony A Mikulec: Otonomy Inc., San Diego, USA: clinical trial site principal investigator, clinical trial safety review committee member, ad hoc consultant.
Lorne Parnes: none known.
Yaamini Premakumar: none known.
Julia Reiber: none known.
Anne GM Schilder: Professor Schilder's research at University College London is funded by the NIHR and EU Horizon2020. Anne Schilder is the national chair of the NIHR Clinical Research Network ENT Specialty and Surgical Specialty Lead for ENT for the Royal College of Surgeons of England's Clinical Trials Initiative. As director of the NIHR UCLH Biomedical Research Centre Hearing Theme, she advises companies developing innovative hearing treatments on clinical trial design and delivery.
Figures
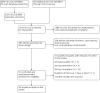
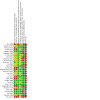

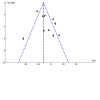
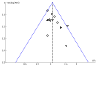





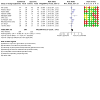



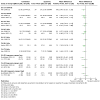





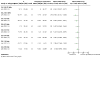


Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Ahn 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ahn JH, Yoo MH, Yoon TH, Chung JW. Can intratympanic dexamethasone added to systemic steroids improve hearing outcome in patients with sudden deafness? Laryngoscope 2008;118(2):279-82. - PubMed
Al‐Shehri 2015 {published data only}
-
- Al-Shehri AMS. Intratympanic vs. oral steroids for treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized controlled study. British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 2015;11(6):1-6.
Arastou 2013 {published data only}
Arslan 2011 {published data only}
-
- Arslan N, Oğuz H, Demirci M, Şafak MA, İslam A, Kaytez SK, et al. Combined intratympanic and systemic use of steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otology & Neurotology 2011;32(3):393-7. - PubMed
Ashtiani 2018 {published data only}
-
- Ashtiani MK, Firouzi F, Bastaninejad S, Dabiri S, Nasirmohtaram S, Saeedi N, et al. Efficacy of systemic and intratympanic corticosteroid combination therapy versus intratympanic or systemic therapy in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2018;275(1):89-97. - PubMed
Battaglia 2008 {published data only}
-
- Battaglia A, Burchette R, Cueva R. Combination therapy (intratympanic dexamethasone + high-dose prednisone taper) for the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otology & Neurotology 2008;29(4):453-60. - PubMed
Chang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Chang WX, Zhong HL, Cai X, Gan Q. Dexamethasone injection in the middle ear for high altitude refractory sudden deafness. Sichuan Medical Journal 2010;31(1):71.
Choi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Choi SJ, Lee YH, Kim YH. Comparison of the efficacy of systemic and combined highly frequent intratympanic steroid treatment on sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Korean Journal of Audiology 2011;15:133-6.
Dispenza 2011 {published data only}
-
- Dispenza F, Amodio E, De Stefano A, Gallina S, Marchese D, Mathur N, et al. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with transtympanic injection of steroids as single therapy: a randomized clinical study. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2011;268(9):1273-8. - PubMed
Ermutlu 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ermutlu G, Süslü N, Yılmaz T, Saraç S. Sudden hearing loss: an effectivity comparison of intratympanic and systemic steroid treatments. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2017;274(10):3585-91. - PubMed
Gundogan 2013 {published data only}
-
- Gundogan O, Pinar E, Imre A, Ozturkcan S, Cokmez O, Yigiter AC. Therapeutic efficacy of the combination of intratympanic methylprednisolone and oral steroid for idiopathic sudden deafness. Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery 2013;149:753-8. - PubMed
Ho 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ho HG, Lin HC, Shu MT, Yang CC, Tsai HT. Effectiveness of intratympanic dexamethasone injection in sudden-deafness patients as salvage treatment. Laryngoscope 2004;114(7):1184-9. - PubMed
Hong 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hong SM, Park CH, Lee JH. Hearing outcomes of daily intratympanic dexamethasone alone as a primary treatment modality for ISSHL. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2009;141(5):579-83. - PubMed
Huang 2021 {published data only}
-
- Huang J, Yang L, Cao X, Wang W. Differences in hearing recovery following intratympanic alone or intravenous dexamethasone with rescue intratympanic steroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomised trial. Clinical Otolaryngology 2021;46(3):546-51. - PubMed
Koltsidopoulos 2013 {published data only}
-
- Koltsidopoulos P, Bibas A, Sismanis A, Tzonou A, Seggas I. Intratympanic and systemic steroids for sudden hearing loss. Otology & Neurotology 2013;34:771-6. - PubMed
Kosyakov 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kosyakov S, Atanesyan A, Gunenkov A, Ashkhatunyan E, Kurlova A. Intratympanic steroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Journal of International Advanced Otology 2011;7(3):323-32.
Lee 2011 {published data only}
-
- Lee JB, Choi SJ, Park K, Park HY, Choo OS, Choung YH. The efficiency of intratympanic dexamethasone injection as a sequential treatment after initial systemic steroid therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2011;268(6):833-9. - PubMed
Li 2011 {published data only}
-
- Li P, Zeng XL, Ye J, Yang QT, Zhang GH, Li Y. Intratympanic methylprednisolone improves hearing function in refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a control study. Audiology & Neurotology 2011;16(3):198-202. - PubMed
Lim 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lim HJ, Kim YT, Choi SJ, Lee JB, Park HY, Park K, et al. Efficacy of 3 different steroid treatments for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a prospective, randomized trial. Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery 2013;148(1):121-7. - PubMed
Peng 2008 {published data only}
-
- Peng Y, Xiong S, Cheng Y, Qi YF, Yang Y. Clinical investigation of different routes of administration of dexamethasone on sudden deafness [Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi]. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (Chinese) 2008;22(10):442-5. - PubMed
Plontke 2009 {published data only}
-
- NCT00335920. Safety and efficacy of intratympanic application of dexamethasone via catheter in patients with sudden hearing loss. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00335920 (first received 12 June 2006).
-
- Plontke SK, Lowenheim H, Mertens J, Engel C, Meisner C, Weidner A, et al. Randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial on the safety and efficacy of continuous intratympanic dexamethasone delivered via a round window catheter for severe to profound sudden idiopathic sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 2009;119(2):359-69. - PubMed
Qu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Qu Y, Chen H, Zhang H, Guo M. Analysis the treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with steroid from different administration routes [Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi]. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery [Chinese] 2015;29(4):324-6. - PubMed
Rauch 2011 {published data only}
-
- Rauch SD, Halpin CF, Antonelli PJ, Babu S, Carey JP, Gantz BJ, et al. Oral vs intratympanic corticosteroid therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized trial. JAMA 2011;305(20):2071-9. - PubMed
Rupasinghe 2017 {published data only}
-
- Rupasinghe RAST. Comparison - Effectiveness of oral steroid versus intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden onset sensorineural hearing loss. Ceylon Journal of Otolaryngology 2017;5(1):7-13.
Swachia 2016 {published data only}
-
- Swachia K, Sharma D, Singh J. Efficacy of oral vs. intratympanic corticosteroids in sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Journal of Basic and Clinical Physiology and Pharmacology 2016;27(4):371-7. - PubMed
Tong 2021 {published data only}
-
- Duan M. Data on frequency specific hearing changes (table 5) [personal communication]. Email to K Webster 9 October 2021.
-
- Tong B, Wang Q, Dai Q, Hellstrom S, Duan M. Efficacy of various corticosteroid treatment modalities for the initial treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Audiology & Neurotology 2021;26(1):45-52. - PubMed
Tsounis 2018 {published data only}
-
- Tsounis M, Psillas G, Tsalighopoulos M, Vital V, Maroudias N, Markou K. Systemic, intratympanic and combined administration of steroids for sudden hearing loss. A prospective randomized multicenter trial. Otorhinolaryngology 2018;275(1):103-10. - PubMed
Wu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wu HP, Chou YF, Yu SH, Wang CP, Hsu CJ, Chen PR. Intratympanic steroid injections as a salvage treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Otology & Neurotology 2011;32(5):774-9. - PubMed
Xenellis 2006 {published data only}
-
- Xenellis J, Papadimitriou N, Nikolopoulos T, Maragoudakis P, Segas J, Tzagaroulakis A, et al. Intratympanic steroid treatment in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a control study. Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery 2006;134(6):940-5. - PubMed
Zhou 2011 {published data only}
-
- Zhou Y, Zheng H, Zhang Q, Campione PA. Early transtympanic steroid injection in patients with 'poor prognosis' idiopathic sensorineural sudden hearing loss. ORL; Journal for Oto-rhino-laryngology and Its Related Specialties 2011;73(1):31-7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Amizadeh 2021 {published data only}
Attanasio 2015 {published data only}
Berjis 2016 {published data only}
Chang 2020 {published data only}
-
- Chang WT, Zee B, Lee HSH, Tong MCF. Dexamethasone eardrop with grommet placement vs intratympanic steroid injection for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized prospective clinical trial. American Journal of Otolaryngology 2020;41(4):102515. - PubMed
Chen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Chen J, Yang J, Jia H, Shi J, Li Y, Wu H. Efficacy of intratympanic steroid injection as supplementary or initial treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi [Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery] 2015;29(19):1691-4. - PubMed
Cho 2018 {published data only}
-
- Cho I, Lee HM, Choi SW, Kong SK, Lee IW, Goh EK, et al. Comparison of two different treatment protocols using systemic and intratympanic steroids with and without hyperbaric oxygen therapy in patients with severe to profound idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized controlled trial. Audiology & Neuro-otology 2018;23(4):199-207. - PubMed
Choo 2017 {published data only}
-
- Choo OS, Yang SM, Park HY, Lee JB, Jang JH, Choi SJ, et al. Differences in clinical characteristics and prognosis of sudden low- and high-frequency hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2017;127(8):1878-84. - PubMed
Cvorovic 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cvorovic L, Jovanovic MB, Milutinovic Z, Arsovic N, Djeric D. Randomized prospective trial of hyperbaric oxygen therapy and intratympanic steroid injection as salvage treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otology & Neurotology 2013;34(6):1021-6. - PubMed
Diao 2012 {published data only}
-
- Diao Y, Dong M. The observation on curative effect of 90 cases of sudden hearing loss. Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery [Chinese] 2012;26(7):306-8. - PubMed
Filipo 2013 {published data only}
-
- Filipo R, Attanasio G, Russo FY, Viccaro M, Mancini P, Covelli E. Intratympanic steroid therapy in moderate sudden hearing loss: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Laryngoscope 2013;123(3):774-8. - PubMed
Gui‐li 2018 {published data only}
-
- Xu G, Lin D, Lin Q. Clinical observations of glucocorticoid combined with hyperbaric oxygen on patients with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Chinese Scientific Journal of Hearing and Speech Rehabilitation 2018;16(1):22-5.
Han 2021 {published data only}
-
- Han X, Wang B, Li C, Wang X, Zhang H, Yang Q, et al. Observation on the efficacy of Eustachian tube dilation hormone under the guidance of endoscope in the treatment of sudden deafness. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke za Zhi [Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery] 2021;35(5):424-7. [CENTRAL: CN-02296088] [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Li 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zheng LI, Chen YAO, Xiaohang CAI. To study the effect of intratympanic injection with mouse nerve growth factor and methylprednisolone on sudden deafness. Lin Chuang er bi yan hou tou Jing wai ke za zhi [Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head, and Neck Surgery] 2016;30(21):1728-31. - PubMed
NCT04766853 {published data only}
-
- NCT04766853. Verification of the efficacy/safety of the dual drug delivery for hearing loss [Verification of the efficacy / safety of the dual drug injectable delivery vehicle for treating intractable hearing loss (pilot study)]. https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04766853 (first received 23 February 2021). [CENTRAL: CN-02249206]
Park 2011 {published data only}
-
- Park MK, Lee CK, Park KH, Lee JD, Lee CG, Lee BD. Simultaneous versus subsequent intratympanic dexamethasone for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery 2011;145(6):1016-21. - PubMed
Rogha 2017 {published data only}
Sevil 2016 {published data only}
-
- Sevil E, Bercin S, Muderris T, Gul F, Kiris M. Comparison of two different steroid treatments with hyperbaric oxygen for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2016;273(9):2419-26. - PubMed
Song 2018 {published data only}
-
- Song J, Zhang L, Chen Y. Analysis of the treatment effects of refractory sudden total frequency deafness with steroid from different topical administration routes. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2018;22(24):1897-9. - PubMed
Sun 2016 {published data only}
-
- Sun RX. Intratympatic budesonide injection for treatment of refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi [Journal of Clinical Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery] 2016;30(12):972-7. - PubMed
Zhou 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zhou XY, Tao Q, Lv LY. The treatment for sudden deafness with intratympanic dexamethasone injection. Chinese Journal of Otorhinolaryngology - Skull Base Surgery 2006;12(1):47-8.
References to ongoing studies
Wang 2021 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR2000036382. Clinical study of oral prednisone vs intratympanic injection of dexamethasone as initial treatment for sudden hearing loss. http://www.chictr.org.cn/hvshowproject.aspx?id=53824 (first received 22 August 2020).
Yang 2020 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR1800015954. A prospective study on the treatment of patients with sudden deafness and diabetes with two different ways of administration. http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=25326 (first received 2 May 2018).
Additional references
Agarwal 2009
Ahmadzai 2019
Akeroyd 2015
-
- Akeroyd MA, Arlinger S, Bentler RA, Boothroyd A, Dillier N, Dreschler WA, et al. International Collegium of Rehabilitative Audiology (ICRA) recommendations for the construction of multilingual speech tests. ICRA Working Group on Multilingual Speech Tests. International Journal of Audiology 2015;54 Suppl 2:17-22. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ashtiani 2012
Bachmann 2001
-
- Bachmann G, Su J, Zumegen C, Wittekindt C, Michel O. Permeability of the round window membrane for prednisolone-21-hydrogen succinate. Prednisolone content of the perilymph after local administration vs. systemic injection [German]. HNO 2001;49(7):538-42. - PubMed
Battaglia 2014
-
- Battaglia A, Lualhati A, Lin H, Burchette R, Cueva R. A prospective, multi-centered study of the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with combination therapy versus high-dose prednisone alone: a 139 patient follow-up. Otology & Neurotology 2014;35(6):1091-8. - PubMed
Begg 1996
-
- Begg C, Cho M, Eastwood S, Horton R, Moher D, Olkin I, et al. Improving the quality of reporting of randomized controlled trials. The CONSORT statement. JAMA 1996;276(8):637-9. - PubMed
Bennett 2007
Bennett 2012
Bird 2007
-
- Bird PA, Begg EJ, Zhang M, Keast AT, Murray DP, Balkany TJ. Intratympanic versus intravenous delivery of methylprednisolone to cochlear perilymph. Otology & Neurotology 2007;28(8):1124-30. - PubMed
Bird 2011
-
- Bird PA, Murray DP, Zhang M, Begg EJ. Intratympanic versus intravenous delivery of dexamethasone and dexamethasone sodium phosphate to cochlear perilymph. Otology & Neurotology 2011;32(6):933-6. - PubMed
Byl 1977
-
- Byl FM. Seventy-six cases of presumed sudden hearing loss occurring in 1973: prognosis and incidence. Laryngoscope 1977;87(5 Pt 1):817-25. - PubMed
Carlsson 2011
-
- Carlsson PI, Hall M, Lind KJ, Danermark B. Quality of life, psychosocial consequences, and audiological rehabilitation after sudden sensorineural hearing loss. International Journal of Audiology 2011;50(2):139-44. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chandrasekhar 2000
-
- Chandrasekhar SS, Rubinstein RY, Kwartler JA, Gatz M, Connelly PE, Huang E, et al. Dexamethasone pharmacokinetics in the inner ear: comparison of route of administration and use of facilitating agents. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2000;122(4):521-8. - PubMed
Chandrasekhar 2019
-
- Chandrasekhar SS, Tsai Do BS, Schwartz SR, Bontempo LJ, Faucett EA, Finestone SA, et al. Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss (Update). Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2019;161(1 Suppl):S1-S45. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chen 2003
-
- Chen CY, Halpin C, Rauch SD. Oral steroid treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a ten year retrospective analysis. Otology & Neurotology 2003;24(5):728-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Conlin 2007a
-
- Conlin AE, Parnes LS. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: I. A systematic review. Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2007a;133(6):573-81. - PubMed
Conlin 2007b
-
- Conlin AE, Parnes LS. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: II. A meta-analysis. Archives of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2007;133(6):582-6. - PubMed
Crane 2015
-
- Crane RA, Camilon M, Nguyen S, Meyer TA. Steroids for treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Laryngoscope 2015;125(1):209-17. - PubMed
Desloovere 1988
-
- Desloovere C, Meyer-Breiting E, Ilberg C. Randomized double-blind study of therapy of sudden deafness: initial results [Randomisierte Doppelblindstudie zur Hörsturztherapie: Erste Ergebnisse]. HNO 1988;36(10):417-22. - PubMed
Eftekharian 2016
-
- Eftekharian A, Amizadeh M. Pulse steroid therapy in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Laryngoscope 2016;126(1):150-5. - PubMed
El Kechai 2015
-
- El Kechai N, Agnely F, Mamelle E, Nguyen Y, Ferrary E, Bochot A. Recent advances in local drug delivery to the inner ear. International journal of pharmaceutics 2015;494(1):83-101. [PMID: ] - PubMed
El Sabbagh 2016
-
- El Sabbagh NG, Sewitch MJ, Bezdjian A, Daniel SJ. Intratympanic dexamethasone in sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2017;127(8):1897–908. - PubMed
Eshraghi 2006
-
- Eshraghi AA, Van de Water TR. Cochlear implantation trauma and noise-induced hearing loss: apoptosis and therapeutic strategies. The Anatomical Record. Part A, Discoveries in Molecular, Cellular, and Evolutionary biology 2006;288(4):473-81. - PubMed
Gao 2016
-
- Gao Y, Liu D. Combined intratympanic and systemic use of steroids for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2016;273(11):3699-711. - PubMed
Garavello 2012
-
- Garavello W, Galluzzi F, Gaini RM, Zanetti D. Intratympanic steroid treatment for sudden deafness: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Otology & Neurotology 2012;33(5):724-9. - PubMed
Garcia‐Berrocal 2008
-
- Garcia-Berrocal JR, Ramirez-Camacho R, Lobo D, Trinidad A, Verdaguer JM. Adverse effects of glucocorticoid therapy for inner ear disorders. ORL; Journal for Oto-rhino-laryngology and Its Related Specialties 2008;70(4):271-4. - PubMed
Grossmann 2004
-
- Grossmann C, Scholz T, Rochel M, Bumke-Vogt C, Oelkers W, Pfeiffer AF, et al. Transactivation via the human glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor by therapeutically used steroids in CV-1 cells: a comparison of their glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid properties. European Journal of Endocrinology 2004;151(3):397-406. - PubMed
Gul 2016
-
- Gul F, Muderris T, Yalciner G, Sevil E, Bercin S, Ergin M, et al. A comprehensive study of oxidative stress in sudden hearing loss. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2016;274(3):1301-8. - PubMed
Günel 2015
-
- Günel C, Başal Y, Toka A, Eryılmaz A, Kurt Ömürlü I. Efficacy of low-dose intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 2015;42(4):284-7. - PubMed
Gurgel 2012
-
- Gurgel RK, Jackler RK, Dobie RA, Popelka GR. A new standardized format for reporting hearing outcome in clinical trials. Otolaryngology--Head and Neck Surgery 2012;147(5):803-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence--imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283-93. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Haake 2009
-
- Haake SM, Dinh CT, Chen S, Eshraghi AA, Van De Water TR. Dexamethasone protects auditory hair cells against TNFalpha-initiated apoptosis via activation of PI3K/Akt and NFkappaB signaling. Hearing Research 2009;255(1-2):22-32. - PubMed
Han 2017
-
- Han X, Yin X, Du X, Sun C. Combined intratympanic and systemic use of steroids as a first-line treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Otology & Neurotology 2017;38(4):487-95. - PubMed
Handbook 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011 Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Handbook 2021
-
- Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.2 (updated February 2021). Cochrane, 2021. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Haynes 2007
-
- Haynes DS, O'Malley M, Cohen S, Watford K, Labadie RF. Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 2007;117(1):3-15. - PubMed
Hoang 2009
-
- Hoang KN, Dinh CT, Bas E, Chen S, Eshraghi AA, Van De Water TR. Dexamethasone treatment of naive organ of Corti explants alters the expression pattern of apoptosis-related genes. Brain Research 2009;1301:1-8. - PubMed
Hoskison 2013
-
- Hoskison E, Daniel M, Al-Zahid S, Shakesheff KM, Bayston R, Birchall JP. Drug delivery to the ear. Therapeutic Delivery 2013;4(1):115-24. - PubMed
Hughes 1996
-
- Hughes GB, Freedman MA, Haberkamp TJ, Guay ME. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America 1996;29(3):393-405. - PubMed
Hultcrantz 2014
-
- Hultcrantz E, Nosrati-Zarenoe R. Corticosteroid treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: analysis of an RCT and material drawn from the Swedish national database. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2015;272(11):3169-75. - PubMed
Jenkinson 1997
-
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D, Lawrence K, Petersen S, Paice C, et al. A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? Journal of Public Health Medicine 1997;19(2):179-86. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Katiri 2020
-
- Katiri R, Hall DA, Buggy N, Hogan N, Horobin A, de Heyning P, et al. Core Rehabilitation Outcome Set for Single Sided Deafness (CROSSSD) study: protocol for an international consensus on outcome measures for single sided deafness interventions using a modified Delphi survey. Trials 2020;21(1):238. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Kiliç 2007
-
- Kiliç R, Safak MA, Oğuz H, Kargin S, Demirci M, Samim E, et al. Intratympanic methylprednisolone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otology & Neurotology 2007;28(3):312-6. - PubMed
King 2011
Klemm 2007
-
- Klemm E, Bepperling F, Burschka MA, Mösges R, Study Group. Hemodilution therapy with hydroxyethyl starch solution (130/0.4) in unilateral idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a dose-finding, double-blind, placebo-controlled, international multicenter trial with 210 patients. Otology & Neurotology 2007;28(2):157-70. - PubMed
Klemm 2009
-
- Klemm E, Deutscher A, Mosges R. A present investigation of the epidemiology in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngo- Rhino- Otologie 2009;88(8):524-7. - PubMed
Kollmeier 2015
-
- Kollmeier B, Warzybok A, Hochmuth S, Zokoll MA, Uslar V, Brand T, et al. The multilingual matrix test: Principles, applications, and comparison across languages: a review. International journal of audiology 2015;54 Suppl 2:3-16. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Labus 2010
-
- Labus J, Breil J, Stutzer H, Michel O. Meta-analysis for the effect of medical therapy vs. placebo on recovery of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2010;120(9):1863-71. - PubMed
Lai 2017
Lavigne 2016
-
- Lavigne P, Lavigne F, Saliba I. Intratympanic corticosteroids injections: a systematic review of literature. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2016;273(9):2271-8. - PubMed
Lawrence 2015
-
- Lawrence R, Thevasagayam R. Controversies in the management of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: an evidence-based review. Clinical Otolaryngology 2015;40(3):176-82. - PubMed
Li 2015
-
- Li H, Feng G, Wang H, Feng Y. Intratympanic steroid therapy as a salvage treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of conventional therapy: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Clinical Therapeutics 2015;37(1):178-87. - PubMed
Li 2020
-
- Li J, Ding L. Effectiveness of steroid treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2020;54(10):949-57. - PubMed
Liebau 2017
Liebau 2018
MacArthur 2015
Mäder 2018
-
- Mäder K, Lehner E, Liebau A, Plontke SK. Controlled drug release to the inner ear: concepts, materials, mechanisms, and performance. Hearing Research 2018;368:49-66. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mao 2005
-
- Mao HJ, Lu ZM, Zahng HR. Comparison of the effects of two different administration routes with hormone on sudden hearing loss. Chinese Journal of Misdiagnostics 2005;5(12):2203-4.
Marx 2018
-
- Marx M, Younes E, Chandrasekhar SS, Ito J, Plontke S, O'Leary S, et al. International consensus (ICON) on treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss. European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Diseases 2018;135(1S):S23-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Merchant 2005
-
- Merchant SN, Adams JC, Nadol JB Jr. Pathology and pathophysiology of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otology & Neurotology 2005;26(2):151-60. - PubMed
Merchant 2008
Mirian 2020
Mösges 2009
-
- Mösges R, Köberlein J, Heibges A, Erdtracht B, Klingel R, Lehmacher W, RHEO-ISHL Study Group. Rheopheresis for idiopathic sudden hearing loss: results from a large prospective, multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial. European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 2009;266(7):943-53. - PubMed
Nakagawa 2011
-
- Nakagawa T, Ito J. Local drug delivery to the inner ear using biodegradable materials. Therapeutic Delivery 2011;2(6):807-14. - PubMed
Ng 2015
-
- Ng JH, Ho RC, Cheong CS, Ng A, Yuen HW, Ngo RY. Intratympanic steroids as a salvage treatment for sudden sensorineural hearing loss? A meta-analysis. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2015;272(10):2777-82. - PubMed
NIDCD 2018
-
- NIDCD. National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. NIDCD Fact Sheet: Sudden Deafness. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2018. https://www.nidcd.nih.gov (accessed 20 April 2022).
Niedermeyer 2003
-
- Niedermeyer HP, Zahneisen G, Luppa P, Busch R, Arnold W. Cortisol levels in the human perilymph after intravenous administration of prednisolone. Audiology & Neuro-otology 2003;8(6):316-21. - PubMed
Nosrati‐Zarenoe 2012
-
- Nosrati-Zarenoe R, Hultcrantz E. Corticosteroid treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: randomized triple-blind placebo-controlled trial. Otology & Neurotology 2012;33(4):523-31. - PubMed
Olzowy 2005
-
- Olzowy B, Osterkorn D, Suckfüll M. The incidence of sudden hearing loss is greater than previously assumed [German]. MMW Fortschritte der Medizin 2005;147(14):37-8. - PubMed
Pararas 2012
Parnes 1999
-
- Parnes LS, Sun AH, Freeman DJ. Corticosteroid pharmacokinetics in the inner ear fluids: an animal study followed by clinical application. Laryngoscope 1999;109(7 Pt 2):1-17. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Phillips 2011
Plaza 2007
-
- Plaza G, Herráiz C. Intratympanic steroids for treatment of sudden hearing loss after failure of intravenous therapy. Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery 2007;137(1):74-8. - PubMed
Plontke 2005
Plontke 2007
-
- Plontke SK, Bauer M, Meisner C. Comparison of pure tone audiometry analysis in sudden hearing loss studies: lack of agreement for different outcome measures. Otology & Neurotology 2007;28(6):753-63. - PubMed
Plontke 2016
-
- Plontke SK, Girndt M, Meisner C, Probst R, Oerlecke I, Richter M, et al. Multicenter trial for sudden hearing loss therapy - planning and concept [Multizentrische Studie zur Hörsturztherapie - Planung und Konzeption]. HNO 2016;64(4):227-36. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Probst 1992
-
- Probst R, Tschopp K, Lüdin E, Kellerhals B, Podvinec M, Pfaltz CR. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of dextran/pentoxifylline medication in acute acoustic trauma and sudden hearing loss. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 1992;112(3):435-43. - PubMed
Quaranta 2016
Quiang 2016
-
- Quiang Q, Wu X, Yang T, Yang C, Sun H. A comparison between systemic and intratympanic steroid therapies as initial therapy for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a meta-analysis. Acta Oto-laryngologica 2017;137(6):598-605. - PubMed
RevMan 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.4. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Rohrmeier 2012
-
- Rohrmeier C, Koemm N, Babilas P, Prahs P, Strutz J, Buettner R. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: systemic steroid therapy and the risk of glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2012;270(4):1255-61. - PubMed
Salt 2009
Salt 2018
Salt 2020
Santesso 2020
-
- Santesso N, Glenton C, Dahm P, Garner P, Akl EA, Alper B, et al. GRADE guidelines 26: informative statements to communicate the findings of systematic reviews of interventions. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2020;119:126-35. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Schulz 2010
Seggas 2011
-
- Seggas I, Koltsidopoulos P, Bibas A, Tzonou A, Sismanis A. Intratympanic steroid therapy for sudden hearing loss: a review of the literature. Otology & Neurotology 2011;32(1):29-35. - PubMed
She 2010
-
- She W, Dai Y, Du X, Yu C, Chen F, Wang J, et al. Hearing evaluation of intratympanic methylprednisolone perfusion for refractory sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery 2010;142(2):266-71. - PubMed
Siegel 1975
-
- Siegel LG. The treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America 1975;8(2):467-73. - PubMed
Silverstein 1996
-
- Silverstein H, Choo D, Rosenberg SI, Kuhn J, Seidman M, Stein I. Intratympanic steroid treatment of inner ear disease and tinnitus (preliminary report). Ear, Nose, and Throat Journal 1996;75(8):468-71, 474, 476 passim. - PubMed
Spear 2011
-
- Spear SA, Schwartz SR. Intratympanic steroids for sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2011;145(4):534-43. - PubMed
Stachler 2012
-
- Stachler RJ, Chandrasekhar SS, Archer SM, Rosenfeld RM, Schwartz SR, Barrs DM, et al. Clinical practice guideline: sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2012;146(3 Suppl):1-35. - PubMed
Stokroos 1996
-
- Stokroos RJ, Albers FW. Therapy of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. A review of the literature. Acta Oto-Rhino-Laryngologica Belgica 1996;50(1):77-84. - PubMed
Suckfuell 2014
-
- Suckfuell M, Lisowska G, Domka W, Kabacinska A, Morawski K, Bodlaj R, et al. Efficacy and safety of AM-111 in the treatment of acute sensorineural hearing loss: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase II study. Otology & Neurotology 2014;35(8):1317-26. - PubMed
Suckfüll 2002
-
- Suckfüll M, Hearing Loss Study Group. Fibrinogen and LDL apheresis in treatment of sudden hearing loss: a randomised multicentre trial. Lancet 2002;360(9348):1811-7. - PubMed
Tran Ba Huy 2005
-
- Tran Ba Huy PT, Sauvaget E. Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is not an otologic emergency. Otology & Neurotology 2005;26(5):896-902. - PubMed
Trune 2006
-
- Trune DR, Kempton JB, Gross ND. Mineralocorticoid receptor mediates glucocorticoid treatment effects in the autoimmune mouse ear. Hearing Research 2006;212(1-2):22-32. - PubMed
Trune 2012
Tucci 2002
-
- Tucci DL, Farmer JC Jr, Kitch RD, Witsell DL. Treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with systemic steroids and valacyclovir. Otology & Neurotology 2002;23(3):301-8. - PubMed
Vambutas 2021
-
- Vambutas A, Davia DV. Biologics for immune-mediated sensorineural hearing loss. Otolaryngologic clinics of North America 2021;54(4):803-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ventry 1982
-
- Ventry IM, Weinstein BE. The hearing handicap inventory for the elderly: a new tool. Ear and Hearing 1982;3(3):128-34. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Vlastarakos 2012
-
- Vlastarakos PV, Papacharalampous G, Maragoudakis P, Kampessis G, Maroudias N, Candiloros D, et al. Are intra-tympanically administered steroids effective in patients with sudden deafness? Implications for current clinical practice. European Archives of Oto-rhino-laryngology 2012;269(2):363-80. - PubMed
Wei 2006
Wei 2013
Wilson 1980
-
- Wilson WR, Byl FM, Laird N. The efficacy of steroids in the treatment of idiopathic sudden hearing loss. A double-blind clinical study. Archives of Otolaryngology 1980;106(12):772-6. - PubMed
Wycherly 2011
Yi 2011
-
- Yi JC, Chen S, Huang CY. Observation on the therapeutic effect of Eustachian tube injection of dexamethasone in treatment of sudden deafness. Guangxi Medical Journal 2011;33(2):179-80.
You 2008
-
- You XL, Lin X, Zhu BC. Local and systemic glucocorticoid treatment for sudden hearing loss. China Practical Medical 2008;3(28):125-7.
Zhang 2021
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

