Structural insights into the RNA interaction with Yam bean Mosaic virus (coat protein) from Pachyrhizus erosus using bioinformatics approach
- PMID: 35867657
- PMCID: PMC9307209
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270534
Structural insights into the RNA interaction with Yam bean Mosaic virus (coat protein) from Pachyrhizus erosus using bioinformatics approach
Abstract
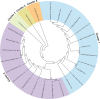
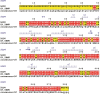
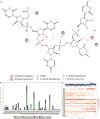
Plants are constantly threatened by a virus infection, i.e., Potyviruses, the second largest genus of plant viruses which results in several million-dollar losses in various essential crops globally. Yam bean (Pachyrhizus erosus) is considered to be one of the essential tuberous legume crops holding a great potential source of starch. Yam Bean Mosaic Virus (YBMV) of Potyvirus group belonging to the family potyviridae affects Yam bean and several angiosperms both in the tropical and sub-tropical regions causing large economical losses in crops. In this study, we attempted to understand the sequence-structure relationship and mode of RNA binding mechanism in YBMV CP using in silico integrative modeling and all-atoms molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The assembly of coat protein (CP) subunits from YBMV and the plausible mode of RNA binding were compared with the experimental structure of CP from Watermelon mosaic virus potyvirus (5ODV). The transmembrane helix region is present in the YBMV CP sequence ranging from 76 to 91 amino acids. Like the close structural-homolog, 24 CPs monomeric sub-units formed YBMV a conserved fold. Our computational study showed that ARG124, ARG155, and TYR151 orient towards the inner side of the virion, while, THR122, GLN125, SER92, ASP94 reside towards the outer side of the virion. Despite sharing very low sequence similarity with CPs from other plant viruses, the strongly conserved residues Ser, Arg, and Asp within the RNA binding pocket of YBMV CP indicate the presence of a highly conserved RNA binding site in CPs from different families. Using several bioinformatics tools and comprehensive analysis from MD simulation, our study has provided novel insights into the RNA binding mechanism in YBMV CP. Thus, we anticipate that our findings from this study will be useful for the development of new therapeutic agents against the pathogen, paving the way for researchers to better control this destructive plant virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist
Figures







References
-
- Reddy PP. Plant protection in tropical root and tuber crops. Springer; 2015.
-
- Pati K, Behera S, Ray DK, Behera PR, Sarkar A, Chauhan VBS, et al. Element Profiling of Thirty Genotypes of Yam bean in eastern India by Using Proton Induced X-ray Emission (PIXE). J Food Compos Anal. 2021; 104006.
-
- de Sá Andrade Medeiros L, de Oliveira IA, Pires LL, Kitajima EW, da Silva GS, Beserra JEA. First report of Yambean mosaic virus in Brazil. Australas Plant Dis Notes. 2019;14: 1–4.
-
- Lim TK. Pachyrhizus erosus. Edible medicinal and non-medicinal plants. Springer; 2016. pp. 465–481.
-
- Thouvenel J-C, Dumont R. Perte de rendement de l’igname infectee par le virus de la mosaique en Côte d’Ivoire. 1990.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

