Aspergillus spp. osteoarticular infections: an updated systematic review on the diagnosis, treatment and outcomes of 186 confirmed cases
- PMID: 35867975
- PMCID: PMC9849853
- DOI: 10.1093/mmy/myac052
Aspergillus spp. osteoarticular infections: an updated systematic review on the diagnosis, treatment and outcomes of 186 confirmed cases
Abstract
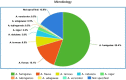
Aspergillus spp. osteoarticular infections are destructive opportunistic infections, while there is no clear consensus on their management. The purpose of this review is to investigate the current literature regarding Aspergillus spp. osteoarticular infections. An electronic search of the PubMed and Scopus databases was conducted considering studies that assessed osteoarticular infections from Aspergillus spp. We included only studies with biopsy proven documentation of positive cultures or histological findings for Aspergillus spp., and those with essential information for each case such as the anatomical location of the infection, the type of treatment (conservative, surgical, combination), the antifungal therapy, and the outcome. Overall, 148 studies from 1965 to 2021 including 186 patients were included in the review. One hundred and seven (57.5%) patients underwent surgical debridement in addition to antifungal therapy, while 79 (42.7%) patients were treated only conservatively. Complete infection resolution was reported in 107 (57.5%) patients, while partial resolution in 29 (15.5%) patients. Surgical debridement resulted in higher complete infection resolution rate compared to only antifungal therapy (70.0% vs. 40.5%, P < 0.001), while complete resolution rate was similar for antifungal monotherapy and combination/sequential therapy (58.3% vs. 54.5%; P = 0.76). Last, complete resolution rate was also similar for monotherapy with amphotericin B (58.1%) and voriconazole (58.6%; P = 0.95). The results of this study indicate that antifungal monotherapy has similar efficacy with combination/sequential therapy, while voriconazole has similar efficacy with amphotericin B. Moreover, surgical debridement of the infected focus results in better outcomes in terms of infection eradication compared to conservative treatment.
Lay summary: Antifungal monotherapy has similar efficacy with combination/sequential therapy, and voriconazole has similar efficacy with amphotericin B for the treatment of Aspergillus spp. osteoarticular infections, while surgical debridement of the infected focus improves the infection eradication rate.
Keywords: Aspergillus spp; antifungal agents; diagnosis; management; osteoarticular infection.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The International Society for Human and Animal Mycology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aspergillus tubingensis Endocarditis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Mycopathologia. 2022 Jun;187(2-3):249-258. doi: 10.1007/s11046-022-00621-0. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Mycopathologia. 2022. PMID: 35267153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Guideline based treatment of invasive aspergillosis].Mycoses. 2010 May;53 Suppl 1:36-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2009.01840.x. Mycoses. 2010. PMID: 20433655 German.
-
Antifungal therapy of aspergillosis of the central nervous system and aspergillus endophthalmitis.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(20):3648-68. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990342. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23278539 Review.
-
COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis (CAPA) in Iranian patients admitted with severe COVID-19 pneumonia.Infection. 2023 Feb;51(1):223-230. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01907-7. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Infection. 2023. PMID: 36107379 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of efficacy of antifungals against Aspergillus fumigatus: value of real-time bioluminescence imaging.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Jul;57(7):3046-59. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01660-12. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 23587947 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Aspergillosis Osteomyelitis of the Mandible: A Case Report and Literature Review.Sage Open Pathol. 2025 May 29;18:30502098251344770. doi: 10.1177/30502098251344770. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Sage Open Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40519329 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, Treatment, and Outcome of Coccidioidal Osseous Infections: A Systematic Review.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Apr 5;10(4):270. doi: 10.3390/jof10040270. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoarticular Mycoses.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022 Dec 21;35(4):e0008619. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00086-19. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36448782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk Factors, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Neonatal Fungal Liver Abscess: A Systematic Review of the Literature.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 6;13(1):167. doi: 10.3390/life13010167. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36676116 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Henry MW, Miller AO, Walsh TJ, Brause BD.. Fungal musculoskeletal infections. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2017; 31 (2): 353–368. - PubMed
-
- Bariteau JT, Waryasz GR, McDonnell Met al. . Fungal osteomyelitis and septic arthritis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014; 22 (6): 390–401. - PubMed
-
- Gabrielli E, Fothergill AW, Brescini Let al. . Osteomyelitis caused by Aspergillus species: a review of 310 reported cases. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014; 20 (6): 559–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous