Non-Oxidized Bare Metal Nanoparticles in Air: A Rational Approach for Large-Scale Synthesis via Wet Chemical Process
- PMID: 35869036
- PMCID: PMC9475554
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202201756
Non-Oxidized Bare Metal Nanoparticles in Air: A Rational Approach for Large-Scale Synthesis via Wet Chemical Process
Abstract
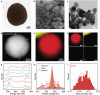
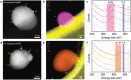
Metal nanoparticles (MeNPs) have been used in various industrial applications, owing to their unique physical and chemical properties different from the bulk counterparts. However, the natural oxidation of MeNPs is an imminent hindrance to their widespread applications despite much research efforts to prevent it. Here, a rational approach for non-oxidized bare MeNPs in air, which requires no additional surface passivation treatment is reported. The direct synthetic route uses the [Gd2 C]2+ · 2e- electride as an exceptional electron-donating agent to reduce diverse metal precursors in alcoholic solvents. All synthesized bare Cu, Ag, and Sn nanoparticles are ultra-stable in ambient air, exhibiting no trace of metal oxides even on their outermost atomic layer. This unique resistance to oxidation is ascribed to the accumulation of excess electrons on the surface of bare MeNPs, which originates from the spontaneous transfer of anionic electrons from the electride during the nanoparticle growth process. This approach provides not only a revolutionary scheme to obtain MeNPs with non-passivated and non-oxidized surfaces, but also fundamental knowledge about metal oxidation.
Keywords: electrides; negatively charged surfaces; non-oxidized metal nanoparticles; wet chemical syntheses.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Gawande M. B., Goswami A., Felpin F. X., Asefa T., Huang X., Silva R., Zou X., Zboril R., Varma R. S., Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3722. - PubMed
-
- Wang L., Kafshgari M. H., Meunier M., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005400.
-
- Abhinav K. V., Rao R. V. K., Karthik P. S., Singh S. P., RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 63985.
-
- Jeong S., Woo K., Kim D., Lim S., Kim J. S., Shin H., Xia Y., Moon J., Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 679.
-
- Chase M. W. Jr., NIST‐JANAF Thermochemical Tables, 4th ed., (National Institute of Standards and Technology), American Institute of Physics, College Park, MD: 1998.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
