In vitro anti-trypanosomal effect of ivermectin on Trypanosoma evansi by targeting multiple metabolic pathways
- PMID: 35869164
- PMCID: PMC9307293
- DOI: 10.1007/s11250-022-03228-1
In vitro anti-trypanosomal effect of ivermectin on Trypanosoma evansi by targeting multiple metabolic pathways
Abstract
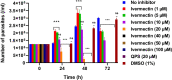
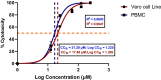
High cytotoxicity and increasing resistance reports of existing chemotherapeutic agents against T. evansi have raised the demand for novel, potent, and high therapeutic index molecules for the treatment of surra in animals. In this regard, repurposing approach of drug discovery has provided an opportunity to explore the therapeutic potential of existing drugs against new organism. With this objective, the macrocyclic lactone representative, ivermectin, has been investigated for the efficacy against T. evansi in the axenic culture medium. To elucidate the potential target of ivermectin in T. evansi, mRNA expression profile of 13 important drug target genes has been studied at 12, 24, and 48 h interval. In the in vitro growth inhibition assay, ivermectin inhibited T. evansi growth and multiplication significantly (p < 0.001) with IC50 values of 13.82 μM, indicating potent trypanocidal activity. Cytotoxicity assays on equine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and Vero cell line showed that ivermectin affected the viability of cells with a half-maximal cytotoxic concentration (CC50) at 17.48 and 22.05 μM, respectively. Data generated showed there was significant down-regulation of hexokinase (p < 0.001), ESAG8 (p < 0.001), aurora kinase (p < 0.001), casein kinase 1 (p < 0.001), topoisomerase II (p < 0.001), calcium ATPase 1 (p < 0.001), ribonucleotide reductase I (p < 0.05), and ornithine decarboxylase (p < 0.01). The mRNA expression of oligopeptidase B remains refractory to the exposure of the ivermectin. The arginine kinase 1 and ribonucleotide reductase II showed up-regulation on treatment with ivermectin. The ivermectin was found to affect glycolytic pathways, ATP-dependent calcium ATPase, cellular kinases, and other pathway involved in proliferation and maintenance of internal homeostasis of T. evansi. These data imply that intervention with alternate strategies like nano-formulation, nano-carriers, and nano-delivery or identification of ivermectin homologs with low cytotoxicity and high bioavailability can be explored in the future as an alternate treatment for surra in animals.
Keywords: HMI-9 medium; Ivermectin; Surra; Trypanosoma evansi.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gene expression study to elucidate the anti-trypanosomal activity of quinapyramine methyl sulphate (QPS).Parasitol Int. 2022 Dec;91:102632. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2022.102632. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Parasitol Int. 2022. PMID: 35870741
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of efficacy of berberine chloride: Phyto-alternative approach against Trypanosoma evansi infection.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2023 Jun;254:111562. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2023.111562. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 37084956
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of kinase and protease inhibitors against Trypanosoma evansi.Vet Res Commun. 2023 Jun;47(2):473-485. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-09964-x. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Vet Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 35751782
-
Shifting Paradigms: Imidocarb dipropionate as an alternative chemotherapeutic strategy for Trypanosoma evansi infection in animals.Vet Parasitol. 2025 Aug;338:110558. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2025.110558. Epub 2025 Jul 29. Vet Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 40743659
-
Trypanosoma evansi and T. equiperdum: distribution, biology, treatment and phylogenetic relationship (a review).Vet Parasitol. 1998 Oct;79(2):95-107. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4017(98)00146-0. Vet Parasitol. 1998. PMID: 9806490 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiproliferative and Morphological Analysis Triggered by Drugs Contained in the Medicines for Malaria Venture COVID-Box Against Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites.Microorganisms. 2024 Dec 16;12(12):2602. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122602. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770804 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic effects of ivermectin on Giardia lamblia: induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1484805. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1484805. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39545240 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

