Modulation of atrazine-induced chromosomal aberrations and cyclin-dependent kinases by aqueous extract of Roylea cinerea (D.Don) Baillon leaves in Allium cepa
- PMID: 35869268
- PMCID: PMC9307653
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-16813-z
Modulation of atrazine-induced chromosomal aberrations and cyclin-dependent kinases by aqueous extract of Roylea cinerea (D.Don) Baillon leaves in Allium cepa
Abstract
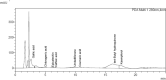
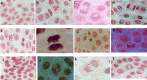
Roylea cinerea (D.Don) Baillon an indigenous medicinal plant of Lamiaceae family used for the treatment of several diseases. In the present study, its aqueous (leaves) extract was tested for genoprotective action against atrazine-induced chromosomal aberrations in the root tip cells of Allium cepa. Atrazine is a herbicide of triazine class commonly used to inhibit the growth of broad leaf and grassy weeds. In order to find the concentration of atrazine that exhibits maximum toxicity, its different concentrations (1, 5 and 10 µg/mL) were tested. It was observed that 10 µg/mL concentration was more toxic as it reduced the mitotic index and also increased the chromosomal aberrations. Among all the tested concentrations of aqueous (leaves) extracts (0.25. 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 3.0 µg/mL), the3.0 µg/mL concentration in both modes of experiments i.e. pre and post showed a significant reduction in chromosomal aberrations induced by atrazine. To understand the mechanism of protection by plant extract on atrazine-induced chromosomal abnormalities the RT-qPCR studies were conducted to observe the expression of marker genes Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) (CDKA:1, CDKB2:1 and CDKD1:1. For this, the RNA was extracted from root tips treated with extract along with atrazine by TRIzol®. It was observed that aqueous extract of Roylea cinerea (D.Don) Baillon leaves upregulated the CDKs gene expression in both the modes i.e. pre and post treatments. A critical analysis of results indicated that aqueous extract ameliorated the chromosomal aberrations caused by atrazine which may be be due to the increased expression level of CDKs genes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Quercetin reduces chromosome aberrations induced by atrazine in the Allium cepa test.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2006 May;47(4):254-9. doi: 10.1002/em.20199. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2006. PMID: 16416428
-
Antiproliferative Effects of Roylea cinerea (D. Don) Baillon Leaves in Immortalized L6 Rat Skeletal Muscle Cell Line: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species Mediated Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 13;11:322. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00322. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32231579 Free PMC article.
-
Roylea cinerea (D.Don) Baillon: Ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2019 Mar 25;232:193-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.12.042. Epub 2018 Dec 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30594605 Review.
-
Clastogenicity of atrazine assessed with the Allium cepa test.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2004;43(2):137-41. doi: 10.1002/em.20007. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2004. PMID: 14991755
-
What can the Allium cepa test say about pesticide safety? A review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jul;29(32):48088-48104. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-20695-z. Epub 2022 May 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35568785 Review.
References
-
- Kumar G, Srivastava A. Comparative genotoxicity of herbicide ingredients glyphosate and atrazine on root meristem of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) Jordan J. Biol. Sci. 2015;8:221–226. doi: 10.12816/0026962. - DOI
-
- Ali I, Alothman ZA, Al-Warthan A. Sorption, kinetics and thermodynamics studies of atrazine herbicide removal from water using iron nano-composite material. Int. J. Environ Sci. Technol. 2016;13:733–742. doi: 10.1007/s13762-015-0919-6. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

