Tobacco Harm Reduction with Vaporised Nicotine (THRiVe): A Feasibility Trial of Nicotine Vaping Products for Smoking Cessation Among People Living with HIV
- PMID: 35869375
- PMCID: PMC9908735
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-022-03797-0
Tobacco Harm Reduction with Vaporised Nicotine (THRiVe): A Feasibility Trial of Nicotine Vaping Products for Smoking Cessation Among People Living with HIV
Abstract
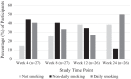
People living with HIV (PLHIV) have high rates of tobacco smoking. Nicotine vaping products (NVPs) may promote tobacco smoking cessation and/or harm reduction. This study aimed to trial the feasibility of NVPs for promoting tobacco smoking cessation among PLHIV. The Tobacco Harm Reduction with Vaporised Nicotine (THRiVe) study was a mixed-methods trial among 29 PLHIV who used tobacco daily. Participants trialled a 12-week intervention of NVPs. This study reports descriptive analyses of quantitative data on tobacco abstinence and associated adverse events. Short-term abstinence (7-day point prevalence; i.e., no tobacco use for 7 days) was achieved by 35% of participants at Week 12 and 31% reported short-term abstinence at Week 24. Sustained medium-term abstinence (8 weeks' abstinence) was achieved by 15% of participants at Week 12 and 31% at Week 24. Most adverse events were mild. NVPs may represent a feasible and potentially effective short-to-medium term tobacco smoking cessation aid and/or harm reduction strategy among PLHIV.
Keywords: HIV; Smoking cessation; Tobacco; Vaping.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures
References
-
- Cooperman NA. Current research on cigarette smoking among people with HIV. Curr Addict Rep. 2016;3(1):19–26.
-
- Helleberg M, Afzal S, Kronborg G, Larsen CS, Pedersen G, Pedersen C, et al. Mortality attributable to smoking among HIV-1-infected individuals: a nationwide, population-based cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(5):727–734. - PubMed
-
- Helleberg M, Gerstoft J, Afzal S, Kronborg G, Larsen CS, Pedersen C, et al. Risk of cancer among HIV-infected individuals compared to the background population: impact of smoking and HIV. AIDS. 2014;28(10):1499–1508. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical