Gene expression profiling before and after internode culture for adventitious shoot formation in ipecac
- PMID: 35869421
- PMCID: PMC9308184
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-022-03756-w
Gene expression profiling before and after internode culture for adventitious shoot formation in ipecac
Abstract
Background: In ipecac (Carapichea ipecacuanha (Brot.) L. Andersson), adventitious shoots can be induced simply by placing internodal segments on phytohormone-free culture medium. The shoots form locally on the epidermis of the apical region of the segments, but not the basal region. Levels of endogenous auxin and cytokinin transiently increase in the segments after 1 week of culture.
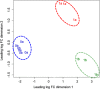
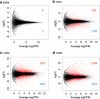
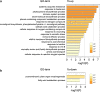
Results: Here, we conducted RNA-seq analysis to compare gene expression patterns in apical and basal regions of segments before culture and after 1 week of culture for adventitious shoot formation. The results revealed 8987 differentially expressed genes in a de novo assembly of 76,684 genes. Among them, 276 genes were upregulated in the apical region after 1 week of culture relative to before culture and the basal region after 1 week of culture. These genes include 18 phytohormone-response genes and shoot-formation-related genes. Validation of the gene expression by quantitative real-time PCR assay confirmed that the expression patterns were similar to those of the RNA-seq data.
Conclusions: The transcriptome data show that expression of cytokinin biosynthesis genes is induced along with the acquisition of cellular pluripotency and the initiation of cell division by wounding in the apical region of internodal segments, that trigger adventitious shoot formation without callusing.
Keywords: Adventitious shoot; Carapichea ipecacuanha; De novo transcriptome assembly; Internodal segment; RNA-seq; Transcriptional change.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ectopic expression of LONELY GUY7 in epidermis of internodal segments for de novo shoot regeneration without phytohormone treatment in ipecac.Physiol Plant. 2025 Jan-Feb;177(1):e70023. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70023. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 39723728 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous auxin determines the pattern of adventitious shoot formation on internodal segments of ipecac.Planta. 2020 Mar 5;251(3):73. doi: 10.1007/s00425-020-03367-5. Planta. 2020. PMID: 32140780
-
Strigolactone signaling inhibition increases adventitious shoot formation on internodal segments of ipecac.Planta. 2021 May 20;253(6):123. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03640-1. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34014387
-
Integrating the Roles for Cytokinin and Auxin in De Novo Shoot Organogenesis: From Hormone Uptake to Signaling Outputs.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 9;22(16):8554. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168554. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The growth of a stable stationary structure: coordinating cell behavior and patterning at the shoot apical meristem.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018 Feb;41:83-88. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 29073502 Review.
Cited by
-
Ectopic expression of LONELY GUY7 in epidermis of internodal segments for de novo shoot regeneration without phytohormone treatment in ipecac.Physiol Plant. 2025 Jan-Feb;177(1):e70023. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70023. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 39723728 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in ENHANCER OF SHOOT REGENERATION2 expression by treatment with strigolactone-related inhibitors and kinetin during adventitious shoot formation in ipecac.Plant Cell Rep. 2023 Dec;42(12):1927-1936. doi: 10.1007/s00299-023-03073-y. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Plant Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37803214
References
-
- Haberlandt G. Kulturversuche mit isolierten Pflanzenzellen. Sitzungsber Math-Naturwiss Kl Akad Wiss Wien. 1902;111:69–92.
-
- Steward FC, Mapes MO, Mears K. Growth and organized development of cultured cells. II. Organization in cultures grown from freely suspended cell. Am J Bot. 1958;45(10):705–708. doi: 10.1002/j.1537-2197.1958.tb10599.x. - DOI
-
- George EF. Plant tissue culture procedure - background. In: George EF, Hall MA, De Klerk GJ, editors. Plant propagation by tissue culture. 3. Dordrecht: Springer; 2008. pp. 1–28.
-
- Skoog F, Miller CO. Chemical regulation of growth and organ formation in plant tissues cultured in vitro. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1957;11:118–130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

