[Juglone induces proliferation inhibition and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via promoting c-Myc ubiquitination]
- PMID: 35869765
- PMCID: PMC9308861
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.07.09
[Juglone induces proliferation inhibition and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells via promoting c-Myc ubiquitination]
Abstract
Objective: To observe the expression of c-Myc protein in cervical cancer HeLa cells and explore the effect of juglone on the proliferation and apoptosis of HeLa cells by affecting c-Myc ubiquitination.
Methods: HeLa cells treated with different concentrations (0, 10, 20, or 50 μmol/L) of juglone or with 20 μmol/L juglone for different time lengths were examined for expression of c-Myc protein with Western blotting. The half-life of c-Myc protein was determined using cycloheximide (CHX) and c-Myc protein degradation was detected using coimmunoprecipitation. We also assessed the effects of 20 μmol/L juglone combined with 0, 1.0 or 2.0 μmol/L MG132 (a proteasome inhibitor) on c-Myc expression. The effects of 20 μmol/L juglone on the proliferation and apoptosis of HeLa cells with RNA interference-mediated knockdown of c-Myc were evaluated with MTT assay and flow cytometry.
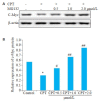
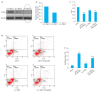
Results: Treatment with juglone significantly lowered c-Myc protein expression in HeLa cells in a concentration-and time-dependent manner (P < 0.05). Juglone obviously shortened the half-life of c-Myc protein, and the addition of MG132 significantly up-regulated the expression level of c-Myc protein (P < 0.05). Juglone treatment also promoted ubiquitination of c-Myc protein in HeLa cells. Compared with the cells transfected with a negative control construct, the cells transfected with si-c-Myc showed significantly decreased proliferation inhibition and a lowered cell rate with early apoptosis after juglone treatment (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Juglone inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of HeLa cells by affecting the ubiquitination of c-Myc protein.
目的: 观察c-Myc蛋白在宫颈癌HeLa细胞中的表达,探讨胡桃醌通过影响c-Myc蛋白泛素化降解进而影响HeLa细胞的增殖与凋亡。
方法: 培养人宫颈癌HeLa细胞,分为对照组:正常培养;10、20、50 μmol/L胡桃醌组:培养液中分别加入对应浓度的胡桃醌。以Western blot方法分析胡桃醌处理后c-Myc蛋白的表达。HeLa细胞分为对照组和20 μmol/L胡桃醌组,在培养0、2、4、8 h分别用Western blot检测c-Myc蛋白表达的变化;放线菌酮(CHX)法检测c-Myc蛋白半衰期的变化;CoIP方法检测cMyc蛋白降解影响。HeLa细胞分为空白对照组:正常培养;胡桃醌组:20 μmol/L胡桃醌培养液培养;0.5、1.0、2.0 μmol/L MG132组:分别与0、1.0、2.0 μmol/L蛋白酶体抑制剂MG132加20 μmol/L胡桃醌培养,检测c-Myc蛋白表达的水平。将si c-Myc转染入HeLa细胞后,将细胞分siNC组:空载体组;si-NC;胡桃醌组:空载体加20 μmol/L胡桃醌处理;si-cMyc组:转染Myc RNA;sicMyc20 μmol/L胡桃醌组:转染Myc RNA加20 μmol/L胡桃醌处理。MTT及流式细胞术检测20 μmol/L胡桃醌处理后对敲除及未敲除c-Myc基因的细胞增殖及凋亡的影响。
结果: 与对照组相比,不同浓度胡桃醌可下调c-Myc蛋白表达且曾时间及剂量依赖性(P < 0.05;P < 0.01);胡桃醌可缩短c-Myc蛋白的半衰期,加入不同浓度的MG132后,即可明显上调c-Myc蛋白水平(P < 0.05;P < 0.01)。未用胡桃醌组相比,胡桃醌可明显增加c-Myc蛋白的泛素降解水平。未敲除c-Myc组相比,敲除组在胡桃醌处理后吸光度值明显增加(P < 0.05)和早期凋亡率明显下降(P < 0.05)。
结论: 胡桃醌通过影响c-Myc蛋白的泛素化降解过程,进而抑制HeLa细胞增殖并促进其凋亡的发生。
Keywords: HeLa cells; c-Myc; cervical cancer; juglone; ubiquitination.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
