Establishment of a time-resolved immunoassay for acute kidney injury based on the detection of Kim-1
- PMID: 35870181
- PMCID: PMC9459273
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24603
Establishment of a time-resolved immunoassay for acute kidney injury based on the detection of Kim-1
Abstract
Aim: To establish a highly sensitive time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay (TRFIA) of kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1) and evaluate its clinical value in acute kidney injury (AKI).
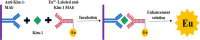
Methods: The Kim-1-TRFIA was established by the double-antibody sandwich method, and the method was evaluated. The established Kim-1-TRFIA was used to detect the concentration of Kim-1 in the serum of healthy controls and patients with AKI.
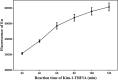
Results: The optimal coating antibody concentration and optimal Eu3+ -labeled antibody dilution ratio for Kim-1-TRFIA are 1 μg/ml and 1:140, respectively. The linear range is 42.71-4666.69 pg/ml. The intra- and inter-assay coefficients of variation are <10%. The specificity of our Kim-1-TRFIA is acceptable. The recovery is between 95.14% and 102.84%. The concentration of Kim-1 in the serum of patients with AKI is 126.50 ± 67.99 pg/ml, which is significantly higher than that in the serum of healthy controls (49.72 ± 16.40 pg/ml, p < 0.001). Staging patients with AKI by glomerular filtration rate shows that the serum concentration of Kim-1 increases significantly with increasing disease severity (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: A highly sensitive Kim-1-TRFIA was established. With this immunoassay, a good differential diagnosis can be made, and healthy people and AKI patients can be differentiated by detecting the concentration of Kim-1 in the serum. Moreover, the severity of AKI patients can be determined.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; double-antibody sandwich method; kidney injury molecule-1; time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Establishment of interleukin-18 time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay and its preliminary application in liver disease.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 May;35(5):e23758. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23758. Epub 2021 Mar 15. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33720453 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Tim3 detection by time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay and its application in membranous nephropathy.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jun;34(6):e23248. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23248. Epub 2020 Feb 20. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32077157 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and Clinical Application of a Highly Sensitive Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunoassay for Tumor-Associated Trypsinogen-2.J Fluoresc. 2022 Jul;32(4):1501-1507. doi: 10.1007/s10895-022-02950-1. Epub 2022 May 5. J Fluoresc. 2022. PMID: 35511384
-
The Predictive Role of the Biomarker Kidney Molecule-1 (KIM-1) in Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 22;20(20):5238. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205238. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31652595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers of kidney injury.Biomarkers. 2011 Jul;16 Suppl 1:S22-30. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2011.587129. Biomarkers. 2011. PMID: 21707441 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and application of an amplified luminescent proximity homogeneous assay-linked immunosorbent assay for the accurate quantification of kidney injury molecule-1.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 18;10:1280681. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1280681. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38304229 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

