Metabolic activity determines survival depending on the level of lymph node involvement in cervical cancer
- PMID: 35870900
- PMCID: PMC9308355
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09785-w
Metabolic activity determines survival depending on the level of lymph node involvement in cervical cancer
Abstract
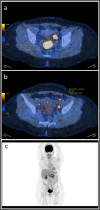
Background: To assess the impact of PET/CT functional parameters on survival, locoregional, and distant failure according to the most distant level of lymph node [18F]FDG uptake in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC).
Methods: Retrospective study including 148 patients with LACC treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy after PET/CT and para-aortic lymph node (PALN) surgical staging. Two senior nuclear medicine physicians reviewed all PET/CT exams and retrieved tumor and lymph node metabolic parameters: SUVmax, MTV, TLG. Oncological outcomes according to metabolic parameters and level of lymph node spread on PET/CT were assessed.
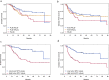
Results: In patients without lymph node uptake on PET/CT, high MTV values of the cervical tumor were associated with DFS (HR = 5.14 95%CI = [2.15-12.31]), OS (HR = 6.10 95%CI = [1.89-19.70]), and time to distant (HR = 4.73 95%CI = [1.55-14.44]) and locoregional recurrence (HR = 5.18 95%CI = [1.72-15.60]). In patients with pelvic lymph node (PLN) uptake but without PALN uptake on [18F]FDG-PET/CT, high MTV values of the cervical tumor were associated with DFS (HR = 3.17 95%CI = [1.02-9.83]) and OS (HR = 3.46 95%CI = [0.96-12.50]), and the number of PLN fixations was associated with DFS (HR = 1.30 95%CI = [1.10-1.53]), OS (HR = 1.35 95%CI = [1.11-1.64]), and time to distant (HR = 1.35 95%CI = [1.08-1.67]) and locoregional recurrence (HR = 1.31 95%CI = [1.08-1.59]). There was no significant association between cervical tumor metabolic or lymph node metrics and survival outcome in patients with PALN uptake.
Conclusions: Cervical MTV is more accurate than SUVmax to predict survival outcome in patients with locoregional disease confined to the pelvis and should be implemented in routine clinical practice. Prognostic value of metabolic metrics disappears with PALN uptake, which is associated with distant failure in nearly half of patients.
Keywords: Fluorodeoxyglucose F18; Locally advanced cervical cancer; Lymphatic metastasis; Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography; Survival Analysis; Uterine Cervical Neoplasms.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumour and pelvic lymph node metabolic activity on FDG-PET/CT to stratify patients for para-aortic surgical staging in locally advanced cervical cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 May;47(5):1252-1260. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04659-z. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31915897
-
Prognostic Value of the Sum of Metabolic Tumor Volume of Primary Tumor and Lymph Nodes Using 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients With Cervical Cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Mar;95(9):e2992. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002992. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 26945420 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced cervix cancer without aortic lymph node involvement: can we consider metabolic parameters of pretherapeutic FDG-PET/CT for treatment tailoring?Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019 Jul;46(7):1551-1559. doi: 10.1007/s00259-018-4219-5. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30729273
-
Diagnostic accuracy of preoperative 18F-FDG PET or PET/CT in detecting pelvic and para-aortic lymph node metastasis in patients with endometrial cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019 Sep;300(3):519-529. doi: 10.1007/s00404-019-05207-8. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2019. PMID: 31165242
-
[18F]FDG-PET or PET/CT in the evaluation of pelvic and para-aortic lymph nodes in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer: A systematic review of the literature.Gynecol Oncol. 2020 Nov;159(2):588-596. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2020.08.021. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Gynecol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32921477
References
-
- Global Cancer Observatory, OMS. Estimated number of incident cases, worldwide ( top 10 cancer sites ) in 2012. Disponible sur http://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-multi-bars?mode=cancer&mode_pop.... 2017. p. 2012.
-
- Choi HJ, Ju W, Myung SK, Kim Y. Diagnostic performance of computer tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography or positron emission tomography/computer tomography for detection of metastatic lymph nodes in patients with cervical cancer: Meta-analysis. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(6):1471–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01532.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

