EPDR1 is a noncanonical effector of insulin-mediated angiogenesis regulated by an endothelial-specific TGF-β receptor complex
- PMID: 35872017
- PMCID: PMC9396412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102297
EPDR1 is a noncanonical effector of insulin-mediated angiogenesis regulated by an endothelial-specific TGF-β receptor complex
Abstract
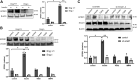
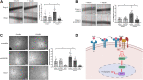
Insulin signaling in blood vessels primarily functions to stimulate angiogenesis and maintain vascular homeostasis through the canonical PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways. However, angiogenesis is a complex process coordinated by multiple other signaling events. Here, we report a distinct crosstalk between the insulin receptor and endoglin/activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1), an endothelial cell-specific TGF-β receptor complex essential for angiogenesis. While the endoglin-ALK1 complex normally binds to TGF-β or bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) to promote gene regulation via transcription factors Smad1/5, we show that insulin drives insulin receptor oligomerization with endoglin-ALK1 at the cell surface to trigger rapid Smad1/5 activation. Through quantitative proteomic analysis, we identify ependymin-related protein 1 (EPDR1) as a major Smad1/5 gene target induced by insulin but not by TGF-β or BMP9. We found endothelial EPDR1 expression is minimal at the basal state but is markedly enhanced upon prolonged insulin treatment to promote cell migration and formation of capillary tubules. Conversely, we demonstrate EPDR1 depletion strongly abrogates these angiogenic effects, indicating that EPDR1 is a crucial mediator of insulin-induced angiogenesis. Taken together, these results suggest important therapeutic implications for EPDR1 and the TGF-β pathways in pathologic angiogenesis during hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance.
Keywords: Smad; TGF beta; angiogenesis; endothelial biology; insulin.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated circulating BMP9 aggravates pulmonary angiogenesis in hepatopulmonary syndrome rats through ALK1-Endoglin-Smad1/5/9 signalling.Eur J Clin Invest. 2024 Aug;54(8):e14212. doi: 10.1111/eci.14212. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38591651
-
ALK1 regulates the internalization of endoglin and the type III TGF-β receptor.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Apr 1;32(7):605-621. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-03-0199. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33566682 Free PMC article.
-
ALK5 phosphorylation of the endoglin cytoplasmic domain regulates Smad1/5/8 signaling and endothelial cell migration.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Mar;31(3):435-41. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp327. Epub 2009 Dec 30. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20042635 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β & BMP receptors endoglin and ALK1: overview of their functional role and status as antiangiogenic targets.Microcirculation. 2014 Feb;21(2):93-103. doi: 10.1111/micc.12099. Microcirculation. 2014. PMID: 25279424 Review.
-
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia, a vascular dysplasia affecting the TGF-beta signaling pathway.Clin Med Res. 2006 Mar;4(1):66-78. doi: 10.3121/cmr.4.1.66. Clin Med Res. 2006. PMID: 16595794 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Apr 10;8(1):152. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01400-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37037849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoproteomic profiling identifies DNMT1 as a key substrate of beta IV spectrin-dependent ERK/MAPK signaling in suppressing angiogenesis.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Jun 4;711:149916. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.149916. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 38613866 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial tip/stalk cell selection requires BMP9-induced βIV-spectrin expression during sprouting angiogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Jun 1;34(7):ar72. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-02-0064. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37126382 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating prosaposin and ependymin-related protein 1 levels are correlated with insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 26;16:1519586. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1519586. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40642507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon K.J., Blobe G.C. Role of transforming growth factor-beta superfamily signaling pathways in human disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008;1782:197–228. - PubMed
-
- Blobe G.C., Schiemann W.P., Lodish H.F. Role of transforming growth factor beta in human disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000;342:1350–1358. - PubMed
-
- Scharpfenecker M., van Dinther M., Liu Z., van Bezooijen R.L., Zhao Q., Pukac L., et al. BMP-9 signals via ALK1 and inhibits bFGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation and VEGF-stimulated angiogenesis. J. Cell Sci. 2007;120:964–972. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

