Termination of Pregnancy Due to COVID-19 Induced Damage to the Placenta: A Case Report
- PMID: 35872673
- PMCID: PMC9272966
- DOI: 10.22088/cjim.13.0.295
Termination of Pregnancy Due to COVID-19 Induced Damage to the Placenta: A Case Report
Abstract
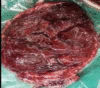
Background: The effects of COVID-19 and its connection with pregnant women and infants have received growing attention of neonatal specialists and gynecologists. COVID-19 causes mild upper respiratory infections, leading to severe illness in patients with defective immune systems. In pregnant women with COVID-19 due to the adverse effects of this disease maintaining maternal health and preventing fetal death is essential and vital. The aim of this study is to report an unusual observation of Termination of pregnancy due to COVID-19 induced damage to the placenta.
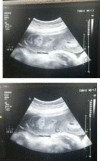
Case presentation: A 33-year-old female patient with a gestational age of 33 weeks. The main symptoms and main concerns of the patient were shortness of breath and cough. Following positive PCR test results and CT, the COVID-19 diagnosis was confirmed. Due to the positive OCT and fetal heart failure, it was decided to terminate pregnancy and thus the patient underwent emergency Cesarean section and the infant was born weighing 2700 g and Apgar 10.
Conclusion: Common manifestations of COVID-19 in pregnant women include fever, cough, and muscle pain. The most common laboratory results are decreased blood lymphocytes and increased blood CRP. Pregnancy and childbirth complications in pregnant women with COVID-19 included elevated preterm delivery, increased Cesarean section rate, and infant mortality. As a result, pregnant women with COVID-19 should immediately have an ultrasound to diagnose placental thrombosis.
Keywords: COVID-19; Placenta damage; Termination of Pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Excerpts from the World Medical Literature: Obstetrics.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2022 Nov;44(11):1125-1127. doi: 10.1016/j.jogc.2022.08.013. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2022. PMID: 36410933 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO. Consensus document on the epidemiology of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) World Health Organization; 2003. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/70863.
-
- Schwartz DA. An analysis of 38 pregnant women with COVID-19, their newborn infants, and maternal-fetal transmission of SARS-CoV-2: maternal coronavirus infections and pregnancy outcomes. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020;144:799–805. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous