Combination of Goniothalamin and Sol-Gel-Derived Bioactive Glass 45S5 Enhances Growth Inhibitory Activity via Apoptosis Induction and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer Cells MCF-7
- PMID: 35872839
- PMCID: PMC9303150
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5653136
Combination of Goniothalamin and Sol-Gel-Derived Bioactive Glass 45S5 Enhances Growth Inhibitory Activity via Apoptosis Induction and Cell Cycle Arrest in Breast Cancer Cells MCF-7
Abstract
Background: Combination of natural products with chemically synthesised biomaterials as cancer therapy has attracted great interest lately. Hence, this study is aimed at investigating the combined effects of goniothalamin and bioactive glass 45S5 (GTN-BG) and evaluating their anticancer properties on human breast cancer cells MCF-7.
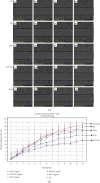
Methods: The BG 45S5 was prepared using the sol-gel process followed by characterisation using PSA, BET, SEM/EDS, XRD, and FTIR. The effects of GTN-BG on the proliferation of MCF-7 were assessed by MTT, PrestoBlue, and scratch wound assays. The cell cycle analysis, Annexin-FITC assay, and activation of caspase-3/7, caspase-8, and caspase-9 assays were determined to further explore its mechanism of action.
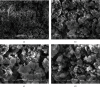
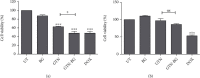
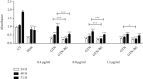
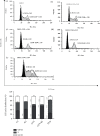
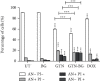
Results: The synthesised BG 45S5 was classified as a fine powder, having a rough surface, and contains mesopores of 12.6 nm. EDS analysis revealed that silica and calcium elements are the primary components of BG powders. Both crystalline and amorphous structures were detected with 73% and 27% similarity to Na2Ca2(Si2O7) and hydroxyapatite, respectively. The combination of GTN-BG was more potent than GTN in inhibiting the proliferation of MCF-7 cells. G0/G1 and G2/M phases of the cell cycle were arrested by GTN and GTN-BG. The percentage of viable cells in GTN-BG treatment was significantly lower than that in GTN. In terms of activation of initiator caspases for both extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis pathways, caspase-8 and caspase-9 were found more effective in response to GTN-BG than GTN.
Conclusion: The anticancer effect of GTN in MCF-7 cells was improved when combined with BG. The findings provide significant insight into the mechanism of GTN-BG against MCF-7 cells, which can potentially be used as a novel anticancer therapeutic approach.
Copyright © 2022 Siti Aishah Abu Bakar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Apoptosis Induction via ATM Phosphorylation, Cell Cycle Arrest, and ER Stress by Goniothalamin and Chemodrugs Combined Effects on Breast Cancer-Derived MDA-MB-231 Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Nov 26;2018:7049053. doi: 10.1155/2018/7049053. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30598998 Free PMC article.
-
Antiproliferative activity of goniothalamin enantiomers involves DNA damage, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in MCF-7 and HB4a cells.Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Dec 25;30(1 Pt B):250-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2015.10.012. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015. PMID: 26522230
-
5-Acetyl goniothalamin suppresses proliferation of breast cancer cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;791:455-464. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.09.024. Epub 2016 Sep 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27640746
-
Goniothalamin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in H400 human oral squamous cell carcinoma: A caspase-dependent mitochondrial-mediated pathway with downregulation of NF-κβ.Arch Oral Biol. 2016 Apr;64:28-38. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.12.002. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Arch Oral Biol. 2016. PMID: 26752226
-
Cytotoxicity and Toxicological Studies of Artocarpus altilis Extracts, Inducing Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest via CASPASE-3 and CASPASE-8 Pathways against Human Breast MCF-7 Cells.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022;25(6):973-985. doi: 10.2174/1386207324666210302095557. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2022. PMID: 33653245
References
-
- Hench L. L. Bioceramics: from concept to clinic. Journal of the American Ceramic Society . 1991;74(7):1487–1510. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1991.tb07132.x. - DOI
-
- Hench L. L., West J. K. The sol-gel process. Chemical Reviews . 1990;90(1):33–72. doi: 10.1021/cr00099a003. - DOI
-
- Pereira M. M., Clark A. E., Hench L. L. Effect of texture on the rate of hydroxyapatite formation on gel-silica surface. Journal of the American Ceramic Society . 1995;78(9):2463–2468. doi: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1995.tb08686.x. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

