Prognostic Factors of Small Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and the Risk of Lymph Node Metastasis: A Population-Level Study
- PMID: 35873006
- PMCID: PMC9299363
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.907415
Prognostic Factors of Small Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and the Risk of Lymph Node Metastasis: A Population-Level Study
Abstract
Background: Small non-functional neuroendocrine tumors (NF-PNETs) are a heterogeneous subset of tumors with controversy regarding their optimal management. We aimed to analyze the prognostic factors of patients with small NF-PNETs and create a risk score for lymph node metastasis (LNM).
Methods: Data of 751 patients with NF-PNETs ≤ 2 cm were obtained from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. Multivariate survival analysis was performed to analyze the prognostic factors. Logistic regression was used to identify risk factors for LNM.
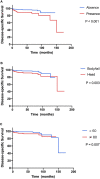
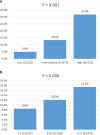
Results: Of the 751 patients, 99 (13.2%) were confirmed to have LNM. In multivariate survival analysis, LNM (hazard ratio [HR], 2.12; 95% CI, 1.04-4.32, p = 0.040) was independently associated with disease-specific survival. Logistic regression identified that tumor location in the head of the pancreas (odds ratio [OR], 4.33; 95% CI, 2.75-6.81; p < 0.001), size ≥ 1.5-2 cm (OR, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.17-2.87; p = 0.009), and grade III-IV (OR, 7.90; 95% CI, 1.79-34.90; p = 0.006) were independent risk factors of LNM. According to the OR value, the risk of LNM was scored as follows: a score of 1 for tumors located in the body/tail of the pancreas and 4 for those located in the head; a score of 1 for tumors <1 cm and 2 for those ≥1.5-2 cm; and a score of 1 for tumors with grade I-II and 8 for those with grade III-IV. Finally, the median score for this cohort was 4, with an interquartile range of 3-6. Therefore, patients were classified as three groups based on the risk score system: a total score of 1-3 for low risk, 4-6 for intermediate risk (OR, 2.98; 95% CI, 1.59-5.60; p = 0.001), and 7-14 for high risk (OR, 8.94; 95% CI, 4.50-17.7; p < 0.001), with an incidence of LNM 5.0%, 13.5%, and 31.8%, respectively (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Surgical resection with regional lymphadenectomy is recommended for small NF-PNETs with malignant potential of LNM. A risk score for LNM based on tumor grade, location, and size may preoperatively predict LNM of small NF-PNETs and guide clinical practice.
Keywords: SEER; lymph node metastasis; non-functional; pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors; prognosis; small tumors.
Copyright © 2022 Tan, Wang, Li, Liu, Liu and Ke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Falconi M, Eriksson B, Kaltsas G, Bartsch DK, Capdevila J, Caplin M, et al. ENETS Consensus Guidelines Update for the Management of Patients With Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors and Non-Functional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Neuroendocrinology (2016) 103:153–71. doi: 10.1159/000443171 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

