Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA): A potential therapeutic target in acute lung injury
- PMID: 35873025
- PMCID: PMC9293716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.07.004
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA): A potential therapeutic target in acute lung injury
Abstract
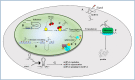
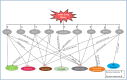
Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and its severe form Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) are the major cause of ICU death worldwide. ALI/ARDS is characterized by severe hypoxemia and inflammation that leads to poor lung compliance. Despite many advances in understanding and management, ALI/ARDS is still causing significant morbidity and mortality. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is a fast-growing topic in lung inflammation and injury. lncRNA is a class of non-coding RNA having a length of more than 200 nucleotides. It has been a center of research for understanding the pathophysiology of various diseases in the past few years. Multiple studies have shown that lncRNAs are abundant in acute lung injury/injuries in mouse models and cell lines. By targeting these long non-coding RNAs, many investigators have demonstrated the alleviation of ALI in various mouse models. Therefore, lncRNAs show great promise as a therapeutic target in ALI. This review provides the current state of knowledge about the relationship between lncRNAs in various biological processes in acute lung injury and its use as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Apoptosis; Inflammation; Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA); Macrophage polarization.
© 2021 Chongqing Medical University. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long Noncoding RNA: A Novel Insight into the Pathogenesis of Acute Lung Injury.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 11;12(2):604. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020604. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tanreqing Injection Attenuates Macrophage Activation and the Inflammatory Response via the lncRNA-SNHG1/HMGB1 Axis in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 25;13:820718. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.820718. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35547731 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA review and implications in acute lung inflammation.Life Sci. 2021 Mar 15;269:119044. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119044. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33454366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microarray profiling of lung long non-coding RNAs and mRNAs in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury mouse model.Biosci Rep. 2019 Apr 30;39(4):BSR20181634. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181634. Print 2019 Apr 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30979832 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA analysis of lung tissues after hUC-MSCs and FTY720 treatment of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mouse models.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Jun;71:68-75. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.03.017. Epub 2019 Mar 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30877876
Cited by
-
FTVI promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through LncRNA HIF1A-AS2.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 May 30;20(1):548. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05952-4. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40448168 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products: A potential immunomodulators against inflammatory-related diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):2821-2859. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01562-4. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39196458 Review.
-
Long Noncoding RNA: A Novel Insight into the Pathogenesis of Acute Lung Injury.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 11;12(2):604. doi: 10.3390/jcm12020604. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36675533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into the lncRNA-mRNA Co-Expression Profile and ceRNA Network in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 24;45(7):6170-6189. doi: 10.3390/cimb45070389. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37504305 Free PMC article.
-
The role of TLR4/NF-kB signaling axis in pneumonia: from molecular mechanisms to regulation by phytochemicals.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 16. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04130-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40377682 Review.
References
-
- Rubenfeld G.D., Caldwell E., Peabody E., et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Dushianthan A., Grocott M.P., Postle A.D., Cusack R. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury. Postgrad Med. 2011;87(1031):612–622. - PubMed
-
- McNicholas B.A., Rooney G.M., Laffey J.G. Lessons to learn from epidemiologic studies in ARDS. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2018;24(1):41–48. - PubMed
-
- Elgar G., Vavouri T. Tuning in to the signals: noncoding sequence conservation in vertebrate genomes. Trends Genet. 2008;24(7):344–352. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

