Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA): A potential therapeutic target in acute lung injury
- PMID: 35873025
- PMCID: PMC9293716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.07.004
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA): A potential therapeutic target in acute lung injury
Abstract
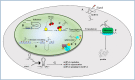
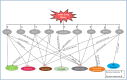
Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and its severe form Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) are the major cause of ICU death worldwide. ALI/ARDS is characterized by severe hypoxemia and inflammation that leads to poor lung compliance. Despite many advances in understanding and management, ALI/ARDS is still causing significant morbidity and mortality. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) is a fast-growing topic in lung inflammation and injury. lncRNA is a class of non-coding RNA having a length of more than 200 nucleotides. It has been a center of research for understanding the pathophysiology of various diseases in the past few years. Multiple studies have shown that lncRNAs are abundant in acute lung injury/injuries in mouse models and cell lines. By targeting these long non-coding RNAs, many investigators have demonstrated the alleviation of ALI in various mouse models. Therefore, lncRNAs show great promise as a therapeutic target in ALI. This review provides the current state of knowledge about the relationship between lncRNAs in various biological processes in acute lung injury and its use as a potential therapeutic target.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Apoptosis; Inflammation; Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA); Macrophage polarization.
© 2021 Chongqing Medical University. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Rubenfeld G.D., Caldwell E., Peabody E., et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(16):1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Dushianthan A., Grocott M.P., Postle A.D., Cusack R. Acute respiratory distress syndrome and acute lung injury. Postgrad Med. 2011;87(1031):612–622. - PubMed
-
- McNicholas B.A., Rooney G.M., Laffey J.G. Lessons to learn from epidemiologic studies in ARDS. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2018;24(1):41–48. - PubMed
-
- Elgar G., Vavouri T. Tuning in to the signals: noncoding sequence conservation in vertebrate genomes. Trends Genet. 2008;24(7):344–352. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

