Evaluation and Clinical Validation of Guanidine-Based Inactivation Transport Medium for Preservation of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35873075
- PMCID: PMC9301760
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1677621
Evaluation and Clinical Validation of Guanidine-Based Inactivation Transport Medium for Preservation of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
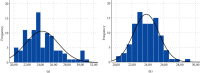
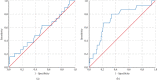
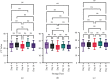
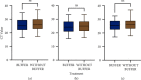
WHO declared the outbreak of COVID-19, caused by SARS-CoV-2, a pandemic in March 2020. More than 223 million cases and approximately 4.6 million deaths have been confirmed. Early diagnosis and immediate treatment became a priority during this pandemic. However, COVID-19 diagnostic testing resources are limited, especially early in the pandemic. Apart from being limited, the COVID-19 diagnostic tests using reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) have encountered storage, transportation, and safety issues. These problems are mainly experienced by developing poor countries, countries in the equatorial region, and archipelagic countries. VITPAD® is a guanidine-based inactivation transport medium (ITM) formulated to maintain the RNA quality of SARS-CoV-2 during transportation without cold chains. This study, conducted from September 2020 to March 2021, performed clinical validation of VITPAD® by comparing its performance with a globally commercially available ITM from the NEST brand. Its stability at room temperature, safety, and resistance at high temperatures was also tested using RT-PCR analysis. VITPAD® can reduce the infectious nature of the specimen, preserve the SARS-CoV-2 for 18 days at an ambient temperature, and resist high temperatures (40°C for 3 hours). A guanidine-based transport medium, such as VITPAD®, is compatible and recommended for RT-PCR-based molecular diagnosis of COVID-19.
Copyright © 2022 Hesti L. Wiraswati et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Alternative Transport Media for RT-qPCR-Based SARS-CoV-2 Testing.Int J Anal Chem. 2022 Aug 10;2022:5020255. doi: 10.1155/2022/5020255. eCollection 2022. Int J Anal Chem. 2022. PMID: 35992557 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of viral-transport-medium heat inactivation upon downstream SARS-CoV-2 detection in patient samples.J Med Microbiol. 2021 Mar;70(3):001301. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001301. Epub 2021 Mar 18. J Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33734960 Free PMC article.
-
Potential False-Negative Nucleic Acid Testing Results for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 from Thermal Inactivation of Samples with Low Viral Loads.Clin Chem. 2020 Jun 1;66(6):794-801. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa091. Clin Chem. 2020. PMID: 32246822 Free PMC article.
-
True or false: what are the factors that influence COVID-19 diagnosis by RT-qPCR?Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022 Feb;22(2):157-167. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2022.2037425. Epub 2022 Feb 21. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35130461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical composition, transmission and diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2.Biosci Rep. 2021 Aug 27;41(8):BSR20211238. doi: 10.1042/BSR20211238. Biosci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34291285 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of nucleic acid extraction methods for rapid detection in pandemic situations or diseases with high prevalence.J Pharm Anal. 2023 Dec;13(12):1577-1579. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.08.005. Epub 2023 Aug 12. J Pharm Anal. 2023. PMID: 38223451 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy Validation of SARS-CoV-2-Inactivation and Viral Genome Stability in Saliva by a Guanidine Hydrochloride and Surfactant-Based Virus Lysis/Transport Buffer.Viruses. 2023 Feb 11;15(2):509. doi: 10.3390/v15020509. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851723 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Amplification-Free Quantitative Detection of Viral RNA in Nasopharyngeal Swab Samples Using a Compact Electrochemical Rapid Test Device.Anal Chem. 2025 Jun 10;97(22):11863-11873. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01605. Epub 2025 May 30. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40443387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. 2021. https://covid19.who.int/table .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
