A systematic review of COVID-19 transport policies and mitigation strategies around the globe
- PMID: 35873107
- PMCID: PMC9289094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trip.2022.100653
A systematic review of COVID-19 transport policies and mitigation strategies around the globe
Abstract
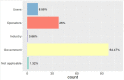
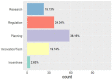
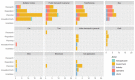
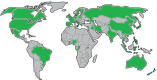
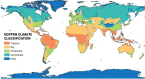
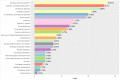
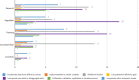
This paper reports a Scopus-based systematic literature review of a wide variety of transportation policies and mitigation strategies that have been conducted around the world to minimize COVID-19 contagion risk in transportation systems. The review offers a representative coverage of countries across all continents of the planet, as well as among representative climate regions - as weather is an important factor to consider. The readership interested in policies and mitigation strategies is expected to involve a wide range of actors, each involving a particular application context; hence, the literature is also characterized by key attributes such as: transportation mode; actor (users, operators, government, industry); jurisdiction (national, provincial, city, neighborhood); and area of application (planning, regulation, operations, research, incentives). An in-depth analysis of the surveyed literature is then reported, focusing first on condensing the literature into 151 distinct policies and strategies, which are subsequently categorized into 25 broad categories that are discussed at length. The compendium and discussion of strategies and policies reported not only provide comprehensive guidelines to inform various courses of action for decision-makers, planners, and social communicators, but also emphasize on future work and the potential of some of these strategies to be the precursors of meaningful, more sustainable behavioral changes in future mobility patterns.
Keywords: COVID-19; Policies; Risks; SARS-CoV-2; Strategies; Transportation.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Aghaei Chadegani A., Salehi H., Md Yunus M.M., Farhadi H., Fooladi M., Farhadi M., Ale Ebrahim N. A comparison between two main academic literature collections: web of science and scopus databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013;9 doi: 10.5539/ASS.V9N5P18. - DOI
-
- Amit S., Kafy A.A. A content-based analysis to identify the influence of COVID-19 on sharing economy activities. Spat. Inf. Res. 2022;30:321–333. doi: 10.1007/S41324-022-00433-W/TABLES/5. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
