Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Antivirulence Strategies to Combat Its Drug Resistance
- PMID: 35873152
- PMCID: PMC9299443
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.926758
Virulence Factors of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Antivirulence Strategies to Combat Its Drug Resistance
Abstract
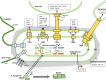
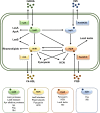
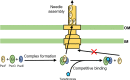
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is an opportunistic pathogen causing nosocomial infections in severely ill and immunocompromised patients. Ubiquitously disseminated in the environment, especially in hospitals, it has become a major threat to human health due to the constant emergence of drug-resistant strains. Multiple resistance mechanisms are exploited by P. aeruginosa, which usually result in chronic infections difficult to eradicate. Diverse virulence factors responsible for bacterial adhesion and colonization, host immune suppression, and immune escape, play important roles in the pathogenic process of P. aeruginosa. As such, antivirulence treatment that aims at reducing virulence while sparing the bacterium for its eventual elimination by the immune system, or combination therapies, has significant advantages over traditional antibiotic therapy, as the former imposes minimal selective pressure on P. aeruginosa, thus less likely to induce drug resistance. In this review, we will discuss the virulence factors of P. aeruginosa, their pathogenic roles, and recent advances in antivirulence drug discovery for the treatment of P. aeruginosa infections.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; antibiotic resistance; antivirulence strategies; infection; virulence factors.
Copyright © 2022 Liao, Huang, Wang, Yao and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aldrovandi M., Banthiya S., Meckelmann S., Zhou Y., Kuhn H. (2018). Specific Oxygenation of Plasma Membrane Phospholipids by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Lipoxygenase Induces Structural and Functional Alterations in Mammalian Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863 (2), 152–164. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.11.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ali S. O., Yu X. Q., Robbie G. J., Wu Y., Shoemaker K., Yu L., et al. (2019). Phase 1 Study of MEDI3902, an Investigational Anti-Pseudomonas Aeruginosa PcrV and Psl Bispecific Human Monoclonal Antibody, in Healthy Adults. Clin. Microbiol. Infect 25 (5), 629.e621–629.e626. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.08.004 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

