Advancing Key Gaps in the Knowledge of Plasmodium vivax Cryptic Infections Using Humanized Mouse Models and Organs-on-Chips
- PMID: 35873153
- PMCID: PMC9302440
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.920204
Advancing Key Gaps in the Knowledge of Plasmodium vivax Cryptic Infections Using Humanized Mouse Models and Organs-on-Chips
Abstract
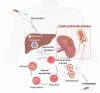
Plasmodium vivax is the most widely distributed human malaria parasite representing 36.3% of disease burden in the South-East Asia region and the most predominant species in the region of the Americas. Recent estimates indicate that 3.3 billion of people are under risk of infection with circa 7 million clinical cases reported each year. This burden is certainly underestimated as the vast majority of chronic infections are asymptomatic. For centuries, it has been widely accepted that the only source of cryptic parasites is the liver dormant stages known as hypnozoites. However, recent evidence indicates that niches outside the liver, in particular in the spleen and the bone marrow, can represent a major source of cryptic chronic erythrocytic infections. The origin of such chronic infections is highly controversial as many key knowledge gaps remain unanswered. Yet, as parasites in these niches seem to be sheltered from immune response and antimalarial drugs, research on this area should be reinforced if elimination of malaria is to be achieved. Due to ethical and technical considerations, working with the liver, bone marrow and spleen from natural infections is very difficult. Recent advances in the development of humanized mouse models and organs-on-a-chip models, offer novel technological frontiers to study human diseases, vaccine validation and drug discovery. Here, we review current data of these frontier technologies in malaria, highlighting major challenges ahead to study P. vivax cryptic niches, which perpetuate transmission and burden.
Keywords: Key gaps in the knowledge; Plasmodium vivax; humanized mouse; models; organs-on-a-chip.
Copyright © 2022 Aparici Herraiz, Caires, Castillo-Fernández, Sima, Méndez-Mora, Risueño, Sattabongkot, Roobsoong, Hernández-Machado, Fernandez-Becerra, Barrias and del Portillo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cryptic erythrocytic infections in Plasmodium vivax, another challenge to its elimination.Parasitol Int. 2022 Apr;87:102527. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2021.102527. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Parasitol Int. 2022. PMID: 34896615
-
Key gaps in the knowledge of Plasmodium vivax, a neglected human malaria parasite.Lancet Infect Dis. 2009 Sep;9(9):555-66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70177-X. Lancet Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19695492 Review.
-
Plasmodium vivax - How hidden reservoirs hinder global malaria elimination.Parasitol Int. 2022 Apr;87:102526. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2021.102526. Epub 2021 Dec 8. Parasitol Int. 2022. PMID: 34896312 Review.
-
Plasmodium vivax pre-erythrocytic vaccines.Parasitol Int. 2021 Oct;84:102411. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2021.102411. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Parasitol Int. 2021. PMID: 34166786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasmodium vivax liver stage development and hypnozoite persistence in human liver-chimeric mice.Cell Host Microbe. 2015 Apr 8;17(4):526-35. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Mar 19. Cell Host Microbe. 2015. PMID: 25800544 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Summary report of the 1st MOVE symposium in Málaga from 24-27th October 2023 - Foster the European mobility for young scientists in extracellular vesicles research.Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024 Feb 26;5(1):95-113. doi: 10.20517/evcna.2024.09. eCollection 2024. Extracell Vesicles Circ Nucl Acids. 2024. PMID: 39698417 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Guidelines for the purification and characterization of extracellular vesicles of parasites.J Extracell Biol. 2023 Oct 19;2(10):e117. doi: 10.1002/jex2.117. eCollection 2023 Oct. J Extracell Biol. 2023. PMID: 38939734 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming the Niche: The Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 17;25(8):4430. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084430. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38674015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Putative Contribution of 8-Aminoquinolines to Preventing Recrudescence of Malaria.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023 May 15;8(5):278. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed8050278. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37235326 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Murine Models in Determining In Vivo Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Efficacy in Antimalarial Drug Discovery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;18(3):424. doi: 10.3390/ph18030424. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akkina R., Allam A., Balazs A. B., Blankson J. N., Burnett J. C., Casares S., et al. . (2016). Improvements and Limitations of Humanized Mouse Models for HIV Research: NIH/NIAID "Meet the Experts" 2015 Workshop Summary. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 32 (2), 109–119. doi: 10.1089/AID.2015.0258 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

