Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Infection Activates the NOD1 Signaling Pathway to Modulate Inflammation
- PMID: 35873172
- PMCID: PMC9304885
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.927840
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Infection Activates the NOD1 Signaling Pathway to Modulate Inflammation
Abstract
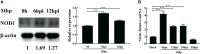
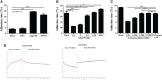
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae is a highly contagious pathogen causing porcine enzootic pneumonia, which elicits prolonged inflammatory response modulated by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). Although significant advances have been achieved in understanding the Toll-Like receptors that recognize M. hyopneumoniae, the role of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain 1 (NOD1) in M. hyopneumoniae infected cells remains poorly understood. This study revealed that M. hyopneumoniae activates the NOD1-RIP2 pathway and is co-localized with host NOD1 during infection. siRNA knockdown of NOD1 significantly impaired the TRIF and MYD88 pathway and blocked the activation of TNF-α. In contrast, NOD1 overexpression significantly suppressed M. hyopneumoniae proliferation. Furthermore, we for the first time investigated the interaction between M. hyopneumoniae mhp390 and NOD1 receptor, and the results suggested that mhp390 and NOD1 are possibly involved in the recognition of M. hyopneumoniae. These findings may improve our understanding of the interaction between PRRs and M. hyopneumoniae and the function of NOD1 in host defense against M. hyopneumoniae infection.
Keywords: Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae; NOD1; inflammation; interaction.; mhp390.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Jiang, Yang, Song, Yuan, Liu, Gao, Zhou, Guo, Li, Sun and Tian.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Surface proteins mhp390 (P68) contributes to cilium adherence and mediates inflammation and apoptosis in Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.Microb Pathog. 2019 Jan;126:92-100. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.10.035. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 30385395
-
Regulatory functional role of NLRP3 inflammasome during Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection in swine.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad216. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad216. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 37351955 Free PMC article.
-
[Interaction between Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and host-a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020 Sep 25;36(9):1741-1753. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200050. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 33164453 Review. Chinese.
-
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Inhibits Porcine Beta-Defensin 2 Production by Blocking the Unfolded Protein Response To Facilitate Epithelial Adhesion and Infection.Infect Immun. 2020 Jun 22;88(7):e00164-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00164-20. Print 2020 Jun 22. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32312764 Free PMC article.
-
[Advances in innate immune responses induced by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023 Dec 25;39(12):4773-4783. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.230504. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 38147980 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on Immune Evasion of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.Microorganisms. 2024 Jul 16;12(7):1439. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071439. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of SepF in Streptococcus suis involving cell division.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Mar 31;25(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03919-3. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40165076 Free PMC article.
-
Mesomycoplasma hyopneumoniae lipoprotein Mhp390 serves as a plasminogen receptor mediating extracellular matrix degradation and respiratory epithelial cells injury.Vet Res. 2025 Jun 21;56(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01551-7. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40544247 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics Reveals the Response Mechanism of Embryonic Bovine Lung Cells to Mycoplasma bovis Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 19;26(2):823. doi: 10.3390/ijms26020823. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39859536 Free PMC article.
-
A Recombinant Chimera Vaccine Composed of LTB and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae Antigens P97R1, mhp390 and P46 Elicits Cellular Immunologic Response in Mice.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;11(8):1291. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11081291. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bai F., Ni B., Liu M., Feng Z., Xiong Q., Xiao S., et al. . (2013). Mycoplasma Hyopneumoniae-Derived Lipid-Associated Membrane Proteins Induce Apoptosis in Porcine Alveolar Macrophage via Increasing Nitric Oxide Production, Oxidative Stress, and Caspase-3 Activation. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 155 (3), 155–161. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2013.07.004 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

