An updated global atmospheric paleo-reanalysis covering the last 400 years
- PMID: 35873191
- PMCID: PMC9292829
- DOI: 10.1002/gdj3.121
An updated global atmospheric paleo-reanalysis covering the last 400 years
Abstract
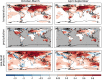
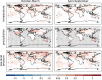
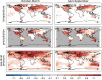
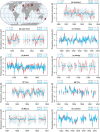
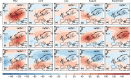
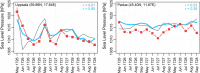
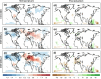
Data assimilation techniques are becoming increasingly popular for climate reconstruction. They benefit from estimating past climate states from both observation information and from model simulations. The first monthly global paleo-reanalysis (EKF400) was generated over the 1600 and 2005 time period, and it provides estimates of several atmospheric fields. Here we present a new, considerably improved version of EKF400 (EKF400v2). EKF400v2 uses atmospheric-only general circulation model simulations with a greatly extended observational network of early instrumental temperature and pressure data, documentary evidences and tree-ring width and density proxy records. Furthermore, new observation types such as monthly precipitation amounts, number of wet days and coral proxy records were also included in the assimilation. In the version 2 system, the assimilation process has undergone methodological improvements such as the background-error covariance matrix is estimated with a blending technique of a time-dependent and a climatological covariance matrices. In general, the applied modifications resulted in enhanced reconstruction skill compared to version 1, especially in precipitation, sea-level pressure and other variables beside the mostly assimilated temperature data, which already had high quality in the previous version. Additionally, two case studies are presented to demonstrate the applicability of EKF400v2 to analyse past climate variations and extreme events, as well as to investigate large-scale climate dynamics.
Keywords: climate reconstruction; ensemble Kalman fitting; paleoclimate data assimilation.
© 2021 The Authors. Geoscience Data Journal published by Royal Meteorological Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Alcoforado, M.J. , Vaquero, J. , Trigo, R. & Taborda, J. (2012) Early Portuguese meteorological measurements (18th century). Climate of the Past, 8, 353–371. 10.5194/cp-8-353-2012 - DOI
-
- Allan, R. & Ansell, T. (2006) A new globally complete monthly historical gridded mean sea level pressure dataset (HadSLP2): 1850–2004. Journal of Climate, 19, 5816–5842. 10.1175/JCLI3937.1 - DOI
-
- Aono, Y. & Kazui, K. (2008) Phenological data series of cherry tree owering in Kyoto, Japan, and its application to reconstruction of springtime temperatures since the 9th century. International Journal of Climatology, 28, 905–914. Wiley Online Library. 10.1002/joc.1594 - DOI
-
- Aono, Y. & Tani, A. (2014) Autumn temperature deduced from historical records of autumn tints phenology of maple tree in Kyoto, Japan. Climate in Biosphere (in Japanese with English abstract), 14, 18–28. 10.2480/cib.J-14-023 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
