Occupational Stress and Insomnia Symptoms Among Nurses During the Outbreak of COVID-19 in China: The Chain Mediating Effect of Perceived Organizational Support and Psychological Capital
- PMID: 35873265
- PMCID: PMC9300995
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.882385
Occupational Stress and Insomnia Symptoms Among Nurses During the Outbreak of COVID-19 in China: The Chain Mediating Effect of Perceived Organizational Support and Psychological Capital
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Occupational Stress and Insomnia Symptoms Among Nurses During the Outbreak of COVID-19 in China: The Chain Mediating Effect of Perceived Organizational Support and Psychological Capital.Front Psychiatry. 2024 May 24;15:1430791. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1430791. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38855636 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Nurses play an important role in medical and health services and insomnia symptoms were relatively high among nurses, especially during the epidemic of 2019 coronavirus disease. Insomnia not only damages the physical and mental health of the individual, but also reduces the efficiency of their work and the quality of care, ultimately impacting on patient care.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to explore the role of perceived organizational support and psychological capital in the relationship between occupational stress and insomnia among Chinese nurses.
Methods: A cross-sectional study has been carried out in a tertiary grade A hospital in Shandong Province, China from March 2021 to May 2021. The self-administered questionnaires were distributed to 810 nurses, which including Chinese Effort-Reward Imbalance Scale, Athens Insomnia Scale, Perceived Organizational Support Questionnaire, Chinese Psychological Capital Questionnaire, gender, age, education level and other demographic characteristics. Effective respondents were 658 (81.2%). Descriptive analysis, independent-samples t-test, one-way analysis of variance, Pearson correlation analyses, ordinary least-squares regression and the bootstrap method were used for data analysis.
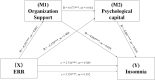
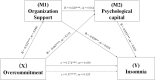
Results: The prevalence of insomnia symptoms in this study was found to be 57.3%. There were significant differences in insomnia symptoms in weekly working hours (t = -2.027, P = 0.043), with chronic disease (t = -2.825, P = 0.005), negative life events (t = -5.340, P < 0.001), departments (F = 3.077, P = 0.006) and position (t = 2.322, P = 0.021) among nurses. Overall, the serial-multiple mediations of perceived organizational support and psychological capital in the relationship between occupational stress and insomnia were found to be statistically significant.
Conclusions: The prevalence of insomnia symptoms was comparatively high among Chinese nurses, and occupational stress had direct negative influence on it. Perceived organizational support and psychological capital acted as chained mediating factor could partially relieve insomnia symptoms related to occupational stress. Supportive working environment should be provided, and improving psychological capital levels to help nurses coping with insomnia symptoms.
Keywords: effort reward imbalance; insomnia symptoms; occupational stress; overcommitment; perceived organizational support; psychological capital.
Copyright © 2022 Du, Liu, Zhang, Shao, Hua, Li, Lang and Ni.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

