Two Faces of the Bi-O Bond: Photochemically and Thermally Induced Dehydrocoupling for Si-O Bond Formation
- PMID: 35873275
- PMCID: PMC9300068
- DOI: 10.1002/ejic.202100934
Two Faces of the Bi-O Bond: Photochemically and Thermally Induced Dehydrocoupling for Si-O Bond Formation
Abstract
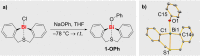
The diorgano(bismuth)alcoholate [Bi((C6H4CH2)2S)OPh] (1-OPh) has been synthesized and fully characterized. Stoichiometric reactions, UV/Vis spectroscopy, and (TD-)DFT calculations suggest its susceptibility to homolytic and heterolytic Bi-O bond cleavage under given reaction conditions. Using the dehydrocoupling of silanes with either TEMPO or phenol as model reactions, the catalytic competency of 1-OPh has been investigated (TEMPO=(tetramethyl-piperidin-1-yl)-oxyl). Different reaction pathways can deliberately be addressed by applying photochemical or thermal reaction conditions and by choosing radical or closed-shell substrates (TEMPO vs. phenol). Applied analytical techniques include NMR, UV/Vis, and EPR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis, and (TD)-DFT calculations.
Keywords: Bismuth; Catalysis; Chalcogens; Dehydrocoupling; Radical reactions.
© 2021 The Authors. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Well-Defined, Molecular Bismuth Compounds: Catalysts in Photochemically Induced Radical Dehydrocoupling Reactions.Chemistry. 2020 Nov 17;26(64):14551-14555. doi: 10.1002/chem.202002219. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 32573876 Free PMC article.
-
Bismuth Amides Mediate Facile and Highly Selective Pn-Pn Radical-Coupling Reactions (Pn=N, P, As).Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Mar 15;60(12):6441-6445. doi: 10.1002/anie.202015514. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 33315293 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, structure and density functional theory calculations of a novel photoluminescent trisarylborane-bismuth(III) complex.Luminescence. 2019 Nov;34(7):731-738. doi: 10.1002/bio.3667. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Luminescence. 2019. PMID: 31251465
-
Catalytic oxidative coupling promoted by bismuth TEMPOxide complexes.Chem Commun (Camb). 2018 Jan 23;54(8):916-919. doi: 10.1039/c7cc08402a. Chem Commun (Camb). 2018. PMID: 29318242
-
Sustainable preparation of aminosilane monomers, oligomers, and polymers through Si-N dehydrocoupling catalysis.Chem Commun (Camb). 2023 Mar 23;59(25):3665-3684. doi: 10.1039/d2cc07092h. Chem Commun (Camb). 2023. PMID: 36857645 Review.
Cited by
-
Organobismuth Compounds as Aryl Radical Precursors via Light-Driven Single-Electron Transfer.ACS Catal. 2024 Feb 16;14(4):2664-2670. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.3c05598. Epub 2024 Feb 6. ACS Catal. 2024. PMID: 40630115 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-Catalyzed Trifluoromethylation of C(sp2)-H Bonds under Light.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Nov 29;145(47):25538-25544. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c10333. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 37963280 Free PMC article.
-
Zwitterionic Heavier Pnictinidenes in Redox Catalysis.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Aug 18;64(34):e202505697. doi: 10.1002/anie.202505697. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40531378 Free PMC article.
-
Insertion of CO2 and CS2 into Bi-N bonds enables catalyzed CH-activation and light-induced bismuthinidene transfer.Chem Sci. 2023 Apr 28;14(19):5214-5219. doi: 10.1039/d3sc01635h. eCollection 2023 May 17. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37206406 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
