The Hepatoprotective Effect of Leonurine Hydrochloride Against Alcoholic Liver Disease Based on Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis
- PMID: 35873419
- PMCID: PMC9301321
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.904557
The Hepatoprotective Effect of Leonurine Hydrochloride Against Alcoholic Liver Disease Based on Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis
Abstract
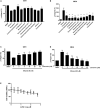
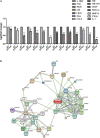
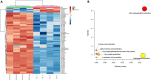
Excessive alcohol consumption can eventually progress to alcoholic liver disease (ALD). The underlying mechanism of ALD toxicity is primarily associated with oxidative damage. Many alkaloids have been reported to possess potential antioxidative efficacy, while the mechanism of their hepatoprotective activity against ALD is still not clear. In this study, eight alkaloids were selected from a monomer library of Traditional Chinese Medicine and evaluated for their antioxidant activity against ALD by the evaluation of Glutathione (GSH) and Malondialdehyde (MDA). The result suggested that Leonurine hydrochloride (LH) was a potent antioxidant that could reduce alcoholic liver damage. To further investigate the underlying mechanism of LH against ALD, the molecular pathway induced by LH was identified by RNA-seq analyses. Transcriptome data revealed the principal mechanism for the protective effect of LH against ALD might be attributed to the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) of PI3K-AKT, AMPK, and HIF-1 signaling pathways involved in the lipid metabolism. Given the hepatoprotective mechanism of LH is involved in lipid metabolism, the lipid metabolism induced by LH was further analyzed by UHPLC-MS/MS. Metabolome analysis indicated that LH significantly regulated glycerophospholipid metabolism including phosphatidylcholine, 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, phosphatidylethanolamine and 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine in the liver. Overall, this study revealed that the hepatoprotective mechanism of LH against alcoholic liver damage might be associated with the genes involved in glycerophospholipid metabolism.
Keywords: alcoholic liver disease; alkaloids; antioxidant; hepatoprotective; leonurine hydrochloride.
Copyright © 2022 Wu, Liu, Chen, Zhou, Liu, Yang, Xu and Gong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel hepatoprotective role of Leonurine hydrochloride against experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis mediated via AMPK/SREBP1 signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Feb;110:571-581. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.003. Epub 2018 Dec 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30537674
-
Multi-omics integration reveals the hepatoprotective mechanisms of ursolic acid intake against chronic alcohol consumption.Eur J Nutr. 2022 Feb;61(1):115-126. doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02632-x. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Eur J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 34215920
-
Hepatoprotective effects of peach gum polysaccharides against alcoholic liver injury: moderation of oxidative stress and promotion of lipid metabolism.Front Nutr. 2024 Jan 11;10:1325450. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1325450. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38283909 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Mechanism of Edible Food Plants against Alcoholic Liver Disease with Special Mention to Polyphenolic Compounds.Nutrients. 2021 May 11;13(5):1612. doi: 10.3390/nu13051612. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34064981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
Cited by
-
The enhancing effects of selenomethionine on harmine in attenuating pathological cardiac hypertrophy via glycolysis metabolism.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Oct;28(19):e70124. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70124. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39351650 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review of leonurine: harnessing its therapeutic potential for chronic diseases.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 9. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04087-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40202674 Review.
-
Volvariella volvacea Polypeptide Mitigates Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury: A Multi-Omics Study.Foods. 2025 Apr 29;14(9):1557. doi: 10.3390/foods14091557. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361639 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Xuanhuang Pill in protecting against alcohol liver disease using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry and network pharmacology.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Apr 4;14:1175985. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1175985. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37082132 Free PMC article.
-
Leonurine: a comprehensive review of pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and toxicology.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 19;15:1428406. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1428406. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39101131 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee EY, Kim SH, Chang SN, Lee J-H, Hwang BS, Woo J-T, et al. Efficacy of polymethoxylated flavonoids from Citrus depressa extract on alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. (2019) 24:907–14.
-
- Mohanty SR, LaBrecque DR, Mitros FA, Layden TJ. Liver transplantation for disulfiram-induced fulminant hepatic failure. J Clin Gastroenterol. (2004) 38:292–5. - PubMed
-
- Soyka M, Rösner S. Emerging drugs to treat alcoholism. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. (2010) 15:695–711. - PubMed
-
- Lieber CS. Alcoholic fatty liver: its pathogenesis and mechanism of progression to inflammation and fibrosis. Alcohol. (2004) 34:9–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

