MiR-199 Aggravates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Targeting TAF9b
- PMID: 35873641
- PMCID: PMC9307339
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4364779
MiR-199 Aggravates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Targeting TAF9b
Retraction in
-
Retracted: MiR-199 Aggravates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Targeting TAF9b.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9890380. doi: 10.1155/2023/9890380. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 38125152 Free PMC article.
Abstract
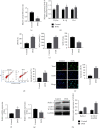
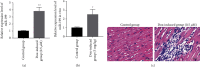
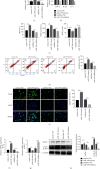
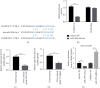
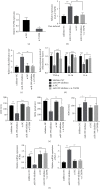
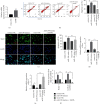
The clinical application of doxorubicin (DOX) is limited because of its cardiotoxicity. However, the pathogenic mechanism of DOX and the role of miRNA in DOX-induced cardiotoxicity remain to be further studied. This study aimed to investigate the role of miR-199 in DOX-mediated cardiotoxicity. A mouse model of myocardial cell injury induced by DOX was established. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression changes of miR-199 and TATA-binding protein associated factor 9B (TAF9b) in DOX-induced cardiac injury. Cell apoptosis was detected by TUNEL staining and flow cytometry. The expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins, namely, Bax and Bcl-2, were detected by qPCR. The expression of Beclin-1 and LC3b was detected by western blotting. The binding effect of miR-199 with TAF9b was verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. In this study, overexpression of miR-199 could promote cardiotoxicity. Inhibition of miR-199 could alleviate DOX-mediated myocardial injury. Further studies showed that miR-199 targeted TAF9b. Moreover, miR-199 promoted apoptosis of myocardial cells and aggravated autophagy. Furthermore, we demonstrated that TAF9B knockdown reversed the myocardial protective effect of miR-199 inhibitors. Therefore, miR-199 promoted DOX-mediated cardiotoxicity by targeting TAF9b, thereby aggravating apoptosis and regulating autophagy.
Copyright © 2022 Yangsheng Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Schilt Y., Berman T., Wei X., Barenholz Y., Raviv U. Using solution X-ray scattering to determine the high-resolution structure and morphology of PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin nanodrugs. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)—General Subjects . 2016;1860 doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.09.012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

