Multi-Coil MRI Reconstruction Challenge-Assessing Brain MRI Reconstruction Models and Their Generalizability to Varying Coil Configurations
- PMID: 35873808
- PMCID: PMC9298878
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.919186
Multi-Coil MRI Reconstruction Challenge-Assessing Brain MRI Reconstruction Models and Their Generalizability to Varying Coil Configurations
Abstract
Deep-learning-based brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction methods have the potential to accelerate the MRI acquisition process. Nevertheless, the scientific community lacks appropriate benchmarks to assess the MRI reconstruction quality of high-resolution brain images, and evaluate how these proposed algorithms will behave in the presence of small, but expected data distribution shifts. The multi-coil MRI (MC-MRI) reconstruction challenge provides a benchmark that aims at addressing these issues, using a large dataset of high-resolution, three-dimensional, T1-weighted MRI scans. The challenge has two primary goals: (1) to compare different MRI reconstruction models on this dataset and (2) to assess the generalizability of these models to data acquired with a different number of receiver coils. In this paper, we describe the challenge experimental design and summarize the results of a set of baseline and state-of-the-art brain MRI reconstruction models. We provide relevant comparative information on the current MRI reconstruction state-of-the-art and highlight the challenges of obtaining generalizable models that are required prior to broader clinical adoption. The MC-MRI benchmark data, evaluation code, and current challenge leaderboard are publicly available. They provide an objective performance assessment for future developments in the field of brain MRI reconstruction.
Keywords: benchmark; brain imaging; image reconstruction; inverse problems; machine learning; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Copyright © 2022 Beauferris, Teuwen, Karkalousos, Moriakov, Caan, Yiasemis, Rodrigues, Lopes, Pedrini, Rittner, Dannecker, Studenyak, Gröger, Vyas, Faghih-Roohi, Kumar Jethi, Chandra Raju, Sivaprakasam, Lasby, Nogovitsyn, Loos, Frayne and Souza.
Conflict of interest statement
MC is a shareholder of Nico.lab International Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
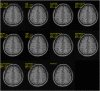
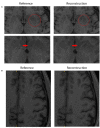
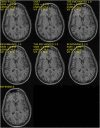
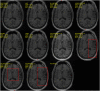
References
-
- Dedmari M. A., Conjeti S., Estrada S., Ehses P., Stöcker T., Reuter M. (2018). “Complex fully convolutional neural networks for MR image reconstruction,” in International Workshop on Machine Learning for Medical Image Reconstruction (Granada: ), 30–38. 10.1007/978-3-030-00129-2_4 - DOI
-
- Duan J., Schlemper J., Qin C., Ouyang C., Bai W., Biffi C., et al. (2019). “VSNet: variable splitting network for accelerated parallel MRI reconstruction,” in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (Shenzhen: ), 713–722. 10.1007/978-3-030-32251-9_78 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

