Prevalence of Revision Adenoidectomy in a Tertiary Otorhinolaryngology Centre in Nigeria
- PMID: 35873876
- PMCID: PMC9302388
- DOI: 10.4103/jwas.jwas_61_22
Prevalence of Revision Adenoidectomy in a Tertiary Otorhinolaryngology Centre in Nigeria
Abstract
Introduction: Remnants or the regrowth of adenoid tissue after adenoidectomy may present with clinical symptoms that could warrant a revision surgery.
Aim and objectives: This study aims to determine the prevalence and risk factors of revision adenoidectomy in our centre.
Materials and methods: This is a retrospective case-control study conducted in a tertiary otorhinolaryngology centre over a 10-year period. Cases of revision adenoidectomies were identified and matched with controlled cases of single-stage adenoidectomies within the same period. All information was entered into the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25 and analysed using descriptive and cross-tabulation analysis.
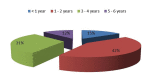
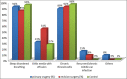
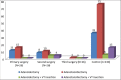
Results: A total of 1249 adenoidectomies were performed during the period of review with 26 being revision cases. The prevalence of revision adenoidectomy was found to be 2.1% with the mean interval between surgeries being 2.1 years. Age ≤ 2 years (odds ratio (OR) = 95.25, P < 0.0001), allergy (OR = 0.09, P < 0.0001), recurrent tonsillitis (OR = 0.79, P = 0.006), recurrent/chronic middle ear infections (OR = 7.5, P < 0.0001), and the primary surgeon being a junior registrar (OR = 11.5, P < 0.0001) were significantly associated with revision adenoidectomy. The performance of adenoidectomy without tonsillectomy also carries a significant odd (P = 0.04).
Conclusion: Revision adenoidectomy is low in our setting. Young age at primary surgery, the presence of allergy, surgeon's designation, the extent of surgery, and recurrent middle ear and tonsil infections are factors associated with revision adenoidectomy. These should be considered in risk stratification and surgery planning.
Keywords: Adenoid; Some risk factors predispose to having revision adenoidectomy. Appropriate surgical risk stratification and planning may reduce the need for revision adenoidectomy.; adenoid regrowth; revision adenoidectomy; risk factors.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of the West African College of Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ingram DG, Friedman NR. Toward adenotonsillectomy in children: A review for the general pediatrician. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169:1155–61. - PubMed
-
- Babakurban TS, Aydın E. Adenoidectomy: Current approaches and review of the literature. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2016;26:181–90. - PubMed
-
- Ramos SD, Mukerji S, Pine HS. Tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2013;60:793–807. - PubMed
-
- Lee CH, Chang WH, Ko JY, Yeh TH, Hsu WC, Kang KT. Revision adenoidectomy in children: A population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2017;274:3627–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources