Rose Rosette Disease Resistance Loci Detected in Two Interconnected Tetraploid Garden Rose Populations
- PMID: 35873988
- PMCID: PMC9302375
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.916231
Rose Rosette Disease Resistance Loci Detected in Two Interconnected Tetraploid Garden Rose Populations
Abstract
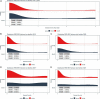
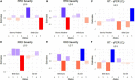
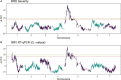
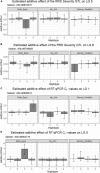
Rose rosette disease (RRD), caused by the Rose rosette emaravirus (RRV), is a major threat to the garden rose industry in the United States. There has been limited work on the genetics of host plant resistance to RRV. Two interconnected tetraploid garden rose F1 biparental mapping populations were created to develop high-quality tetraploid rose linkage maps that allowed the discovery of RRD resistance quantitative trait loci (QTLs) on linkage groups (LGs) 5, 6, and 7. These QTLs individually accounted for around 18-40% of the phenotypic variance. The locus with the greatest effect on partial resistance was found in LG 5. Most individuals with the LG 5 QTL were in the simplex configuration; however, two individuals were duplex (likely due to double reduction). Identification of resistant individuals and regions of interest can help the development of diagnostic markers for marker-assisted selection in a breeding program.
Keywords: Phyllocoptes fructiphilus; Rosa; Rose rosette emaravirus; emaravirus; eriophyid mite; quantitative trait loci; rose rosette virus.
Copyright © 2022 Lau, Young, Collins, Windham, Klein, Byrne and Riera-Lizarazu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Allington W. B., Staples R., Viehmeyer G. (1968). Transmission of Rose Rosette Virus by the Eriophyid Mite Phyllocoptes fructiphilus. J. Econ. Entomol. 61 1137–1140. 10.1093/jee/61.5.1137 - DOI
-
- Amrine J. W., Jr., Hindal D. F., Stasny T. A., Williams R. L., Coffman C. C. (1988). Transmission of the rose rosette disease agent to Rosa multiflora by Phyllocoptes fructiphilus (Acari: Eriophyidae). Entomol. News U.S.A. 99 239-252.
-
- Amrine J. W. (1996). “4.1.2 Phyllocoptes fructiphilus and biological control of multiflora rose,” in World Crop Pests Eriophyoid Mites Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control, eds Lindquist E. E., Sabelis M. W., Bruin J. (Amsterdam: Elsevier; ), 741–749. 10.1016/S1572-4379(96)80050-9 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

