Design and Development of a Scale for Evaluating the Acceptance of Social Robotics for Older People: The Robot Era Inventory
- PMID: 35874107
- PMCID: PMC9302437
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbot.2022.883106
Design and Development of a Scale for Evaluating the Acceptance of Social Robotics for Older People: The Robot Era Inventory
Abstract
Introduction: Nowadays, several robots have been developed to provide not only companionship to older adults, but also to cooperate with them during health and lifestyle activities. Despite the undeniable wealth of socially assistive robots (SARs), there is an increasing need to customize the tools used for measuring their acceptance in real-life applications.
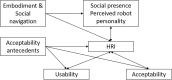
Methods: Within the Robot-Era project, a scale was developed to understand the degree of acceptance of the robotic platform. A preliminary test with 21 participants was performed to assess the statistical validity of the Robot-Era Inventory (REI) scales.
Results: Based on the criteria observed in the literature, 41 items were developed and grouped in different scales (perceived robot personality, human-robot interaction, perceived benefit, ease of use, and perceived usefulness). The reliability of the Robot-Era Inventory scale was analyzed with Cronbach's alpha, with a mean value of 0.79 (range = 0.61-0.91). Furthermore, the preliminary validity of this scale has been tested by using the correlation analysis with a gold standard, the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) model.
Discussion: The Robot-Era Inventory represents a useful tool that can be easily personalized and included in the assessment of any SARs that cooperate with older people in real environment applications.
Keywords: embodiment; older people; scale validity; social assistive robotics; social presence; technology acceptance; usability.
Copyright © 2022 Bevilacqua, Di Rosa, Riccardi, Pelliccioni, Lattanzio, Felici, Margaritini, Amabili and Maranesi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Al-Youssef I. Y. (2015). Student. Acceptance. and. Use. of. Internet-Based. Distance. Education. in. Saudi. Electronic. University. (SEU):. A. Mixed. Method. Study (Doctoral dissertation, Ohio University). OhioLINK Electronic Theses and Dissertations Center. Available online atg: http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=ohiou1424175265
-
- Bartneck C., Forlizzi J. (2004). A design-centred framework for social human-robot interaction. Proc.. Ro-Man. 591–594. 10.1109/ROMAN.2004.1374827 - DOI
-
- Bartneck C., Kulić D., Croft E. (2009). Measurement Instruments for the Anthropomorphism, Animacy, Likeability, Perceived Intelligence, and Perceived Safety of Robots. Int.. J.. Soc.. Robot. 1, 71–81. 10.1007/s12369-008-0001-3 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous