Primary Brainstem Lymphoma: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 35874127
- PMCID: PMC9299248
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.829048
Primary Brainstem Lymphoma: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
Background: Primary brainstem lymphoma (PBSL) is rare and malignant. An understanding of this disease is lacking. We aimed to characterize clinical features, estimate survival, and explore survival-related factors of PBSL.
Methods: Patients with a histological diagnosis of primary lymphoma in the brainstem (C71.7) from 1975 to 2016 were retrieved from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) program. Log-rank tests and univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard analyses were used to identify survival-related factors.
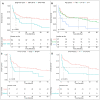
Results: PBSL constituted 2.7% of brainstem malignancies. The median age of the PBSL patients was 59.5 years. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (n = 49, 84.5%) was the most prevalent histology among the 58 cases with reported specific lymphoma subtype. The majority of PBSLs were localized (n = 46, 52.3%), at low Ann Arbor Stage (I/II, n = 63, 70.5%), and presented as a single primary (n = 71, 80.7%). Chemotherapy was applied in 50 (56.8%) cases. Three-year overall survival (OS) and disease-specific survival (DSS) rates were 42.7% and 53.5%, respectively. Multivariate analyses showed that independent predictive/prognostic factors for OS were age (P = 0.004), tumor number (P = 0.029), and chemotherapy (P = 0.001); DSS-related factors only included age (P = 0.014) and chemotherapy (P = 0.008).
Conclusions: We estimated survival rates for PBSL patients. Factors associated with OS and DSS were also identified. Our findings addressed the importance of chemotherapy in treating PBSL patients.
Keywords: SEER; chemotherapy; primary brainstem lymphoma; surgery; survival.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Cen, Hu, Qiu, Xiao, Zhou, Ma and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The incidence and survival outcomes of patients with primary cardiac lymphoma: A SEER-based analysis.Hematol Oncol. 2020 Aug;38(3):334-343. doi: 10.1002/hon.2741. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32311106
-
Epidemiology and prognostic indicators in laryngeal lymphoma: A population-based analysis.Laryngoscope. 2018 Sep;128(9):2044-2049. doi: 10.1002/lary.27074. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Laryngoscope. 2018. PMID: 29392765
-
Primary lymphoma of bone: a population-based study of 2558 patients.Ther Adv Hematol. 2020 Sep 17;11:2040620720958538. doi: 10.1177/2040620720958538. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32994912 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and survival outcome of primary effusion lymphoma: A review of 105 patients.Hematol Oncol. 2017 Dec;35(4):878-883. doi: 10.1002/hon.2372. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27859456 Review.
-
[Primary gastric lymphoma].Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2004 Jul-Sep;24(3):238-62. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2004. PMID: 15483686 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Clinical impact and safety of brain biopsy in unexplained central nervous system disorders: a real-world cohort study.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2025 Apr;12(4):792-804. doi: 10.1002/acn3.70000. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39981762 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

