Lung Immune Prognostic Index Could Predict Metastasis in Patients With Osteosarcoma
- PMID: 35874141
- PMCID: PMC9304694
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.923427
Lung Immune Prognostic Index Could Predict Metastasis in Patients With Osteosarcoma
Abstract
Background: The lung immune prognostic index (LIPI), composed of serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and the derived neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (dNLR), is a novel prognostic factor of lung cancer. The prognostic effect of the LIPI has never been verified in osteosarcoma.
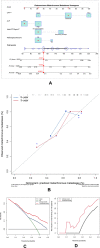
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the osteosarcoma patients with metachronous metastasis from January 2016 to January 2021 in West China Hospital. We collected and analyzed the clinical data and constructed the LIPI for osteosarcoma. The correlation between the LIPI and metastasis was analyzed according to the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression analysis with hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis were conducted to clarify the independent risk factors of metastasis. The nomogram model was established by R software, version 4.1.0.
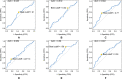
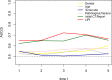
Results: The area under the curve (AUC) and best cutoff value were 0.535 and 91, 0.519, and 5.02, 0.594 and 2.77, 0.569 and 227.14, 0.59 and 158, and 0.607 and 2.05 for ALP, LMR, NLR, PLR, LDH, and dNLR, respectively. The LIPI was composed of LDH and dNLR and showed a larger AUC than other hematological factors in the time-dependent operator curve (t-ROC). In total, 184 patients, 42 (22.8%), 96 (52.2%), and 46 (25.0%) patients had LIPIs of good, moderate, and poor, respectively (P < 0.0001). Univariate analysis revealed that pathological fracture, the initial CT report of suspicious nodule, and the NLR, PLR, ALP, and the LIPI were significantly associated with metastasis, and multivariate analysis showed that the initial CT report of suspicious nodule and the PLR, ALP, and LIPI were dependent risk factors for metastasis. Metastatic predictive factors were selected and incorporated into the nomogram construction, including the LIPI, ALP, PLR, initial CT report, and pathological fracture. The C-index of our model was 0.71. According to the calibration plot, this predictive nomogram could accurately predict 3- and 5-year metachronous metastasis. Based on the result of decision curve and clinical impact curve, this predictive nomogram could also help patients obtain significant net benefits.
Conclusion: We first demonstrated the metastatic predictive effect of the LIPI on osteosarcoma. This LIPI-based model is useful for clinicians to predict metastasis in osteosarcoma patients and could help conduct timely intervention and facilitate personalized management of osteosarcoma patients.
Keywords: derived neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (dNLR); lactate dehydrogenase (LDH); lung immune prognostic index (LIPI); metastasis; osteosarcoma.
Copyright © 2022 He, Wang, Ye, Wang, Min, Luo, Zhou and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The application of lung immune prognostic index in predicting the prognosis of 302 STS patients.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 9;14:1460600. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1460600. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39314631 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of modified lung immune prognostic index in osteosarcoma patients.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 11;13:972352. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.972352. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36303539 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the immune-inflammatory indices for patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive and castration-resistant prostate cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):817. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12593-z. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38978000 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Markers of Survival in Epidermal Growth Factor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Single-Institution Analysis, Systematic Review, and Meta-analysis.Clin Lung Cancer. 2021 Sep;22(5):390-407. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 10. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33582072
-
The Predictive Value of Pretreatment Lactate Dehydrogenase and Derived Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors: A Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 18;12:791496. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.791496. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35924149 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Electrolyte prognosis scoring system can predict overall survival in patients with osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2024 Oct 9;14:1466912. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1466912. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39445057 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative lung immune prognostic index predicts survival in patients with pancreatic cancer undergoing radical resection.Front Surg. 2023 Jan 6;9:1002075. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1002075. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2023. PMID: 36684178 Free PMC article.
-
Association of lung immune prognostic index with overall survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients treated using chemotherapy.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Mar 3;22(7):1672-1679. doi: 10.7150/ijms.102404. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40093811 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Pre-Operative Lung Immune Prognostic Index Score Is a Prognostic Factor in Cases of Pathological T3 Renal Cell Carcinoma.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jun 7;32(6):335. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32060335. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40558278 Free PMC article.
-
The application of lung immune prognostic index in predicting the prognosis of 302 STS patients.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 9;14:1460600. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1460600. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39314631 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

