Experimental and Analytical Framework for "Mix-and-Read" Assays Based on Split Luciferase
- PMID: 35874239
- PMCID: PMC9301641
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02319
Experimental and Analytical Framework for "Mix-and-Read" Assays Based on Split Luciferase
Abstract
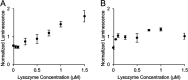
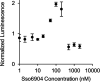
The use of immunodetection assays including the widely used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in applications such as point-of-care detection is often limited by the need for protein immobilization and multiple binding and washing steps. Here, we describe an experimental and analytical framework for the development of simple and modular "mix-and-read" enzymatic complementation assays based on split luciferase that enable sensitive detection and quantification of analytes in solution. In this assay, two engineered protein binders targeting nonoverlapping epitopes on the target analyte were each fused to nonactive fragments of luciferase to create biosensor probes. Binding proteins to two model targets, lysozyme and Sso6904, were isolated from a combinatorial library of Sso7d mutants using yeast surface display. In the presence of the analyte, probes were brought into close proximity, reconstituting enzymatic activity of luciferase and enabling detection of low picomolar concentrations of the analyte by chemiluminescence. Subsequently, we constructed an equilibrium binding model that relates binding affinities of the binding proteins for the target, assay parameters such as the concentrations of probes used, and assay performance (limit of detection and concentration range over which the target can be quantified). Overall, our experimental and analytical framework provides the foundation for the development of split luciferase assays for detection and quantification of various targets.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Yousefi M.; Dehghani S.; Nosrati R.; Zare H.; Evazalipour M.; Mosafer J.; Tehrani B. S.; Pasdar A.; Mokhtarzadeh A.; Ramezani M. Aptasensors as a New Sensing Technology Developed for the Detection of MUC1 Mucin: A Review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 1–19. 10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.015. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

