HSF-1: Guardian of the Proteome Through Integration of Longevity Signals to the Proteostatic Network
- PMID: 35874276
- PMCID: PMC9304931
- DOI: 10.3389/fragi.2022.861686
HSF-1: Guardian of the Proteome Through Integration of Longevity Signals to the Proteostatic Network
Abstract
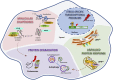
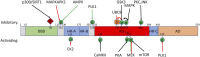
Discoveries made in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans revealed that aging is under genetic control. Since these transformative initial studies, C. elegans has become a premier model system for aging research. Critically, the genes, pathways, and processes that have fundamental roles in organismal aging are deeply conserved throughout evolution. This conservation has led to a wealth of knowledge regarding both the processes that influence aging and the identification of molecular and cellular hallmarks that play a causative role in the physiological decline of organisms. One key feature of age-associated decline is the failure of mechanisms that maintain proper function of the proteome (proteostasis). Here we highlight components of the proteostatic network that act to maintain the proteome and how this network integrates into major longevity signaling pathways. We focus in depth on the heat shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1), the central regulator of gene expression for proteins that maintain the cytosolic and nuclear proteomes, and a key effector of longevity signals.
Keywords: Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans); HSF-1 = heat-shock factor-1; aging; cell stress and aging; genetics; longevity; proteostasis.
Copyright © 2022 Lazaro-Pena, Ward, Yang, Strohm, Merrill, Soto and Samuelson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

