Ameliorative effects of Dictyota dichotoma on hepatotoxicity induced by gibberellic acid in albino rats
- PMID: 35874501
- PMCID: PMC9247131
- DOI: 10.1007/s43188-022-00122-8
Ameliorative effects of Dictyota dichotoma on hepatotoxicity induced by gibberellic acid in albino rats
Abstract
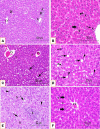
Gibberellic acid (GA3) is a natural plant growth regulator that is crucial for plant structural and functional development. We examined the alleviating capacity of brown algae (Dictyota dichotoma) on biochemical and molecular degenerative processes caused by sub-chronic exposure to gibberellic acid resulting in hepatic cell apoptosis. Adult male albino rats were divided into five equal groups: the first group received distilled water, the second group was treated with GA3, the third group was administered D. dichotoma extract suspended in 1% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), the fourth group was administered both GA3 and D. dichotoma simultaneously, and the fifth group received 1% CMC orally, 5 days per week for a total of 50 days. The results indicated that GA3 induced a significant increase in liver function parameters based on serum levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and albumin, which indicate hepatotoxicity. A marked increase in malondialdehyde (MDA) levels and a marked decrease in reduced glutathione (GSH), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) were observed as a result of induction of lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress. Histopathology revealed severely degenerated hepatocytes including cytoplasmic vacuolations and many apoptotic cells with weak Bcl2 expression. Similarly, there was a significant up-regulation of gene and protein expression levels for the pro-apoptotic markers, Caspase-3 and Bax, and an increase in pro-inflammatory marker levels, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) as well as C-reactive protein (CRP). The co-administration of D. dichotoma restored the disrupted biochemical, histopathological, molecular, and inflammatory changes resulting from GA3 toxicity. Our results confirm the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and hepatoprotective potential of D. dichotoma.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Brown algae; Gibberellic acid; Hepatotoxicity; Plant growth regulators.
© The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Korean Society of Toxicology 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Davies PJ. Plant hormones: biosynthesis, signal transduction, action! Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media; 2004.
-
- Bisht TS, Rawat L, Chakraborty B, Yadav V. A recent advances in use of plant growth regulators (pgrs) in fruit crops-a review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. 2018;7:1307–1336. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2018.705.159. - DOI
-
- Shi X, Jin F, Huang Y, Du X, Li C, Wang M, Shao H, Jin M, Wang J. Simultaneous determination of five plant growth regulators in fruits by modified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe (QuEChERS) extraction and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem. 2012;60:60–65. doi: 10.1021/jf204183d. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

