Short- and long-term effect of colorectal cancer targeting peptides conjugated to gold nanoparticles in rats' liver and colon after single exposure
- PMID: 35874503
- PMCID: PMC9247135
- DOI: 10.1007/s43188-021-00108-y
Short- and long-term effect of colorectal cancer targeting peptides conjugated to gold nanoparticles in rats' liver and colon after single exposure
Abstract
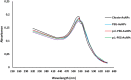
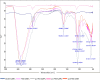
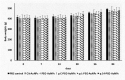
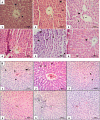
Peptides play important roles in the diagnosis, prognostic predictors, and treatment of various kinds of cancer. Peptides (p.C, p.L and p.14), derived from the phage display peptide libraries, specifically binds to colorectal cancer (CRC) cells in vitro. To allow tumor specificity and selectivity for in vivo diagnosis of CRC, biotinylated p.C, p.L and p.14 were conjugated to AuNPs (14 nm) via the biotin-streptavidin interaction. Male Wistar rats were intravenously injected with a single dose (100 µg/kg body weight) of AuNPs (citrate-AuNPs, PEG-AuNPs, p.C-PEG-, p.L-PEG- and p.14-PEG-AuNPs). Animals were monitored for behavioral changes, and sacrificed either 14 days or 84 days post-injection. Biochemical changes, oxidative stress, and histology of the liver and colon were assessed. No significant changes were noted in the rats injected with all the AuNPs, except p.L-PEG-AuNPs that caused significant toxicity (p < 0.05) 14 days post-exposure when compared to control group, as evidenced by increased relative liver weight, increased malondialdehyde levels and histological changes in the liver. These changes, however, returned to normalcy 84 days post-injection. It can be concluded, based on these findings, that p.L induced a transient toxicity in rats after a single intravenous injection, and can therefore be considered non-toxic long-term after a single exposure.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Diagnosis; Gold nanoparticles; Peptides; Polyethylene glycol.
© Korean Society of Toxicology 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare no conflict of interest with this work. This work is contained in the PhD thesis of Olusola B. Adewale at Nelson Mandela University, South Africa. Part of this work has been presented at the 14th International Conference of Nanosciences and Nanotechnologies, 4–7 July 2017, Thessaloniki, Greece, and LAUTECH NANO Conference, 22–24 October 2019, Ogbomoso, Nigeria.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Biochemical assessment of the neurotoxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with colorectal cancer-targeting peptides in a rat model.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021 Nov;40(11):1962-1973. doi: 10.1177/09603271211017611. Epub 2021 May 18. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34002645
-
Short- and long-term distribution and toxicity of gold nanoparticles in the rat after a single-dose intravenous administration.Nanomedicine. 2014 Nov;10(8):1757-66. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2014.06.005. Epub 2014 Jun 15. Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24941462
-
Biological activity of gold nanoparticles combined with the NFL-TBS.40-63 peptide, or with other cell penetrating peptides, on rat glioblastoma cells.Int J Pharm X. 2022 Sep 16;4:100129. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2022.100129. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2022. PMID: 36164551 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Polyethylene Glycol-Coated Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Inflammation In Vivo Using NF-κB Reporter Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 31;21(21):8158. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218158. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33142808 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of gene expression profiles in mice liver following intravenous injection of 4 and 100 nm-sized PEG-coated gold nanoparticles.Toxicol Lett. 2009 Dec 1;191(1):96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.08.010. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Toxicol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19695318
References
-
- American Cancer Society . Colorectal cancer facts and figures. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2014.
-
- American Cancer Society . Colorectal cancer facts and figures 2017–2019. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

