Lactobacillus paracasei X11 Ameliorates Hyperuricemia and Modulates Gut Microbiota in Mice
- PMID: 35874662
- PMCID: PMC9296831
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.940228
Lactobacillus paracasei X11 Ameliorates Hyperuricemia and Modulates Gut Microbiota in Mice
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Lactobacillus paracasei X11 ameliorates hyperuricemia and modulates gut microbiota in mice.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 6;15:1517021. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1517021. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39569193 Free PMC article.
Abstract
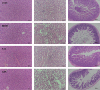
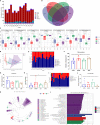
Hyperuricemia (HUA) is the presence of excessive uric acid (UA) in blood, which leads to an increased risk of chronic kidney disease and gout. Probiotics have the potential effect of alleviating HUA. The purpose of this study was to screen probiotics with UA-lowering activity and explore the underlying mechanism. The UA-lowering activity of 20 lactic acid bacteria strains was investigated in vitro, and the effect of candidate probiotics on UA metabolism was evaluated using the HUA Balb/c mouse model. The results showed that Lactobacillus paracasei X11 had excellent UA-lowering activity in vitro, which could degrade nucleotides and nucleosides completely within 30 min, and the degradation rates of purine and trioxypurine could reach 83.25% and 80.42%, respectively. In addition, oral administration of L. paracasei X11 could reduce serum UA by 52.45% and inhibit renal proinflammatory cytokine IL-1β by 50.69%, regulating adenosine deaminase (ADA), xanthine oxidase (XOD), and transporter expression (GLUT9, NPT1, and URAT1) to a normal level. Moreover, it could restore the ratio of Bacteroidetes to Firmicutes (Bac/Firm ratio) and showed a positive effect on the recovery of the intestinal microbiota. These findings provided fundamental information about the UA-lowering properties of probiotics, which suggested that L. paracasei X11 had the potential to be developed as a novel probiotic strain to ameliorate HUA.
Keywords: Lactobacillus paracasei X11; ameliorating; gut microbiota; hyperuricemia; uric acid-lowering.
Copyright © 2022 Cao, Liu, Hao, Bu, Tian, Wang and Yi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Host-derived Lactobacillus plantarum alleviates hyperuricemia by improving gut microbial community and hydrolase-mediated degradation of purine nucleosides.Elife. 2024 Nov 7;13:e100068. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100068. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39508089 Free PMC article.
-
Rosmarinic acid attenuates hyperuricemia via restoring hyperuricemia-induced renal and intestinal dysfunctions.Phytomedicine. 2025 Sep;145:157084. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157084. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40684489
-
Effect and Potential Mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum Q7 on Hyperuricemia in vitro and in vivo.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 6;9:954545. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.954545. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. Retraction in: Front Nutr. 2024 Nov 01;11:1517030. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1517030. PMID: 35873427 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The gut microbiota as a target to control hyperuricemia pathogenesis: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(14):3979-3989. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1874287. Epub 2021 Jan 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33480266 Review.
-
Elucidating the role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in hyperuricemia and gout: Insights and therapeutic strategies.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Oct 28;30(40):4404-4410. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i40.4404. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39494101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ameliorative Effect of Mannuronate Oligosaccharides on Hyperuricemic Mice via Promoting Uric Acid Excretion and Modulating Gut Microbiota.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 13;15(2):417. doi: 10.3390/nu15020417. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678288 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of traditional Chinese medicine lyophilized powder of Poecilobdella manillensis in the treatment of hyperuricemia.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Dec 26;12(36):6939-6943. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6939. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39726925 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperuricemia and its related diseases: mechanisms and advances in therapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Aug 28;9(1):212. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01916-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39191722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purine metabolism-associated key genes depict the immune landscape in gout patients.Discov Oncol. 2025 Feb 17;16(1):193. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01956-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39960566 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of a Probiotic Lacticaseibacillus paracasei MSMC39-1 on Kidney Damage in Aged Mice: Functional Foods Potential.Foods. 2025 May 25;14(11):1874. doi: 10.3390/foods14111874. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40509402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

