Hepatocyte-Conditional Knockout of Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein 4 Aggravated LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Injury via the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway
- PMID: 35874667
- PMCID: PMC9304715
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.901566
Hepatocyte-Conditional Knockout of Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein 4 Aggravated LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Injury via the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway
Abstract
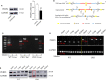
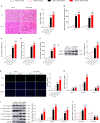
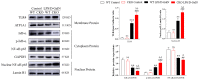
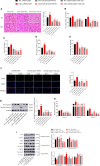
Acute liver injury (ALI) is a disease that seriously threatens human health and life, and a dysregulated inflammation response is one of the main mechanisms of ALI induced by various factors. Phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein 4 (PEBP4) is a secreted protein with multiple biological functions. At present, studies on PEBP4 exist mainly in the field of tumors and rarely in inflammation. This study aimed to explore the potential roles and mechanisms of PEBP4 on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/D-galactosamine (D-GalN)-induced ALI. PEBP4 was downregulated after treatment with LPS/D-GalN in wild-type mice. PEBP4 hepatocyte-conditional knockout (CKO) aggravated liver damage and repressed liver functions, including hepatocellular edema, red blood cell infiltration, and increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST)/alanine aminotrans-ferase (ALT) activities. The inflammatory response was promoted through increased neutrophil infiltration, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activities, and cytokine secretions (interleukin-1β, IL-1β; tumor necrosis factor alpha, TNF-α; and cyclooxygenase-2, COX-2) in PEBP4 CKO mice. PEBP4 CKO also induced an apoptotic effect, including increasing the degree of apoptotic hepatocytes, the expressions and activities of caspases, and pro-apoptotic factor Bax while decreasing anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2. Furthermore, the data demonstrated the levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), phosphorylation-inhibitor of nuclear factor kappaB Alpha (p-IκB-α), and nuclear factor kappaB (NF-κB) p65 were upregulated, while the expressions of cytoplasmic IκB-α and NF-κB p65 were downregulated after PEBP4 CKO. More importantly, both the NF-κB inhibitor (Ammonium pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate, PDTC) and a small-molecule inhibitor of TLR4 (TAK-242) could inhibit TLR4/NF-κB signaling activation and reverse the effects of PEBP4 CKO. In summary, the data suggested that hepatocyte-conditional knockout of PEBP4 aggravated LPS/D-GalN-induced ALI, and the effect is partly mediated by activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.
Keywords: NF-κB; PEBP4; TLR4; acute liver injury; apoptosis; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Qu, Chen, Shi, Luo, Zheng, Li, Bai, Gan and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isorhamnetin protects against D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver injury in mice through anti-oxidative stress, anti-inflammation, and anti-apoptosis.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Aug 2;25(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04949-0. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40753249 Free PMC article.
-
4-hydroxybenzo[d]oxazol-2(3H)-one ameliorates LPS/D-GalN-induced acute liver injury by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Jun;83:106445. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106445. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32272395
-
Protective effects of sea buckthorn polysaccharide extracts against LPS/d-GalN-induced acute liver failure in mice via suppressing TLR4-NF-κB signaling.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Dec 24;176:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.10.029. Epub 2015 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26494508
-
Alcohol-induced liver injury in signalling pathways and curcumin's therapeutic potential.Toxicol Rep. 2023 Oct 12;11:355-367. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2023.10.005. eCollection 2023 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37868808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding nature: multi-target anti-inflammatory mechanisms of natural products in the TLR4/NF-κB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 14;15:1467193. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1467193. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39877388 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing hepatoprotective action: oxyberberine amorphous solid dispersion system targeting TLR4.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 28;14(1):14924. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65190-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38942824 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Sophorae tonkinensis Gagnep. (Fabaceae) Radix et Rhizoma Water Extract on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury.Molecules. 2022 Dec 7;27(24):8650. doi: 10.3390/molecules27248650. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36557783 Free PMC article.
-
PEBP4 deficiency aggravates LPS-induced acute lung injury and alveolar fluid clearance impairment via modulating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Mar 13;81(1):133. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05168-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38472560 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated-omics analysis with explainable deep networks on pathobiology of infant bronchiolitis.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024 Aug 22;10(1):93. doi: 10.1038/s41540-024-00420-x. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024. PMID: 39174575 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

