Effects of Small Peptide Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier of Laying Hens During the Brooding and Growing Periods
- PMID: 35874672
- PMCID: PMC9301363
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.925256
Effects of Small Peptide Supplementation on Growth Performance, Intestinal Barrier of Laying Hens During the Brooding and Growing Periods
Abstract
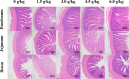
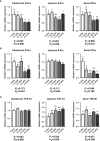
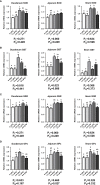
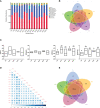
The growing period is a critical period for growth and development in laying hens. During this period, chicks grow rapidly, but are accompanied by unstable digestive function, incomplete organ development, and high mortality. Small peptide, a feed additive, which has been proved to promote intestinal development and immunity in poultry. In order to elucidate the effects of small peptides on growth performance, immunity, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal health of growing laying hens, a total of 900 Tianfu green shell laying hens (1-day-old) were randomly divided into 5 treatments with 6 replicates of 30 birds each in this 18-week trial. Dietary treatments included a corn-soybean meal-based diet supplemented with 0 g/kg, 1.5 g/kg, 3.0 g/kg, 4.5 g/kg and 6.0 g/kg small peptide, respectively. The results showed that the supplementation of small peptides significantly increased growth rate (P<0.05) in laying hens, as well as elevated the serum immunoglobulins (P<0.05) and antioxidant indices (P<0.05), however, it decreased inflammation parameters (P<0.05). The supplementation of small peptides enhanced the intestinal function by promoting gut development (P<0.05) and improving gut integrity (P<0.05), barrier function (P<0.05) and the diversity of gut microbiota (P<0.05) in the growing hens. The best performance was recorded among the hens fed 4.5 g/kg level of small peptide. Taken together, these results showed that small peptide supplementation could improve the economic value of growing hens by promoting growth rate, disease resistance, and the optimal amount of addition for Tianfu green shell laying hens was 4.5 g/kg.
Keywords: anti-oxidation; growth performance; immune; intestinal health; laying hen; small peptide.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Zhang, He, Wei, Han, Xia, Tan, Yu, Kang, Ma, Zhu, Yin and Cui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
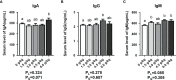
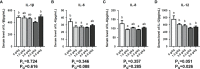


References
-
- Abd El-Hack ME, Mahrose K, Askar AA, Alagawany M, Arif M, Saeed M, et al. Single and Combined Impacts of Vitamin a and Selenium in Diet on Productive Performance, Egg Quality, and Some Blood Parameters of Laying Hens During Hot Season. Biol Trace Elem Res (2017) 177(1):169–79. doi: 10.1007/s12011-016-0862-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

