G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Recent Insights into Mechanisms and Functional Roles
- PMID: 35874704
- PMCID: PMC9304905
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.907733
G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Recent Insights into Mechanisms and Functional Roles
Abstract
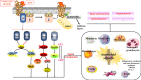
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease that leads to joint damage and even disability. Although there are various clinical therapies for RA, some patients still have poor or no response. Thus, the development of new drug targets remains a high priority. In this review, we discuss the role of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), including chemokine receptors, melanocortin receptors, lipid metabolism-related receptors, adenosine receptors, and other inflammation-related receptors, on mechanisms of RA, such as inflammation, lipid metabolism, angiogenesis, and bone destruction. Additionally, we summarize the latest clinical trials on GPCR targeting to provide a theoretical basis and guidance for the development of innovative GPCR-based clinical drugs for RA.
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptors; angiogenesis; bone destruction; inflammation; lipid metabolism; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Wei, Jiang, Chang, Xu, Xu, Shi, Guo and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemokines and chemokine receptors as promising targets in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 13;14:1100869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1100869. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36860872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein-coupled receptors in rheumatology.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014 Jul;10(7):429-36. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.62. Epub 2014 May 6. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24798574 Review.
-
Metabolite-sensing GPCRs in rheumatoid arthritis.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2024 Feb;45(2):118-133. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.12.001. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38182481 Review.
-
Tackling Pain Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Proton-Sensing Receptors.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1099:49-64. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-1756-9_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30306514 Review.
-
Role and Function of Adenosine and its Receptors in Inflammation, Neuroinflammation, IBS, Autoimmune Inflammatory Disorders, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Psoriasis.Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(26):2875-2891. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190716145206. Curr Pharm Des. 2019. PMID: 31333103 Review.
Cited by
-
The intersection of GRK2 and PGE2 in rheumatoid arthritis: a comprehensive update on pathophysiology and treatment.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 22. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04163-2. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40261352 Review.
-
Single-cell characterisation of tissue homing CD4 + and CD8 + T cell clones in immune-mediated refractory arthritis.Mol Med. 2024 Apr 9;30(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00802-1. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38594612 Free PMC article.
-
The protective activity of genistein against bone and cartilage diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 8;13:1016981. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1016981. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36160403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Understanding the function of the GABAergic system and its potential role in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 7;14:1114350. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1114350. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36825000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Ammodaucus leucotrichus Seed Extracts: A Multi-Faceted Analysis of Phytochemical Composition, Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy, Predictive Anti-Arthritic Properties, and Molecular Docking Insights.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;17(3):385. doi: 10.3390/ph17030385. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38543170 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

