Selenium Deficiency Leads to Inflammation, Autophagy, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Apoptosis and Contraction Abnormalities via Affecting Intestinal Flora in Intestinal Smooth Muscle of Mice
- PMID: 35874733
- PMCID: PMC9299101
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947655
Selenium Deficiency Leads to Inflammation, Autophagy, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Apoptosis and Contraction Abnormalities via Affecting Intestinal Flora in Intestinal Smooth Muscle of Mice
Abstract
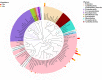
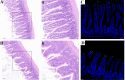
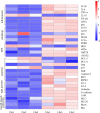
Selenium (Se) is a micronutrient that plays a predominant role in various physiological processes in humans and animals. Long-term lack of Se will lead to many metabolic diseases. Studies have found that chronic Se deficiency can cause chronic diarrhea. The gut flora is closely related to the health of the body. Changes in environmental factors can cause changes in the intestinal flora. Our study found that Se deficiency can disrupt intestinal flora. Through 16s high-throughput sequencing analysis of small intestinal contents of mice, we found that compared with CSe group, the abundance of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Ileibacterium in the low selenium group was significantly increased, while Romboutsia abundance was significantly decreased. Histological analysis showed that compared with CSe group, the small intestine tissues of the LSe group had obvious pathological changes. We examined mRNA expression levels in the small intestine associated with inflammation, autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, tight junctions, and smooth muscle contraction. The mRNA levels of NF-κB, IκB, p38, IL-1β, TNF-α, Beclin, ATG7, ATG5, LC3α, BaK, Pum, Caspase-3, RIP1, RIPK3, PERK, IRE1, elF2α, GRP78, CHOP2, ZO-1, ZO-2, Occludin, E-cadherin, CaM, MLC, MLCK, Rho, and RhoA in the LSe group were significantly increased. The mRNA levels of IL-10, p62 BcL-2 and BcL-w were significantly decreased in the LSe group compared with the CSe group. These results suggest that changes in the abundance of Lactobacillus, bifidobacterium, ileum, and Romboutsia may be associated with cellular inflammation, autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, tight junction, and abnormal smooth muscle contraction. Intestinal flora may play an important role in chronic diarrhea caused by selenium deficiency.
Keywords: ERS; apoptosis; autophagy; inflammatory; intestinal flora; selenium; smooth muscle contraction; tight junction.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Sun, Zeng, Gao, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Liu GX, Jiang GZ, Lu KL, Li XF, Zhou M, Zhang DD, et al. Effects of Dietary Selenium on the Growth, Selenium Status, Antioxidant Activities, Muscle Composition and Meat Quality of Blunt Snout Bream, Megalobrama Amblycephala. Aquacult Nutr (2017) 23:777–87. doi: 10.1111/anu.12444 - DOI
-
- Dehghani M, Shokrgozar N, Ramzi M, Kalani M, Golmoghaddam H, Arandi N. The Impact of Selenium on Regulatory T Cell Frequency and Immune Checkpoint Receptor Expression in Patients With Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Cancer Immunol Immunother (2021) 70:2961–9. doi: 10.1007/s00262-021-02889-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee SH, Park BY, Yeo JM, Lee SS, Lee JH, Ha JK, et al. Effects of Different Selenium Sources on Performance, Carcass Characteristics, Plasma Glutathione Peroxidase Activity and Selenium Deposition in Finishing Hanwoo Steers. Asian-Australasian J Anim Sci (2007) 20:229–36. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2007.229 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

